RUDN University Scientists In Pharmaceutical Technology Proved Effectiveness Of New Dosage Form
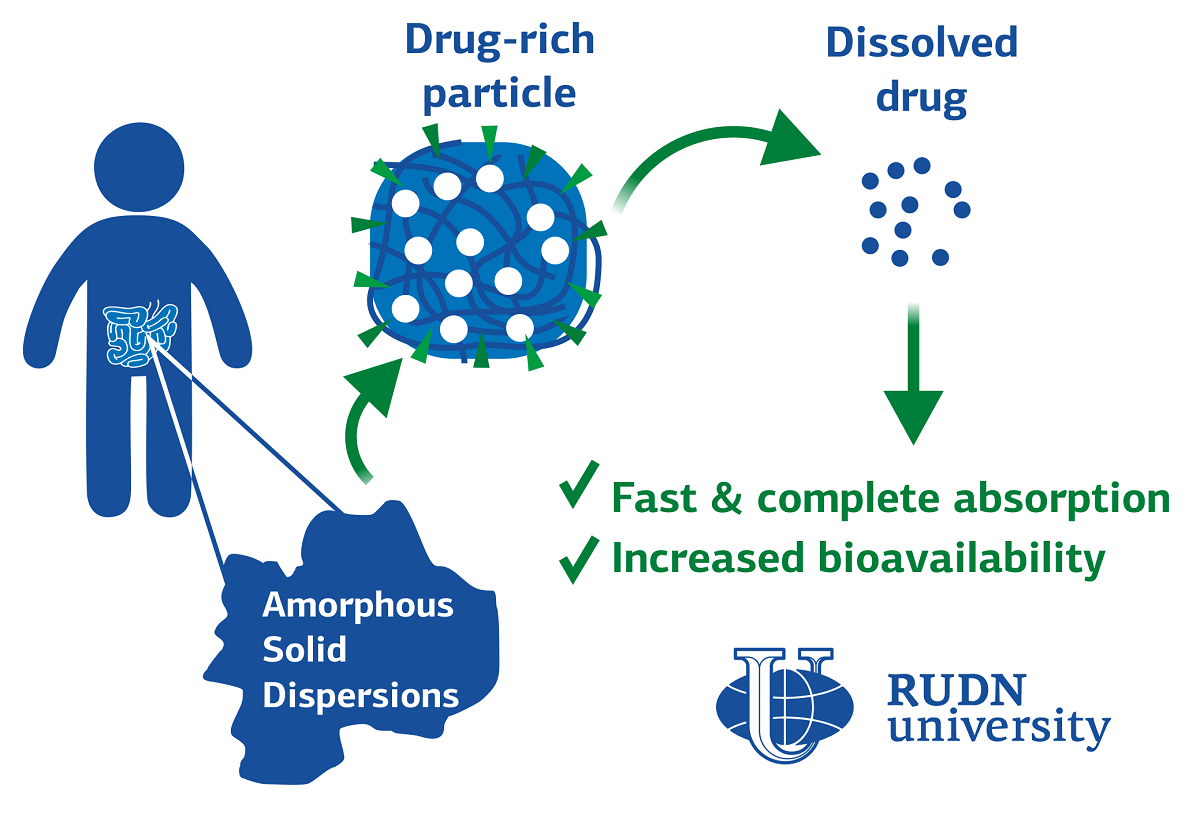
One of the main reasons for the dropout of new oral drugs at the preclinical and clinical stages of development is low bioavailability. The drug itself can be effective, but because of its low solubility, it is poorly absorbed in the body. Amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) is a new form of drug release that has the potential to solve this problem. ASD consists of a drug substance and a polymer framework that “binds” the drug and improves its solubility, thus increasing bioavailability. RUDN University scientists in the field of pharmaceutical technology, together with colleagues from Switzerland, conducted a clinical study and proved the effectiveness of ASD. This is the first such human trial.
“Despite the research effort on mechanisms of increased bioavailability through ASDs during the last decades, these mechanisms are far from being understood in every detail. Furthermore, the translation from preclinical studies to clinical outcomes in humans has not been validated. It was the aim of this clinical study to investigate the mechanisms and effects of a particle forming ASD on bioavailability in humans to gain an understanding of the complex absorption from ASDs in humans. To our best knowledge, there are currently neither documented data nor methods providing such insights”, Rimma Abramovich, Doctor of Pharmaceutical.
The clinical study involved 16 volunteers; healthy men aged 20 to 38 years. As a model medicine, doctors used the antiviral drug efavirenz, which is used in the treatment of HIV infection. Participants in the study took efavirenz orally in three different forms in three interventions — 50 mg in the form of solid ASD, 50 mg in the form of dissolved ASD, and 3 mg of a molecular solution of efavirenz. To avoid distortion of the results, doctors maintain a washout period of 14 to 21 days. After each intervention, the doctors took a blood test and measured the pharmacokinetic profile — the dynamics of efavirenz concentration in blood plasma over time.
It turned out that ASD in solid form works in the same way as a regular efavirenz tablet — the maximum concentration of about 6.5 nanograms per millilitre is reached in two hours. And the dissolved ASD acts as a molecular solution of the drug — the concentration of the drug in the blood reached approximately the same value after the same time — about 10 nanograms per millilitre after 50-60 minutes. However, given that the molecular solution is absorbed from the intestine into the blood passively (that is, without additional chemical reactions), the scientists calculated that the actual concentration of the drug in the intestine in the case of dissolved ASD is 16.7 times higher than in the case of conventional efavirenz. This means that the dissolved ASD behaves like a so-called supersaturated solution; meaning that it contains 10 times more dissolved matter than it can dissolve under normal conditions.
“We could show that drug absorption from drug-rich particles, formed upon the dissolution of the ASD, was fast and complete in humans”, Rimma Abramovich, Doctor of Pharmaceutical.
Results were published in Pharmaceutics.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.