RUDN Mathematicians Model 5G Network for the Future Factories
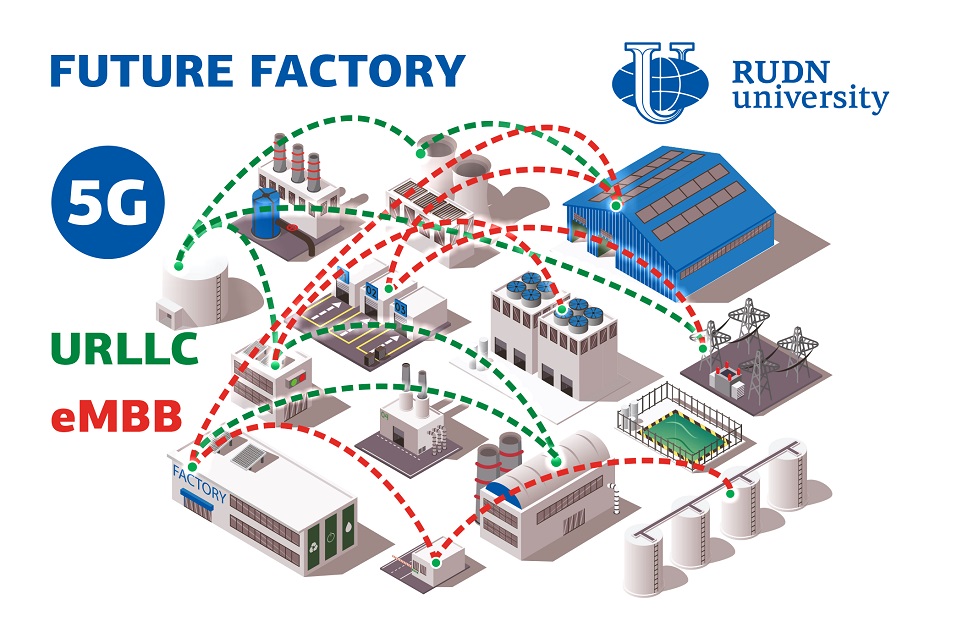
5G or New Radio (NR) supports simultaneous support for two services — eMBB (enhanced Mobile BroadBand) and URLLC (Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication). The eMBB is the next step after the 4G stage in mobile data networks. URLLC is designed for remote control of mechanisms and robots — for example, unmanned vehicles. In real conditions, eMBB and URLLC traffic is mixed. It can reduce the speed and reliability of the connection. RUDN University mathematicians found the solution of this problem. The key step is to find the best strategy for prioritizing services within the network.
“Fifth-generation (5G) mobile systems have been developed for a wide range of applications. Therefore, NR base stations must support both eMBB and URLLC. Now research is aimed at mechanisms to support these services in isolation. However, joint support for these types of traffic is little studied. We investigated the possibility of simultaneous support of eMBB and URLLC in industrial 5G NR networks through prioritization,” said Daria Ivanova, Postgraduate Student at Department of Applied Informatics and Probability Theory, RUDN University.
RUDN mathematicians considered the model of future factory. 5G-network is deployed at that factory, equipped with mobile robots and a variety of devices and sensors. They transfer data to the cloud service, where the control module makes decisions and translates new tasks. Sensors and detectors generate URLLC traffic while surveillance devices generate eMBB traffic. At the same time, everything moves interfering the signal. Having described this system mathematically, scientists have selected the optimal network strategy that provides better speed and reliability with a minimum number of base stations.
It turned out that it is possible to completely separate eMBB and URLLC traffics by prioritization. The D2D (device-to-device) strategy allows one to achieve the most reliable connection, namely, to ensure the probability of URLLC breaking out by only one thousandth of a percent. The secret of D2D is that the base station knowingly reserves part of the resources for the direct exchange of information between the devices themselves.
“Our numerical results show that prioritization allows you to effectively isolate traffic and does not require external control. A D2D-aware strategy, where the base station reserves some resources for direct communication, is significantly superior to those where explicit redundancy is not used, as well as a strategy in which all traffic passes through the base station. Our model can be used to calculate the required density of base stations for all the strategies considered,” said Ekaterina Markova, PhD, Associate Professor at Department of Applied Informatics and Probability Theory, RUDN University.
The results are publishedin IEEE Access.
The RUDN Prize for Scientific Achievements in Chemistry for 2025, with a monetary award of 2 million rubles, was awarded to Alexander Davidovich Dilman, Deputy Director of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The researcher received the award during the celebration marking RUDN’s 66th anniversary.
Sergey Ivanov, a scholar from St. Petersburg, has been named the first winner of RUDN University’s International Prize for Scientific Achievements in Mathematics, worth 5 million rubles.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.