RUDN University medics created a wound-healing gel with metabolic products of trichoderma
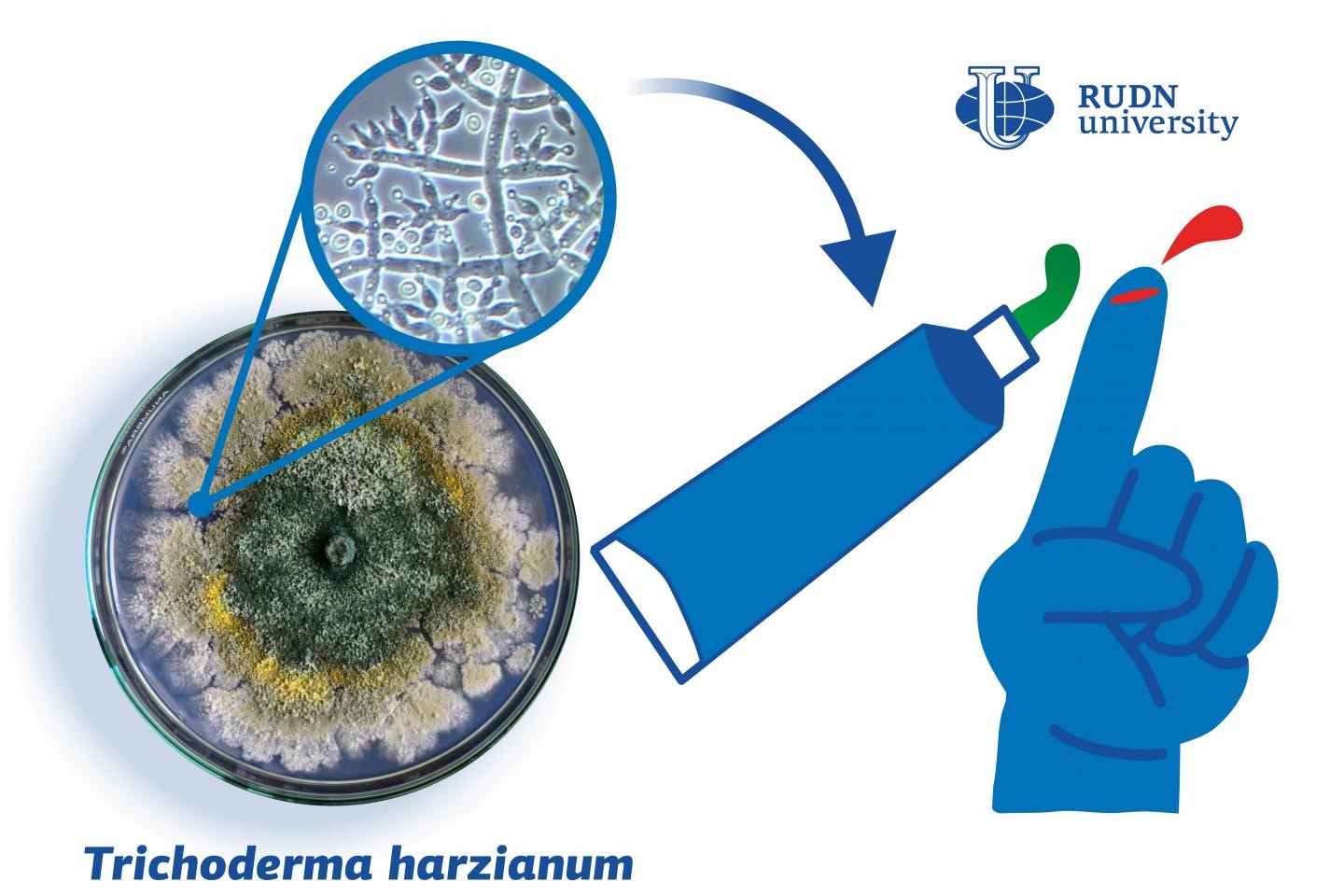
The best way to treat skin damage is to accelerate cell regeneration using ointments with different active ingredients such as metabolic products of microorganisms. Fungi, bacteria, and other organisms produce antibiotics, enzymes, growth promoters, vitamins, and amino acids, and scientists are always looking for ways to turn them into medicinal drugs. One of these useful substances is L-lysine-oxidase produced by Trichoderma fungi. A team of researchers from RUDN University developed a technology to incorporate this enzyme into a wound-healing gel. The method does not require expensive purification of the initial biological liquids and therefore is economically feasible.
“Modern-day microbiology is focused on physiologically active metabolic products of microorganisms. The fungi of the genus Trichoderma are well-studied, and the Trichoderma harzianum Rifai F-180 strain can produce large quantities of a protein called L-lysine-oxidase that has confirmed antiviral and anti-tumor properties. This opens a range of prospects for the development of new pharmaceutical forms that could be used to treat infections and skin damage,” said Prof. Irina Smirnova, a PhD. in Biology, from Berezov Department of Biochemistry at RUDN University.
Based on the results of earlier studies, the team chose the optimal active ingredient concentration of 1%. When selecting additional components for the gel, the scientists followed a set of rules. The base of the gel had to match the active ingredient, support the activity of L-lysine-oxidase, secure easy application and storage, and cause no irritation. Following these principles, the team chose and tested three base options: methylcellulose, carbopol, and mARS.
The experiment was conducted on nine adult guinea pigs divided into groups of three. The skin of the animals was mechanically damaged, and 18 hours after that the team started the treatment. Each animal was treated with one of the three types of gel for two weeks. The product based on methylcellulose demonstrated the worst results with wounds healing for 9 to 10 days on average. The best results were registered in the group that received the carbopol-based gel: the wounds of the animals healed after 6 to 7 days.
“Based on the results of the experiment, we can confirm that 1% carbopol-based gel with the culture liquid of Trichoderma has advanced wound-healing properties. The next stage for us will be a pre-clinical trial. The new pharmaceutical form could be used in veterinary medicine to treat wounds, viral skin infections, and ocular herpes. Moreover, it could find application in medical cosmetology, gynecology, and skin cancer therapy,” added Prof. Irina Smirnova from RUDN University.
The article was published in Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.