RUDN University Chemist created a niobium-silica catalyst to boost petrochemical reactions
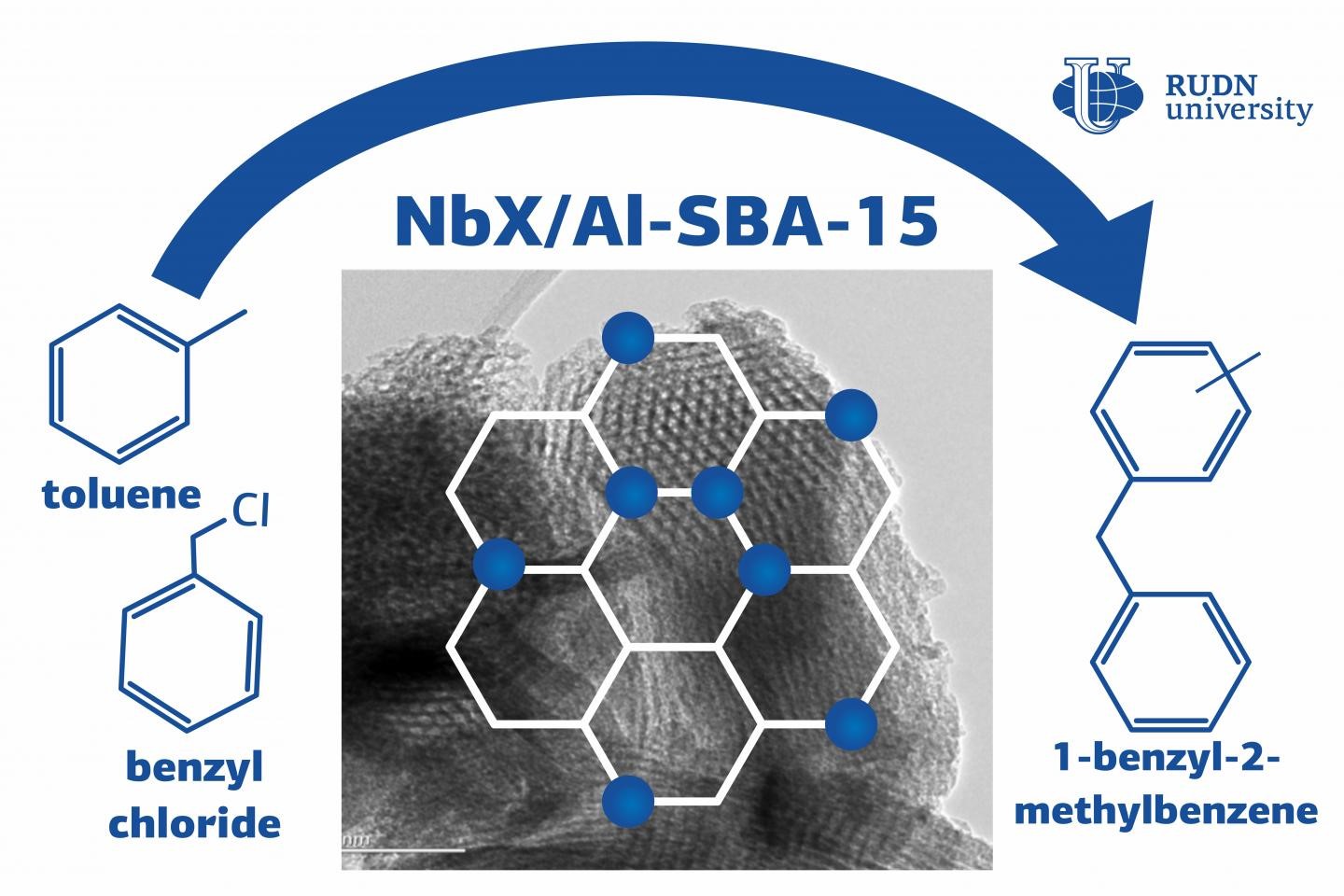
In the course of alkylation, an atom of hydrogen in an organic compound is replaced with other substances, the so-called alkylating agents. Alkylation is used in the chemical and petrochemical industries, for example, to obtain high-octane number components in gasolines. For the process to go on quickly and efficiently, it needs catalysts including mineral acids and zeolites—minerals that are capable of selectively releasing substances and then adsorbing them back. However, mineral (e.g. sulphuric or phosphoric) acids can be expensive and dangerous: in order to extract them from the reaction mix, one needs additional reagents that can be hard to handle. Unlike mineral acids, zeolites are safe and cheap to produce. The only problem lies in their microporous structure that limits the size of the molecules they can react with. A chemist from RUDN University created a catalyst that is free from these disadvantages and able to speed up the alkylation reaction up to 24 times. To do so, his team used niobium and SBA-15, a mesoporous ordered form of silica.
“SBA-15 materials are relevant as catalytic support due to their high surface area and pore volume in the mesopore range that convert it in an outstanding catalyst support. We aimed to evaluate the acidity of several Al-SBA-15 supported niobium oxide catalysts prepared by a mechanochemical protocol with different metal loadings,” said Rafael Luque PhD, the head of the Molecular Design and Synthesis of Innovative Compounds for Medicine Science Center at RUDN University.
The team paid attention to the reductive-oxidative and acidic properties of niobium-based compounds that are important for a catalyst and decided to test niobium in an alkylation reaction. To do so, they put niobium oxide nanoparticles (that had been mechanochemically ground down to several nanometers in size) on the support. The metal content in the new material varied from 0.5% to 1% and the size of the particles was controlled with a transmission electron microscope. The team used energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy to secure even distribution of particles across the surface of the support.
To analyze the catalytic properties of the new material, the chemists carried out the reaction of toluene alkylation with benzyl alcohol and benzyl chloride that acted as alkylating agents. As a result of the experiment, the team confirmed a positive effect of niobium particles on the reaction: its time of reaction reduced from 4 hours to 10 minutes. The catalyst with lower niobium content (0.5%) turned out to be more effective due to better dispersion. The team believes that when the catalyst was synthesized, niobium oxide deposited on the support, and the more niobium, the bigger the catalyst particles turned out to be. This reduced the effective contact area of the particles and therefore had a negative impact on the material’s catalytic activity.
“We managed to create a catalyst that reduces the time of alkylation reactions from several hours to just 10 minutes, is free from the chemical limitations of zeolites, and poses no danger unlike mineral acids,” added Rafael Luque.
The article was published in Molecular Catalysis.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.