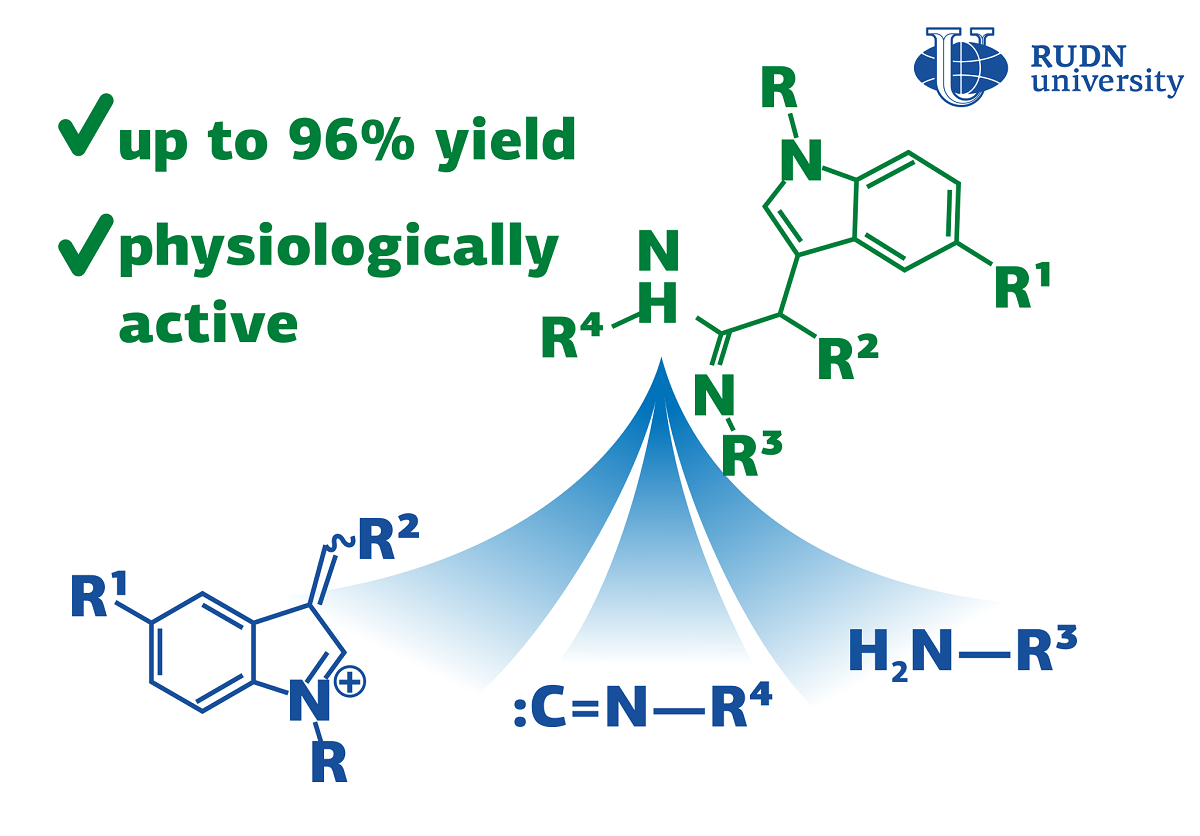
RUDN University Chemists Propose a One-Step Synthesis of Substances for Medicine
Traditional chemical synthesis goes in several stages and requires the isolation and purification of intermediates at each stage. It is not efficient and not environmentally friendly as it increases the loss of substances and the consumption of solvents, and there is a problem of waste disposal. Therefore, modern chemistry is trying to replace multi-stage reactions with multicomponent ones, in which several compounds react to form a product in a single stage. Reactions with isocyanides are the most popular in multicomponent chemistry. Isocyanides are organic compounds with high reactivity. RUDN University chemists have discovered a new three-component reaction with isocyanides that results in a heterocyclic compound with biological activity, acetimidamides. They contain a fragment of indole, which is used for the synthesis of hormones, indomethacin, and other drugs. This work is a development of the famous Ugi reaction.
“Isocyanide-based multicomponent reactions play an outstanding role in the syntheses of heterocycles, biologically relevant compounds and for diversity-oriented synthesis. In the case of the famous Ugi reaction, isocyanide interacts with iminium salt generated in situ. The potency of methods, based on the Ugi reaction, increases with the possibility of subsequent modification or cyclization of obtained products of multicomponent reaction. This is promising from the point of view of medical chemistry”, said Nikita Golantsov, PhD, Professor of the Department of Organic Chemistry of the RUDN University.
Apart from isocyanides, the new three-component reaction involves a 3-arylidenindoleninium salt and an amine. In total chemists used 8 salts and 13 amines. To choose the optimal reaction conditions, they tested 6 types of solvents, alternated the reaction time and temperature. After the reaction was completed, the chemists isolated the final product by treatment with a saturated baking soda solution followed by chromatography and studied its composition and structure using various methods, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
In total, the RUDN University chemists obtained 16 acetimidamides. When using isocyanoacetic ester, imidamides were further cyclized with the formation of an imidazolone fragment. Thus, a series of 19 imidazolones containing an indole substituent was synthesized. The most suitable solvent was acetonitrile. It allowed to minimize the formation of by-products. After three hours at a temperature of 20℃, the reaction yield (the ratio of the actual mass of the product obtained to the theoretical one), was 75%. And after 12 hours, the output reached 96%. Chemists tried to accelerate the reaction by increasing the temperature, but this attempt was unsuccessful due to a tar formation and an increase in the amount of the by-product.
“These reactions furnish a new practical synthetic approach to a series of compounds with a privileged indole scaffold, which are prospective choices for seeking new physiologically active compounds”, said Nikita Golantsov, PhD, Professor of the Department of Organic Chemistry of the RUDN University.
The results are published in the journal Molecules.
The RUDN Prize for Scientific Achievements in Chemistry for 2025, with a monetary award of 2 million rubles, was awarded to Alexander Davidovich Dilman, Deputy Director of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The researcher received the award during the celebration marking RUDN’s 66th anniversary.
Sergey Ivanov, a scholar from St. Petersburg, has been named the first winner of RUDN University’s International Prize for Scientific Achievements in Mathematics, worth 5 million rubles.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.