RUDN University soil scientist: Paddy soil fertilization can help reduce greenhouse effect
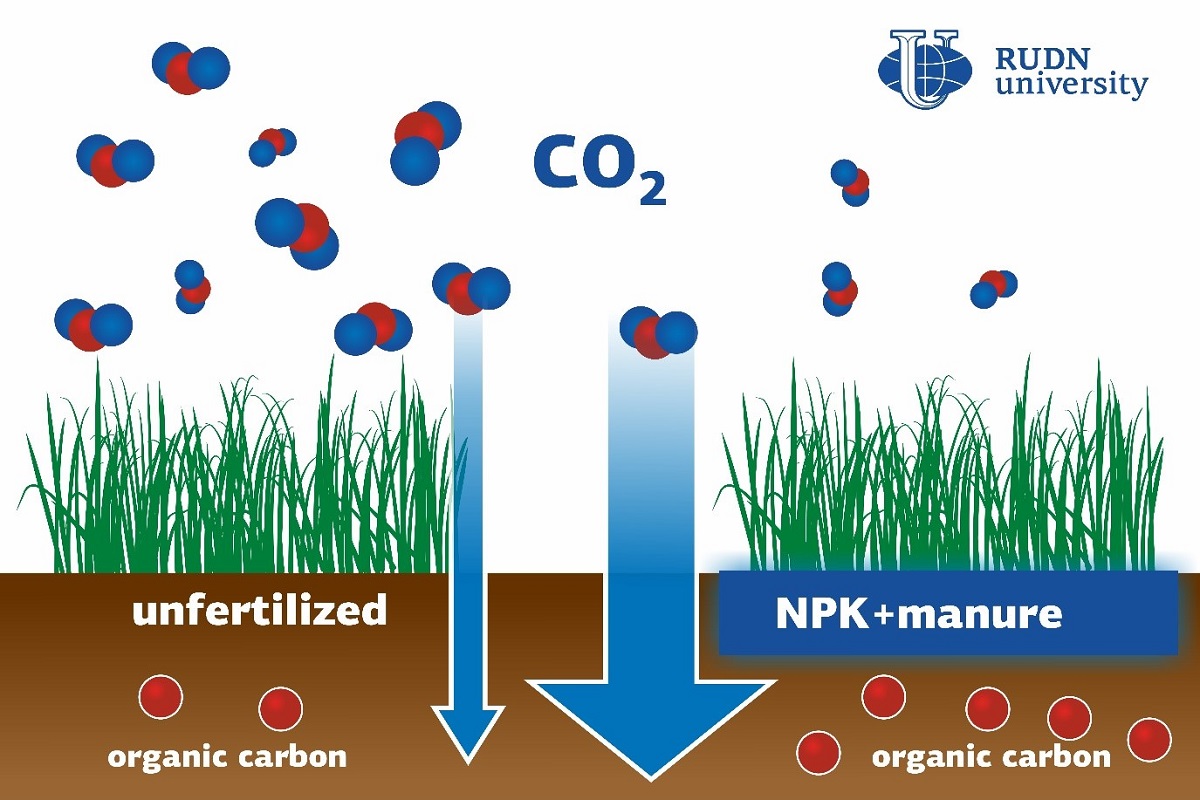
The main reason for global climate change is the increasing amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. CO2 prevents thermal emissions from leaving our planet, and the so-called greenhouse effect occurs. Being able to absorb up to 10% of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere (which amounts to approximately 20,000 megatons of carbon in 25 years), soils could mitigate this effect. A soil scientist from RUDN University studied the mechanism of carbon retention in the soils of rice paddies that account for 40% of natural atmospheric carbon absorption in China. According to him, the ability of the soil to retain carbon depends, among other factors, on its structure and the presence of fertilizers.
"The soils of rice paddies play an important role in mitigating the consequences of global warming and contribute a lot to the retention of carbon. The most effective way to study the processes that lead to the accumulation of organic carbon in the soil is to measure the concentration of its isotopes. We used this method to find out how mineral and organic fertilizers affect carbon flows between fractions of different density in rice paddy soils," said Yakov Kuzyakov, the Head of the Center for Mathematical Modeling and Design of Sustainable Ecosystems at RUDN University.
The team studied three groups of soils with different types of fertilizers: azophoska, or nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizer, was added to the first group; the second one contained azophoska with straw, and the third--azophoska with organic supplements. The content of carbon in the soils and its movement between density fractions was determined based on the ratio of 13C and 12? isotopes. The second and the third group showed better carbon retention results: after fertilization, their carbon content grew by 69%, while the increase in the first group amounted to 30%.
The scientists also paid attention to the changes in soil structure under the influence of fertilizers and the effect of such changes on carbon retention. Fertilizers consolidate the structural elements of the soil, and the number of large soil particles (over 0.25 mm in diameter) grows. Soils of medium density showed the highest carbon retention efficiency after fertilization: the amount of accumulated carbon increased by 70% compared to unfertilized soils. Less dense soil fractions showed a 21-56% increase, and carbon retention in dust and clay grew by 24-49%.
"We confirmed that fertilizers support organic carbon retention in the soil. Knowing this, we could better understand the processes that lead to the accumulation of soil carbon in rice paddies. These agricultural ecosystems already play an important role in world food security and now can also help us combat climate change," added Yakov Kuzyakov.
An article about the study was published in the Soil Biology and Biochemistry journal.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.