RUDN University chemist showed that water plays a crucial role in the mechanism of the Henry reaction catalyzed by new copper complexes
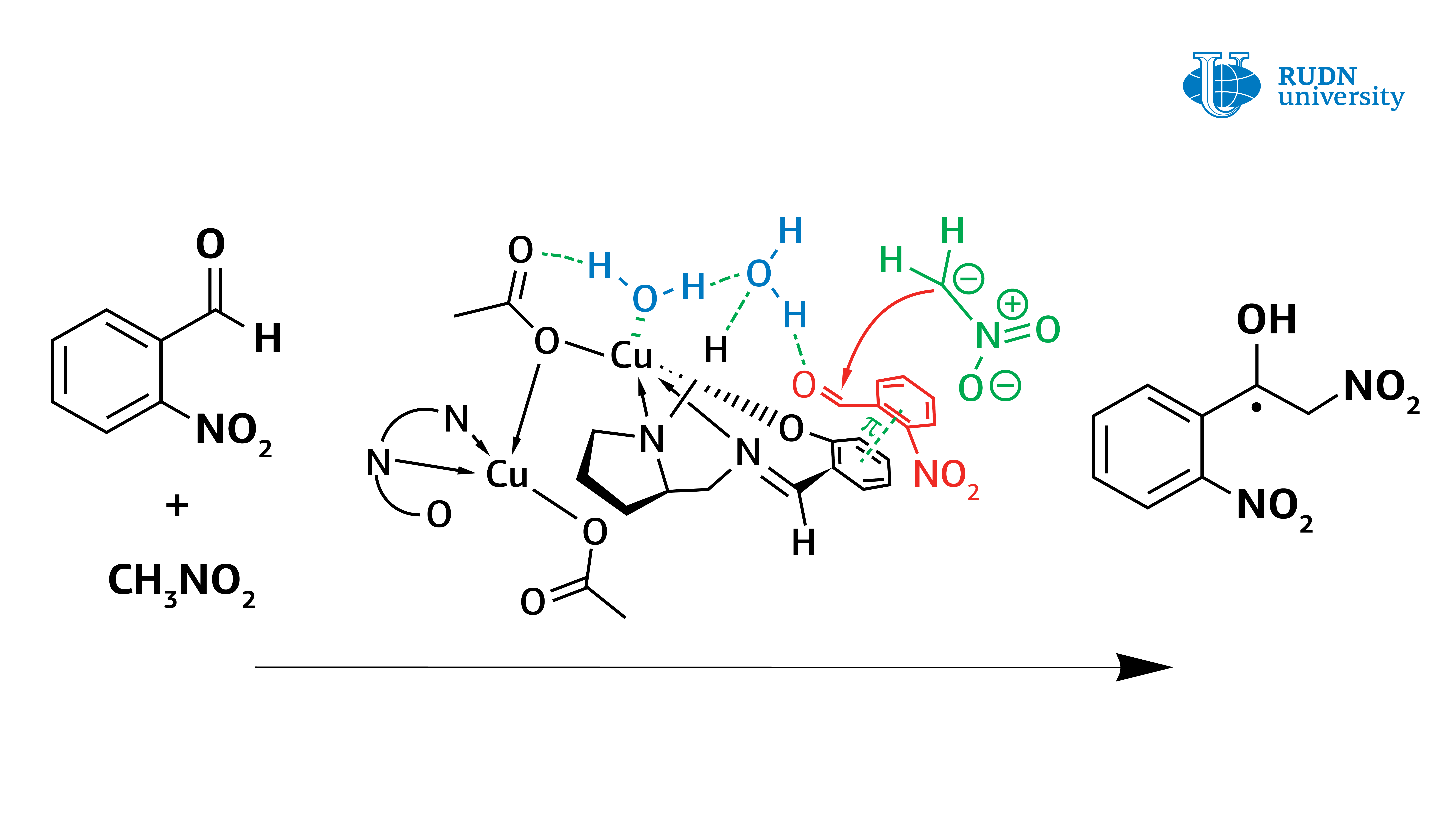
In fact, it turned out that the copper complex in coordination with the water molecule activates it, turning it into Bronsted acid, and thus the water activates the original aldehyde. The data obtained from the experiment allow us to understand the mechanism of the Henry reaction and will help in the creation of the most important classes of substances for the pharmaceutical industry: α-nitroketones, ketones, nitroalkenes and β-amino alcohols.
Asymmetric Henry reaction, allowing the synthesis of valuable organic molecules, was first conducted by Japanese chemist Masakatsu Shibasaki in 1992. He was able to conduct a reaction with high enantioselectivity, using catalysts based on copper complexes. However, before this work, there were still questions about the mechanism of this reaction. Vladimir Larionov, an employee of the Department of Inorganic Chemistry of RUDN University, Ph.D. in Chemistry, using new copper(II) complexes showed that the water molecule plays a crucial role in the Henry reaction and is directly involved in the catalytic cycle. Previously, scientists did not pay much attention to this, but only stated the fact that the reaction rate increases by several orders with the participation of water.
These complexes can be used to produce precursors of drugs such as (S)-propranolol (β-blocker), ®-norepinephrine and ®-salbutamol (β-receptor agonists), amprenavir-Vertex 478 (HIV protease inhibitor) and L-acosamine (class of anthracycline antibiotics).
It was known from previous studies that the asymmetric Henry reaction is better performed in aqueous and alcoholic solvents. Therefore, the authors of the study tested the reaction in solvents (methanol, aldehyde-nitromethane-water) with two catalytic systems — cobalt (III) and copper(II) complexes. In the case of the cobalt complex, the metal ion did not participate in the reaction, and the copper ion could coordinate the water molecule (or molecules). The reaction was faster with the copper complex, and chemists obtained several necessary types of chemicals (ligands and nitrated alcohol). Cobalt catalyst functioned worse, especially in the production of nitrated alcohol. That is why the authors decided to focus on the copper catalyst.
However, the use of a copper catalyst in methanol also caused problems. The formation of nitrated alcohol only of the racemic form was observed during the condensation. In this case, the reaction rate did not slow down, and blocking of the catalytic center of the copper ion did not occur. Calculations have shown that water forms a strong bond between the copper center and the carbonyl group. The reaction was completed within 1 hour, and the yield of nitrated alcohol reached 61%. At the same time, nitrated alcohol was displaced by water and did not block the catalytic center of the copper complex. Thus, contrary to previous ideas, it was
Chemists concluded that the effectiveness of previously studied chiral catalysts based on copper (II) was underestimated because the water (or alcohol) content of the reaction was not taken into account and was not evaluated. This research will open the way to study the Henry reaction mechanism and to create the new catalytic systems based on copper complexes.
The results are published in the international American journal Inorganic Chemistry.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.