Chemists propose a new method for the synthesis of pyrroles
Pyrrole and its derivatives play an important role in the synthesis of biologically active substances. Dozens of medications are based on pyrrole, including the antitumor drug Sunitinib; BM212, which suppresses the growth of tubercle bacillus, and Toradol, which is used as an anti-inflammatory agent and painkiller. Pyrrole derivatives are also used to produce borondipyrromethenes (BODIPY) that are a part of photodynamic cancer therapy.
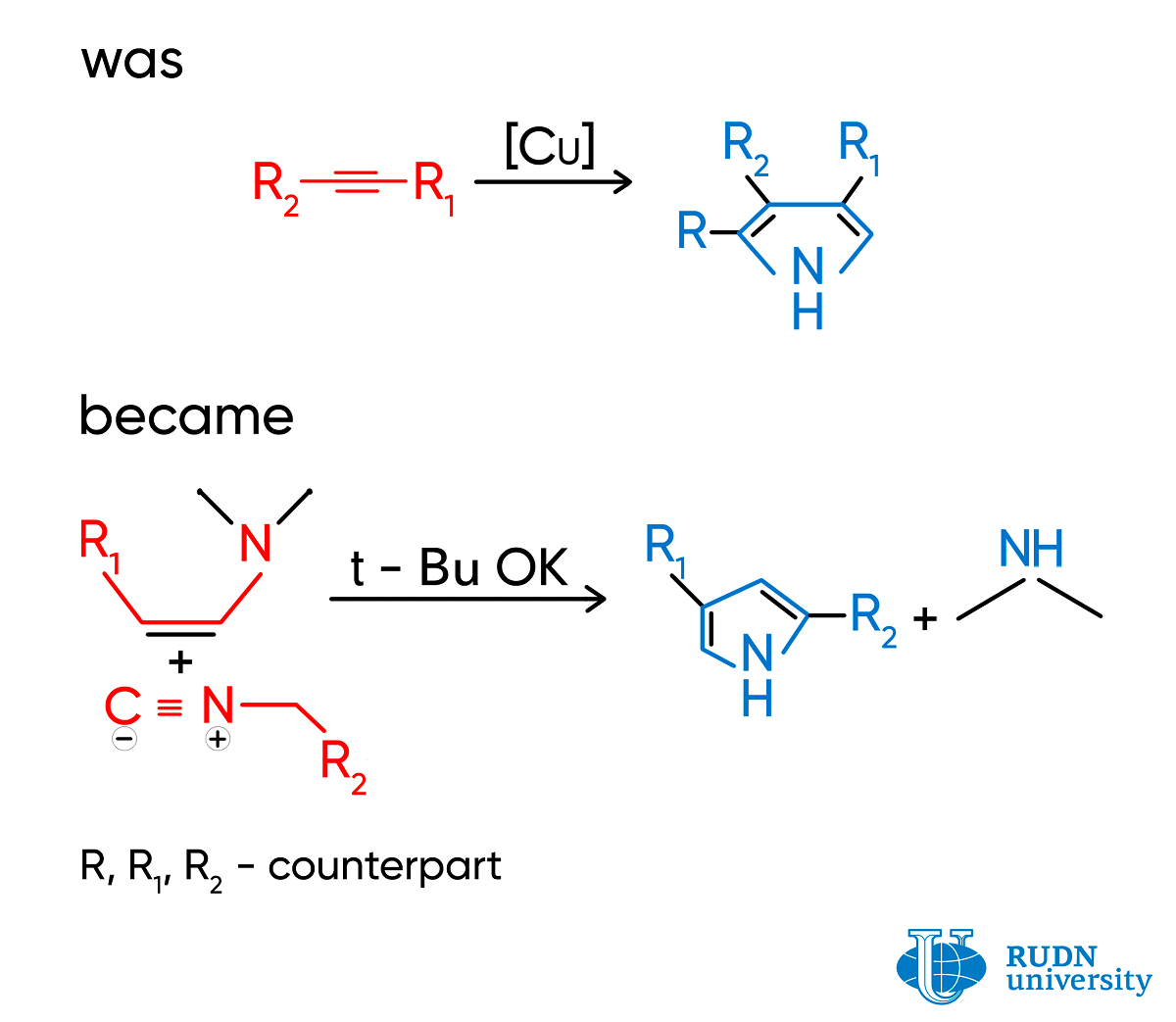
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring. Pyrroles are synthesized in a combination reaction of isocyanides (molecules with an N≡C group) and alkynes (hydrocarbons with a C≡C ternary bond). Depending on the structure of the original reagents, different molecular fragments (substitutes) bind with the pyrrole ring. Copper salts that are toxic for living cells are used for catalysis. The reaction has several stages, as pyrroles have to be purified from byproducts.
Ilya Efimov and Rafael Luque, two chemists from RUND University, working together with Prof. Leonid Voskressensky, proposed an alternative method for producing pyrroles that does not involve copper salts. Instead of alkynes, scientists used enamines. In their molecules, the С=С double bond is bound with nitrogen, and as a result of the reaction, pyrroles with two substitutes in a ring are formed. The reaction has just one stage and is practically immediate. The process allows for the selective production of pyrroles from reagents without byproducts that normally require many stages of purification. The only extra product is dimethylamine that can be easily removed by treating with hydrochloric acid. Pyrroles can be separated by simple filtration. In some cases, the cost of original reagents for the suggested method is 225 times lower than for alkynes.
According to the scientists, the yield of pyrroles exceeds 40% only when the strong base potassium tert-butoxide is used as a base. However, it is easily removed with hydrochloric acid. Donor substitutes that are present in the isocyanide structure and increase the electron density of the molecule also show a positive effect on the yield.
"The new method is simpler and safer than the traditional alkyne-based synthesis. When applied on a scale production, it would reduce the cost of products and make them less toxic. Also, it can be used to produce some pyrroles that were previously unavailable for us," said Ilya Efimov, a junior researcher at RUDN University, Candidate of Chemical Sciences.
The group of scientists used the new method to synthesize 4-azolylpyrroles that had never been studied before. To do so, they investigated enamines with isoxazole, 1,2,4-oxadiazole, and 1,2,3-thiadiazole fragments to the reaction with isocyanides. The new compounds can become precursors for the development of medicinal drugs against amoebas, lamblia, trichomonads, and toxoplasma.
The article was published in the European Journal of Organic Chemistry.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.