RUDN University Biologists Obtain 7 Metal Nanoparticles Using Strawberry
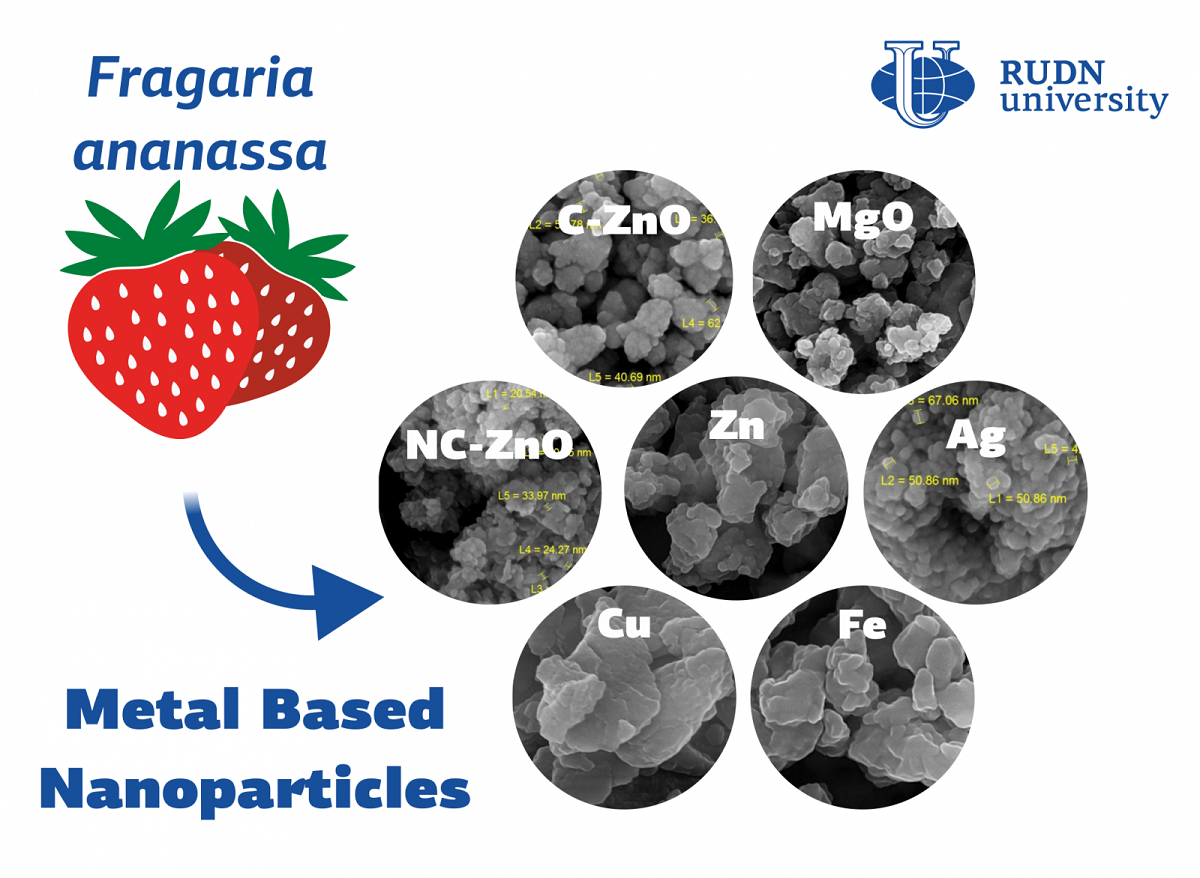
Metal nanoparticles are used in medicine, cosmetology, electronics and agriculture. Usually, they are obtained either physically or chemically. In the first case, expensive equipment and a lot of energy are required, in the second-expensive and toxic chemicals that are harmful to the environment. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new methods that will avoid these problems — for example, a biological method. RUDN biologists have proposed an eco-friendly and safe method for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles from strawberry leaves.
“For the first time, we used Fragaria ananassa (strawberry) leaf extract as a source of natural reducing, capping or stabilizing agents to develop an eco-friendly, cost-effective and safe process for the biosynthesis of metal-based nanoparticles including silver, copper, iron, zinc and magnesium oxide”, Maryam Bayat, PhD student at RUDN University.
Biologists have created 7 types of nanoparticles — silver, iron, copper, zinc, magnesium oxide and two types of particles with zinc oxide. To do this, scientists used metal salts and strawberry leaf extract. The extract contains minerals which support biochemical reactions of biomolecules with metal salts forming nanoparticles. To comply with the “green” protocol, the RUDN University biologists did not use any additional chemicals during extraction. After adding metal salt to the extract, it was mixed, heated, washed, and centrifuged. After drying it out, scientists obtained a precipitate and ground it getting the nanoparticles. The specific conditions of this process depended on the desired type of nanoparticles. For example, to obtain zinc nanoparticles, biologists used zinc acetate. It was added to strawberry extract and heated to 90 ° C, then centrifuged for 25 minutes at 10,000 rpm.
RUDN University biologists studied the obtained particles using ultraviolet spectroscopy, determined their size, shape, structure and uniformity using a scanning electron microscope. The results confirmed the composition and nanostructure of the particles. According to biologists, “green” synthesis makes it possible to use such nanoparticles in medicine and agriculture — for example, to fight bacteria and fungi, as well as to improve plant growth.
“As in this investigation a green, sustainable and highly benign method is introduced, a wide variety of potential applications could be explored for such biosynthesized metal-based nanoparticles, especially in the fields of medicine, drug delivery, biotechnology, catalysis, agriculture and so on. For example, we evaluated the antibacterial activity of biosyntheized silver, copper and ZnO nanoparticles on Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium and antifungal activity on Botrytis cinerea and some other pathogenic fungi; we also studied the effect of these seven biosynthesized nanoparticles on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat and flax seeds which will be published in our future reports”, Meisam Zargar, PhD in agricultural sciences, professor at RUDN University.
The results are published in the Molecules.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.