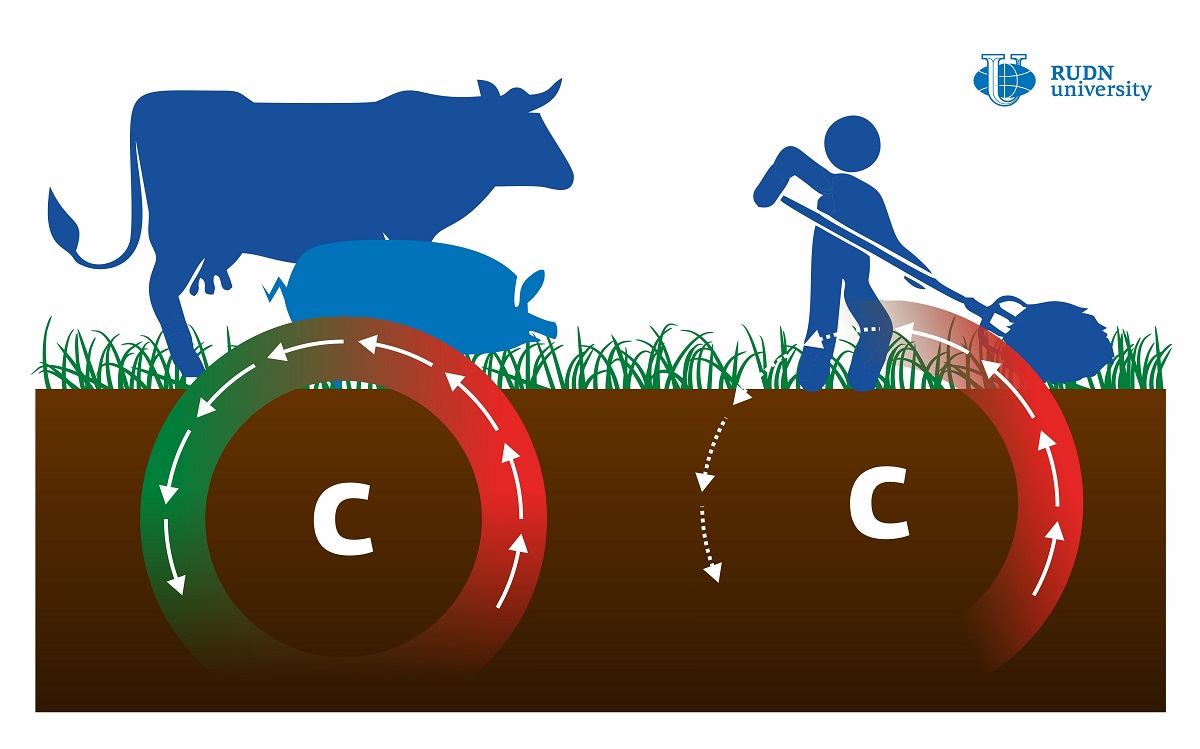
Mowing Is More Harmful to Soil Than Grazing
The cycle of organic carbon in the meadow soil depends to a great extent on how the soil is managed. Meadows are often mowed or used as pastures, and both these practices can lead to unwanted damage and tearing of the main aerial parts of plants. However, it is still not clear which process is more harmful to the soil. A team of biologists including a scientist from RUDN University analyzed soil samples taken at experimental land plots in Western France that have been used as pastures or regularly mowed for 13 years. Using mass spectrometry and gas chromatography, the team measured the levels of organic carbon and other compounds and analyzed microbial activity in the samples. The soil of the pasture turned out to contain more carbon than that of the mowed meadow. According to the biologists, the sources of carbon in the pastures are more diverse and easily available which supports the activity of microorganisms. 50% to 70% of all carbon consumed by grazing animals returns to the soil in the form of manure within several days. This makes microbial functioning more efficient and increases carbon reserves in the soil. In the case of mowed meadows, the loss of soil nutrients has to be compensated by mineral fertilizers that stimulate enzyme activity, thus accelerating the decay of organic compounds. This might have a negative impact on the environment.
“According to our study, mowing and grazing have a different effect on the biogeochemical functioning of meadow soils. Although both systems are generally beneficial for organic carbon reserves, moderate cattle grazing is more advantageous because it leads to better soil quality and more efficient microbial functioning,” said Evgeniya Blagodatskaya, a Ph.D. in Biology and a senior researcher at the Center for Mathematical Modeling and Design of Sustainable Ecosystems at RUDN University.
The results of the study were published in the Applied Soil Ecology journal.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.
Ambassadors of Russian education and science met at a conference in RUDN University to discuss how they can increase the visibility of Russian universities and research organizations in the world, and attract more international students in Russia.
The international scientific seminar hosted by RUDN Institute of Ecology “Experience of participation in student organizations as a way to form career skills” united scholarship recipients of the International Student Mobility Awards 2024 and Open Doors, along with members of the scientific student society “GreenLab” and the professional student association “Kostyor (Bonfire)” shared their projects focused on environmental protection.