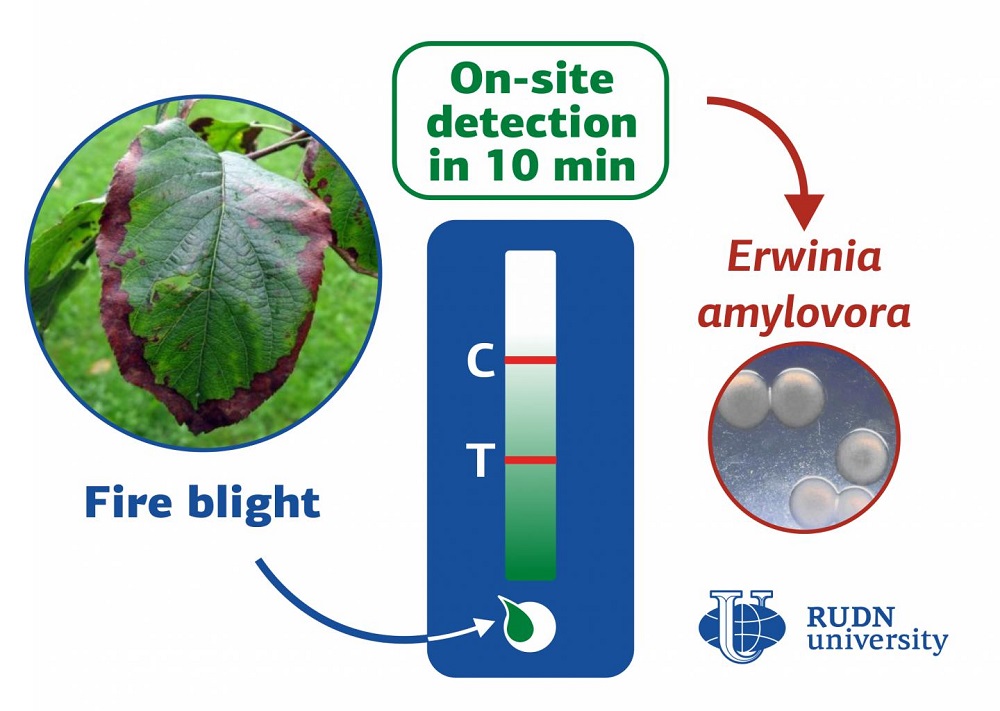
RUDN University biologists develop a rapid test for detecting the fire blight in plants
Erwinia amylovora bacteria causes a dangerous infectious disease in plants — a fire blight. Most plants of the Rosaceae family are vulnerable to it, for example, hawthorn, apple, pear. The bacteria causes the blossom to wither, the leaves dry up and curl, the bark develop necrotic lesions. The disease can spread through infected plants, garden tools, and with the wind, which carries the exudate produced by lesions. To stop the spread of infection in time, we need ways to diagnose it quickly and effectively. Existing testing methods require laboratory equipment. This slows down diagnostics. RUDN University biotechnologists have developed a method that gives the results in 10 minutes right “on the spot”.
“To control E. amylovora, disease diagnosis right in the orchard or nursery is important, especially for monitoring disease outbreaks or independent control of farm and private orchards. Thus our main objective was to develop an express-test to detect E. amylovora and compare different organs of infected plants for optimization”, Shyatesa Razo, PhD student at RUDN University
The new test is based on immunochromatographic analysis. This is one of the most universal diagnostic methods — this is how most modern express tests works (for example, a pregnancy test or SARS-CoV-2 test) are arranged. A test strip is placed in a biological liquid — for example, a leaf extract. Specific antibodies are applied to the strip, which “bind” to the desired substance and color certain areas forming the stripes. By their number, it can be concluded that a particular substance is present in the biological fluid. The aim of the RUDN University biotechnologists was to select such antibodies that would allow to determine the presence of Erwinia amylovora in the plant liquids.
To obtain specific antibodies, biologists immunized chinchilla rabbits with Erwinia amylovora. 7-10 days after the last injections, biologists took blood samples from the animals and isolated the necessary immunoglobulin IgG (protein cells that neutralize the pathogen).
The resulting test was verified on infected plants from the Voronezh region — 121 samples of apple, pear, hawthorn, quince, blackthorn and cherry. The test fluid was isolated from leaves, twigs, flowers, fruits, and bacterial mucus. As a result, in 93.5% of cases, the results of the rapid test coincided with the results of the PCR test, which requires more time and special laboratory equipment. RUDN University biotechnologists also determined that it is best to use the vascular tissues of the plant.
“Today, the diagnosis of plant pathogens is on the rise; the number of rapid and sensitive methods of analysis, both laboratory and non-laboratory, is increasing. However, the distribution of the pathogen in the plant determines the appropriate sampling for any assay. We determined which plant parts are more accurate for fire blight detection using LFIA. In this aspect, our study will be helpful for more effective and thoughtful diagnosis of fire blight in non-laboratory conditions”, Shyatesa Razo, PhD student at RUDN University.
The results are published in Physiological and Molecular Pathology of Plants.
The RUDN Prize for Scientific Achievements in Chemistry for 2025, with a monetary award of 2 million rubles, was awarded to Alexander Davidovich Dilman, Deputy Director of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The researcher received the award during the celebration marking RUDN’s 66th anniversary.
Sergey Ivanov, a scholar from St. Petersburg, has been named the first winner of RUDN University’s International Prize for Scientific Achievements in Mathematics, worth 5 million rubles.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.