Soil Scientists from RUDN University Have Determined the Optimal Size of Soil Pores for the Activity of Microorganisms
Soil types differ from each other not only in their chemical properties, but also in their location, shape, and pore size. Although any soil has both small and large pores, their ratio may be different. Larger pores (from 100 micrometers) are filled with air and are located between the soil lumps, small pores (10-100 micrometers) inside the lumps are filled with water. The pores are home to colonies of microbes that are responsible for biochemical reactions associated with the circulation of carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen and other chemical elements. Microorganisms improve soil fertility and carbon sequestration, so understanding what parameters (including pore sizes) determine the ‘well-being’ of microorganisms will help farmers increase yield.
Previously, the distribution of enzymes that secrete soil microorganisms was associated only with the chemical and biological properties of the soil. However, the physical structure of the soil also affects beneficial microbial communities and, consequently, enzymes. For the first time, soil scientists from RUDN University found optimal parameters of soil pores for microbial communities. To do this, they examined the pores using soil 2D-zymography — a biochemical method for studying the activity of enzymes, and X-ray computed tomography.
Soil samples from five land-use systems were taken from plots prepared for experiments by The Kellogg Biological Station in Michigan (USA): soil on which only corn was grown (1); white rye (2); millet (3); hybrid poplar with grassy undergrowth, (4) and soil on which plant communities successively changed as a result of natural factors or human activity (5). There were no live roots in the samples, meaning all the enzymes are produced by microorganisms.
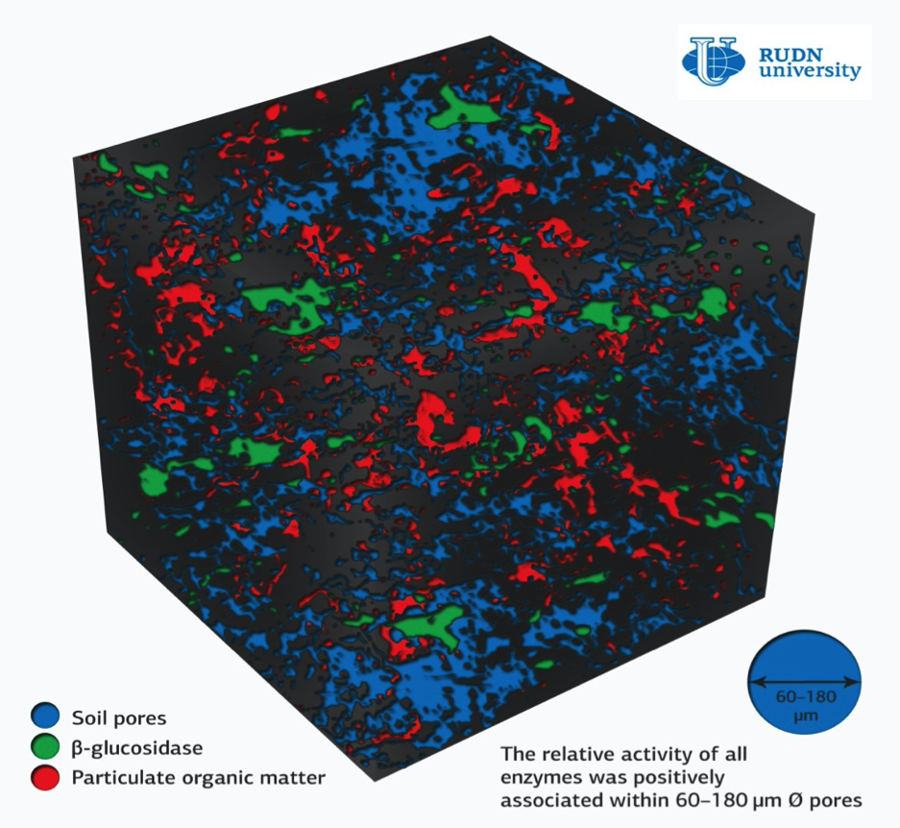
To determine the distribution and size of pores in soils, samples measuring 5-10 centimeters were scanned with X-rays. Enzyme activity was mapped using zymography. Special membranes with substrates were placed on the surface of the samples, which emit fluorescent products upon contact. These products display the activity of enzymes in ultraviolet light. We studied the enzymes involved in the turnover of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the soil: cellobiohydrolase, xylonase, acid phosphatase, β-glucosidase, leucinaminopeptidase and N-acetylglucosaminidase. Combining zymography and computer microtomography data allowed creating 3D maps that visualize the size of soil pores and enzyme activity in an intact soil sample.
In all the studied soil samples, regardless of the type, the most enzymes (and therefore the highest activity of microorganisms) were observed in pores with a diameter of 60-180 micrometers. Therefore, pores of this size are an ideal habitat for soil microbes. In smaller or larger pores, the activity of all six enzymes was less. Whole microbial colonies are located in the pores of this size (60-180 microns), and the access of water and oxygen is optimal. In the pores of this size (60-180 microns), more small roots grow, which provides greater saturation of the soil with readily available carbon. Thus, the size of soil pores does affect the distribution of enzymes.
The experiment confirmed for the first time that the combination of these two methods is effective for studying enzymes. In the future, soil scientists plan to improve the resolution of images and take into account additional factors such as fresh carbon intake, soil moisture and acidity. This will provide more accurate data and strengthen understanding of biochemical processes in situ — in the place where they occur, without any interference.
Article in Soil Biology and Biochemistry
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.