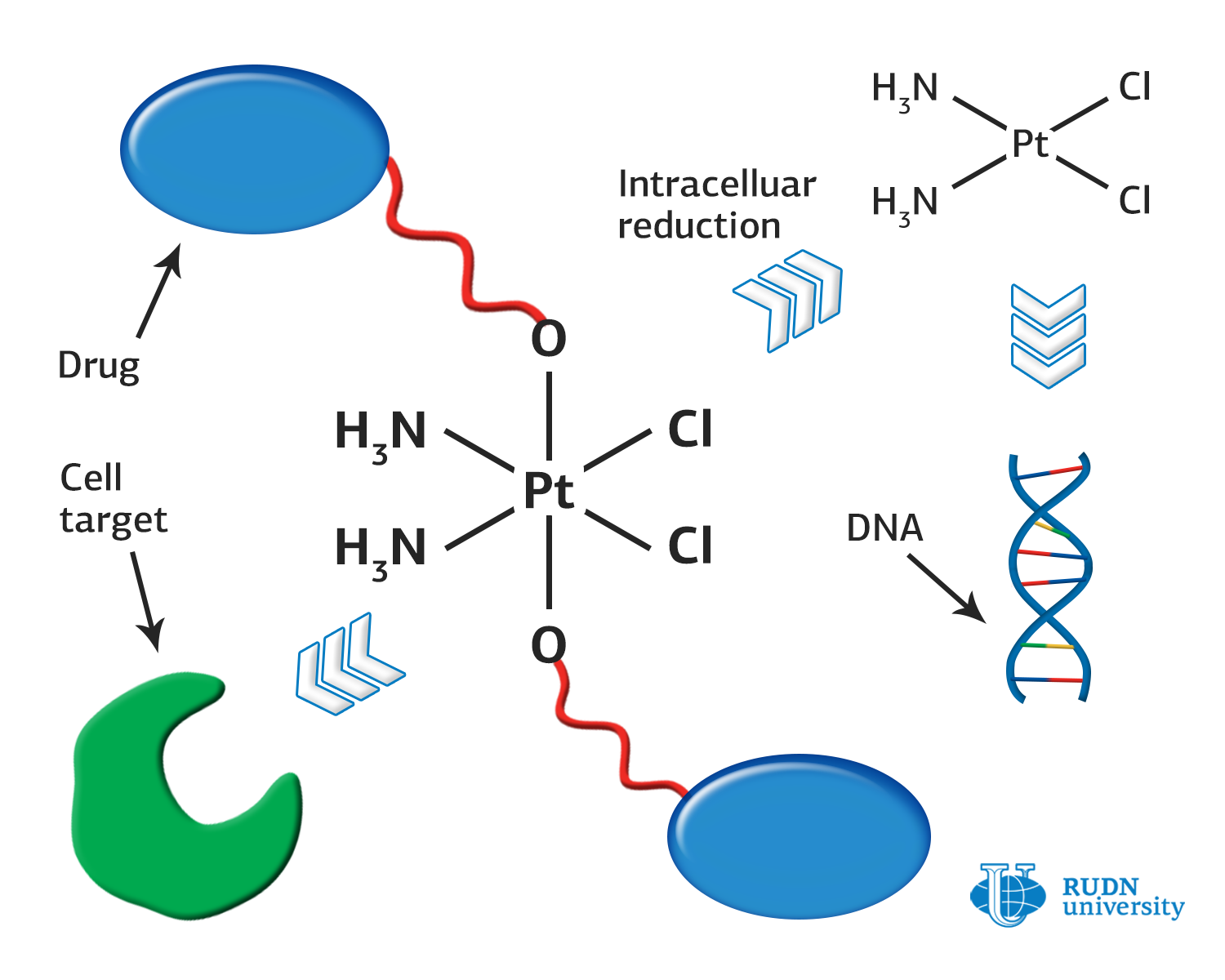
A RUDN University chemist created anti-tumour compounds that are up to 80 times more effective than their counterparts
Platinum-based anticancer drugs — cisplatin, oxaliplatin, and carboplatin — are used for chemotherapy in about half of cancer cases. They penetrate cells and interact with DNA molecules. The process is fatal for rapidly dividing cancer cells because the drugs prevent the duplication of DNA molecules, which is necessary for successful division. Since cancer cells divide rapidly, they are the first to be affected. Still, platinum derivatives have certain disadvantages: low stability under physiological conditions and high toxicity.
To create new drugs, a strategy that involves the development of hybrid molecules is often used in modern chemistry. Such substances consist of two or more active fragments that are linked by a linker into one molecule. They usually have a double action, characteristic of each of the fragments.
A chemist from RUDN University, candidate of biological sciences Kirill Kirsanov, created a series of new drugs: hybrids of cisplatin, lonidamine, and bexarotene. Lonidamine itself has an anti-tumour effect due to its ability to suppress energy metabolism in cancer cells. In combination with radiation therapy, it is used to treat brain tumours. Bexarotene is used for the treatment of lung cancer and breast cancer, as it inhibits the growth of tumour cells of hematopoietic and squamous origin.
A derivative of cisplatin with bexarotene turned out to be the most promising. A combination of succinic acid and ethylenediamine was used as a linker. In tests conducted on four tumour cell lines, the hybrid drug was 80 times more active than bexaroten and 20 times higher on average than cisplatin, and the new drug was 80 times more active than cisplatin on MCF7D cell line. Based on the resulting leading compound, new and more effective anti-tumour medications can be developed.
The paper was published in the journal Inorganica Chimica Acta.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.
Ambassadors of Russian education and science met at a conference in RUDN University to discuss how they can increase the visibility of Russian universities and research organizations in the world, and attract more international students in Russia.
The international scientific seminar hosted by RUDN Institute of Ecology “Experience of participation in student organizations as a way to form career skills” united scholarship recipients of the International Student Mobility Awards 2024 and Open Doors, along with members of the scientific student society “GreenLab” and the professional student association “Kostyor (Bonfire)” shared their projects focused on environmental protection.