RUDN University scientist suggested a simple model of dense plasma spectral properties
Plasma is the fourth state of matter, along with solid matter, liquid, and gas. High-density (up to ~1 g/cm3) plasma is used in many technical and experimental installations such as heavy-current electrical discharge devices, control fusion targets, or laser targets that are used to study the properties of matter under extreme pressure.
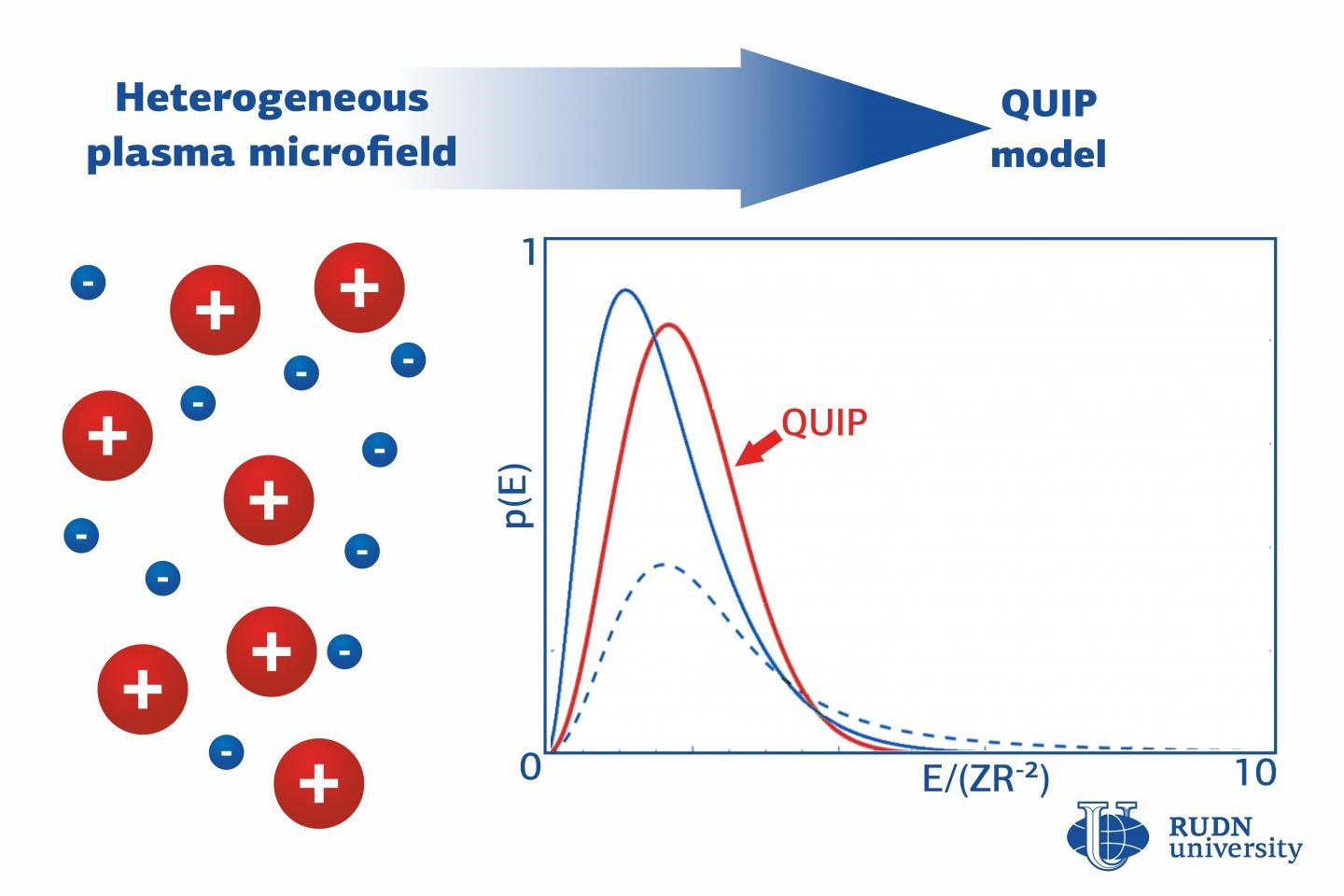
An important feature of plasma is its light absorptance coefficient. Its value is to a great extent dependent on the photo effect (the transfer of energy from the photons to the electrons of a substance) and light absorptance in optical lines. Both of these processes, in turn, are due to the so-called microfield—an electric field inside plasma produced by the chaotic thermal movement of ions and free electrons. This field can fluctuate from its average value in time and space, and knowing its characteristics is important for solving numerous scientific and technical tasks.
“We have analyzed all models described in scientific literature and identified their disadvantages. Namely, these models provide for the infinite density of the electric field energy in an atomic cell which contradicts the laws of physics. The only model that doesn’t have these disadvantages is the Quasi Independent Particle model or QUIP. We developed a generalized version of this model that takes into account the inhomogeneity of plasma microfield. This helped us extrapolate the model to high-density plasma for which homogeneous microfield approximations cannot be used. The generalized QUIP model is very simple and does not require complex calculations, because all formulas are presented in an explicit manner,” said Alexander Belov, a Candidate of Physics and Mathematics and a senior lecturer at the Department of Applied Informatics and Probability Theory, RUDN University.
To confirm a theoretical model, one has to test it against experimental results. For this purpose, the team chose experiments on the fluorescence of laser-based plasma that have been going on since the 1980s. In these experiments, tiny glass bubbles were filled with a mix of deuterium, argon, krypton, neon, and other gases, covered with aluminum coating and then heated with a powerful multi-beam laser system. As a result, plasma with high temperature and density was formed inside the bubbles and emitted a series of lines in the X-ray range.
“The number of observable spectral lines can be theoretically predicted by a model. In the majority of works, this parameter was neither calculated nor compared to experimental data. Our analysis shows that all models except for QUIP gave wrong predictions that did not match experimental results. Therefore, our model is better at describing the experiment. This test is a convincing proof of the advantage that the generalized QUIP model has over other known models,” added Alexander Belov.
Description of heterogeneous plasma microfield and optical properties of plasma by the QUIP model
The article was published in Annals of Physics.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.