RUDN University biologist found that Chinese date improves the immune system of fish
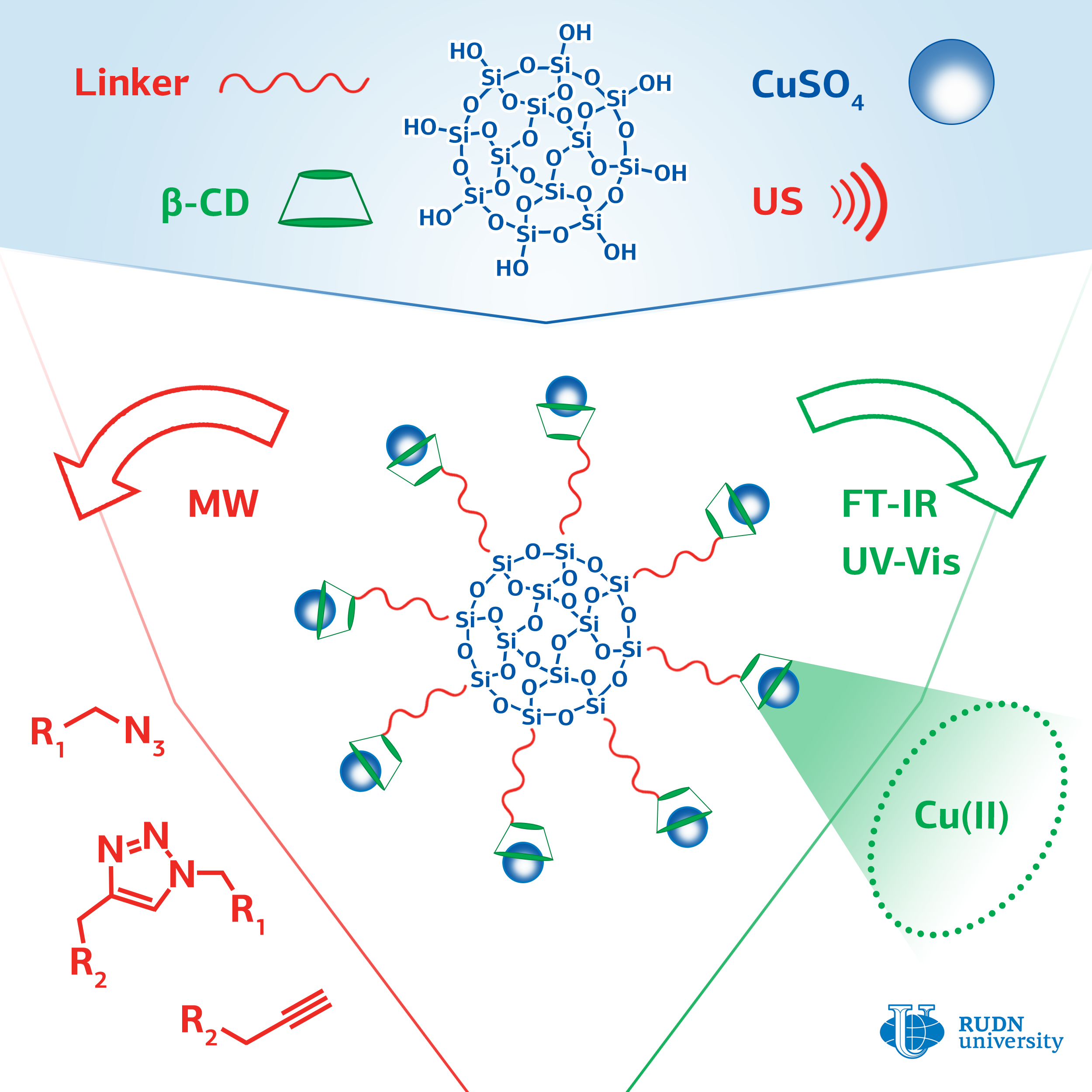
Click chemistry methods are used to synthesize libraries of substances with high chemical diversity, which is important when developing new drugs. These reactions are necessary for introduction of labels (for example, fluorescent ones) into biological macromolecules, proteins, and DNA molecules. This is used in biological and medical research.
The most commonly used click chemistry reaction is the addition of a substance that contains a carbon-carbon triple bond (alkine) to a compound containing a fragment with three nitrogen atoms in a row (azide). The classic version of the reaction involves the use of copper in oxidation state (I) as a catalyst. For this, ions of copper (II) and an excess of a reducing agent are introduced into the reaction, or copper (I) is used and the reaction is conducted with protection against oxygen, which imposes certain restrictions on the application of this reaction.
A chemist from RUDN University Rafael Luque and his colleagues have developed a series of catalysts with copper ions attached to the surface of silica gel particles using cyclic cyclodextrin oligosaccharide. Cyclodextrin consists of seven glucose molecules closed in a cycle. Inside the cycle there is a container that can hold the copper ion and increase its catalytic activity. Ultrasound irradiation was used to facilitate the binding of cyclodextrin to the surface of silica gel.
The effectiveness of the created catalysts was evaluated on a model reaction of phenylacetylene with benzylazide. The researchers managed to achieve a yield of the reaction product of more than 99%. The yield with copper (II) acetate was 14%, and in the case of copper (II) sulfate, the reaction did not occur at all. The method for producing the catalyst is simple, safe for the environment, and cheap; its use does not require to add reducing agents or oxygen-free conditions. The catalysts can find application in the pharmaceutical industry and in biomedical research.
The paper was published in the journal Molecules.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.