RUDN University physicist developed software solution to measure the black holes stability
The existence of black holes was first predicted by Einstein’s general theory of relativity. These objects have so strong gravitational pull that nothing, not even light, can escape them. Dense and massive, black holes deform space-time (a physical construct with three spatial and one temporal dimension). Many mathematical models used to describe black holes include corrections to account for such space-time curvatures. The main condition of existence for every black hole model is its stability in cases of minor spatial or temporal changes. Mathematically unstable black holes make no physical sense, as the objects they describe cannot exist in reality. A physicist from RUDN University suggested a method to identify black hole instability parameters in 4D space-time.
“For a model to be considered feasible, a black hole described by it has to remain stable in case of minor space-time fluctuations. One of the most promising approaches to developing alternative gravity theories includes adding corrections to Einstein’s equation, including the fourth-order Gauss-Bonnet correction and the Lovelock correction that provides a higher level of generalization,” said Roman Konoplya, a researcher at the Educational and Research Institute of Gravitation and Cosmology, RUDN University.
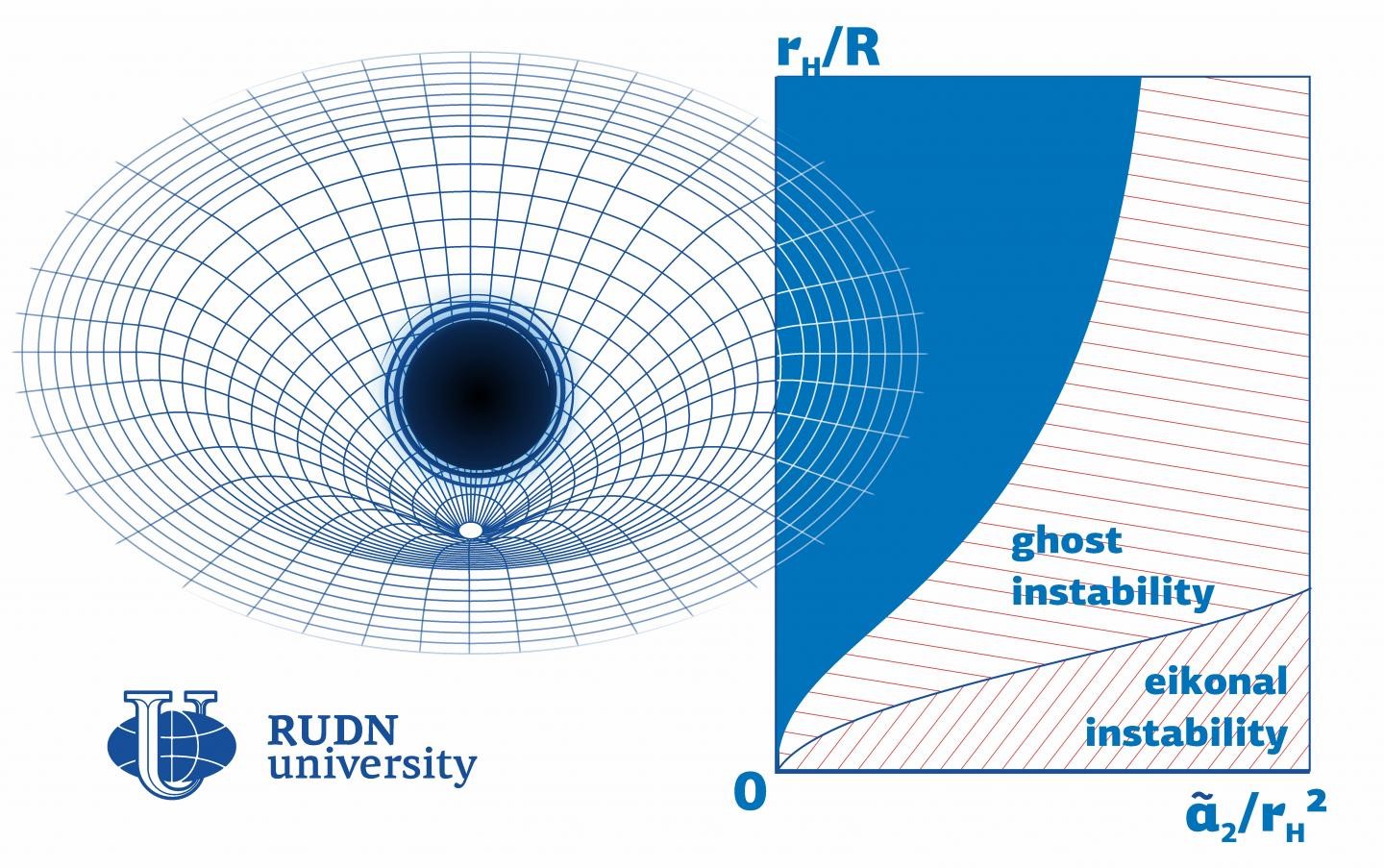
The physicist studied stability in the Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet theory in which a black hole is described by Einstein’s equation with a fourth additional component. Previously, he had focused on a different mathematical description of a black hole, the so-called Lovelock theory, that describes a black hole as a sum of an infinite number of components. The instability region turned out to be closely associated with the values of the so-called coupling constants: numerical coefficients by which the corrections to Einstein’s equation are multiplied.
According to the physicist, the Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet model does not provide for the existence of small black holes, because if coupling constants are relatively big compared to other parameters (such as the radius of a black hole), the model almost always turns out to be unstable. The stability region is much bigger if the coupling constant has a negative value. Based on these calculations, he and his team developed a program to calculate black hole stability based on any of its parameters.
“Our approach helps test black hole models for stability. We made the code publicly available so that any of our colleagues could use it to calculate instability regions for models with an unspecified set of parameters,” added Roman Konoplya.
The work was published in the Physics of the Dark Universe journal.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.