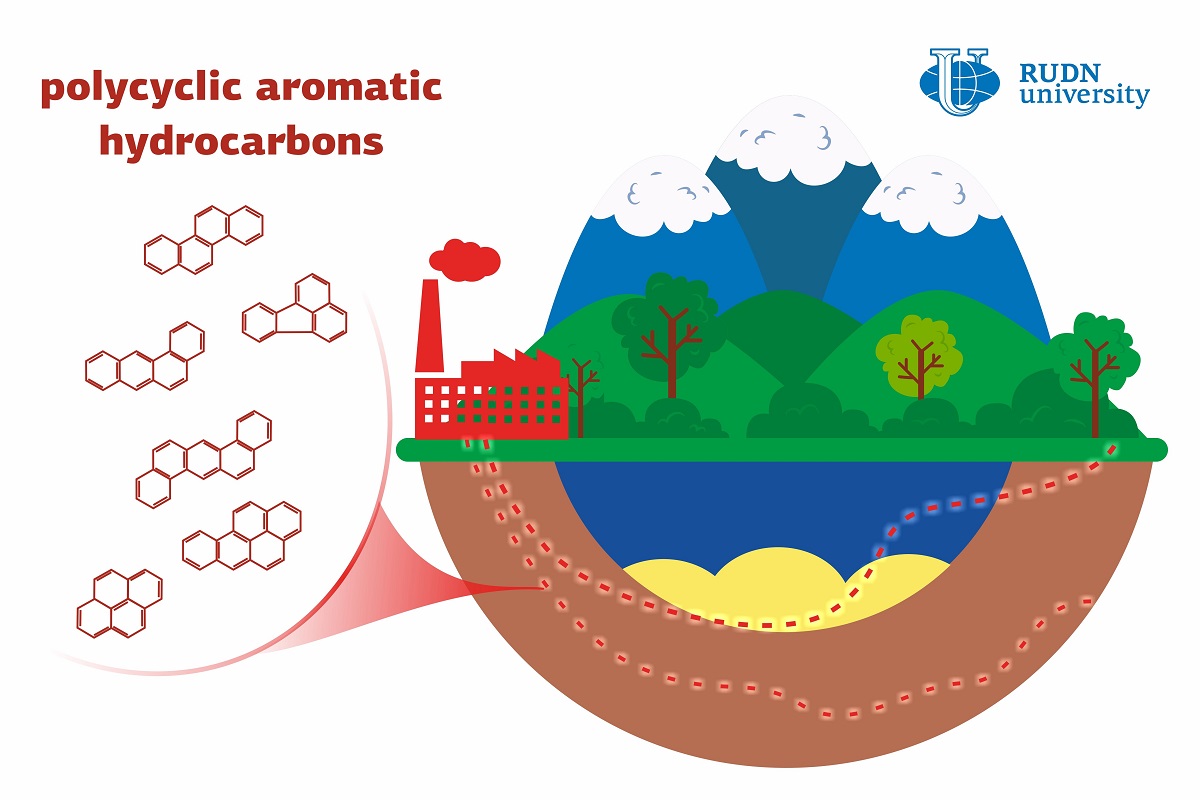
Ecologists from RUDN University Developed New Models to Identify Environmental Pollution Sources
Geochemical barriers mark the borders between natural environments at which the nature of element transfer changes dramatically. For example, the concentration of oxygen rapidly increases at groundwater outlets, because different chemical elements oxidize and accumulate on the barrier. A team of ecologists from RUDN University was the first in the world to suggest a model that describes the energy of mass transfer, i.e. the movement of matter in an ecosystem. In this model, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are used as the markers of moving substances. PAHs are mainly toxic organic substances that accumulate in the soil. The team used their composition to monitor pollutions and track down their sources. To do so, the ecologists calculated the physical and chemical properties of PAHs and classified them.
“We developed a model that shows the accumulation, transformation, and migration of PAHs. It is based on quantitative measurements that produce more consistent results than descriptive visualizations. This helped us understand how physical and chemical properties of PAHs determine their accumulation in the environment,” said Prof. Aleksander Khaustov, a PhD in Geology and Mineralogy, from the Department of Applied Ecology at RUDN University.
PAHs can form due to natural causes (e.g. wildfires) or as a result of human activity, for example as the waste products of the chemical and oil industry. The team studied 142 water, plant, soil, and silt samples from different geographical regions. Namely, some samples were taken in the hydrologic systems of the Kerch Peninsula, some came from leather industry areas in China, from the vicinity of Irkutsk aluminum smelter, and different regions of the Arctic and Antarctic. Several snow samples were taken on RUDN University campus in Moscow. All collected data were unified, and then the amount of PAHs in each sample was calculated. After that, the results were analyzed in line with the thermodynamic theory to calculate entropy, enthalpy, and Gibbs energy variations. The first value describes the deviation of an actual process from the ideal one; the second one shows the amounts of released or consumed energy, and the third points out the possibility of mass transfer.
“Though our samples were not genetically uniform, they allowed us to apply thermodynamic analysis to matter and energy transfer in natural dissipative systems,” added Prof. Aleksander Khaustov.
The team identified several factors that have the biggest impact on PAHs accumulation. For example, in the ecosystems surrounding leather facilities in China, the key factor turned to be entropy variations, while on RUDN University campus it was the changes in Gibbs energy. The team described three types of processes that are characterized by the reduction, stability, or increase of all three thermodynamic parameters, respectively. Based on this classification and the composition of PAHs one can monitor pollution and track down its source.
The results of the study were published in the Applied Geochemistry journal.
The RUDN Prize for Scientific Achievements in Chemistry for 2025, with a monetary award of 2 million rubles, was awarded to Alexander Davidovich Dilman, Deputy Director of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The researcher received the award during the celebration marking RUDN’s 66th anniversary.
Sergey Ivanov, a scholar from St. Petersburg, has been named the first winner of RUDN University’s International Prize for Scientific Achievements in Mathematics, worth 5 million rubles.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.