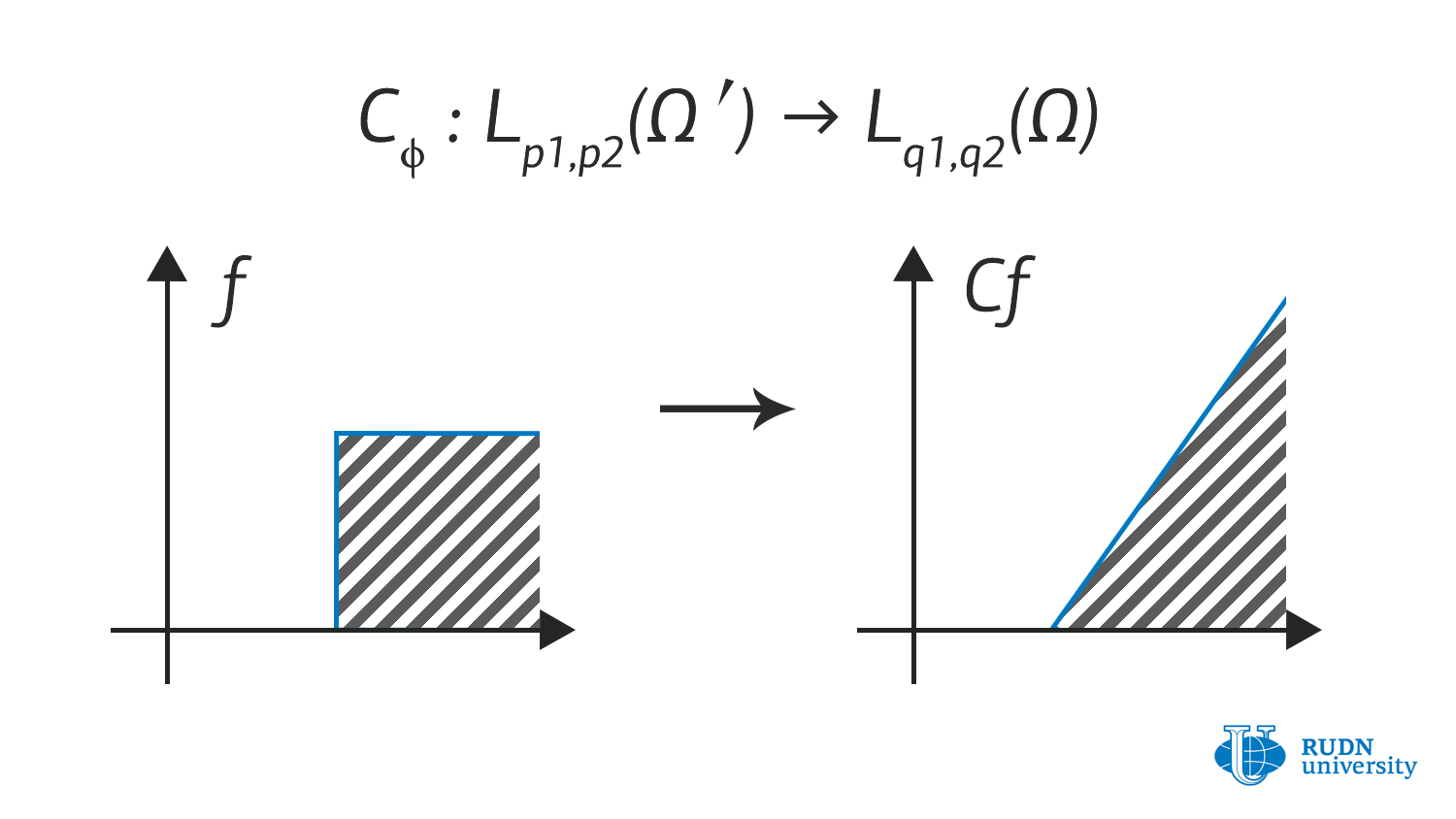RUDN University mathematicians created a method for study the properties of porous materials
Just as any scientific and engineering field cannot exist without a theory, modern science of partial differential equations has its own “theory”: the language of functional analysis. Studies of function spaces in which solutions to equations are sought, started in the XIX century and continue to the present. At first, we learned to apply Fourier theory to solutions to the simplest linear partial differential equations, then studied Banach and Hilbert spaces, as well as spaces of generalised functions, which is essentially the language of quantum mechanics.
Around the middle of the XX century, Sobolev spaces were discovered, which now occupy one of the central positions in the theory of partial differential equations. Over the next 50 years they helped find many solutions to applied problems, that cannot be found in ordinary functional spaces.
Closer to the beginning of the XXI century, it became necessary to find new methods to study nonlinear partial differential equations, so, computational mathematics and the theory of integrable systems were developed. However, methods from these fields turned out to be too narrowly focused, and the need to develop the language is still there.
Lebesgue spaces with mixed norms are sometimes more universal and flexible objects. These spaces are determined as follows: in the space of functions in several variables, define the norm by iterating Lebesgue norm. They initially arose as one of the generalisations of Sobolev spaces and have already attracted a lot of interest from theorists from several countries of Europe, as well as China, Canada, and Russia.
Scientists from the Mathematical Institute of RUDN University, Nikita Evseev and Alexander Menovshchikov, develop a theory of operators for such spaces, which allows for them to be used in applied problems formulated in the language of partial differential equations. They received quite a number of new results describing the properties of operators on such spaces: criteria for boundedness of operators, properties of integral operators, multiplication operators, composition operators, and many others. They also obtained a few auxiliary results useful for the further development of this field.
“Our methods and results, we believe, can be applied to evolutionary problems and differential problems on non-cylindrical regions. For example, in (mathematical) biology, where the surface or the area under study changes with time, or in hydrodynamics for problems with a variable boundary,” says Evseev.
Research in this field is useful for studying the Navier-Stokes equations, a system of equations describing aero- and hydrodynamics. Lebesgue spaces with mixed norms make it possible to evaluate solutions, which, in turn, allows predicting an absence of turbulence, for example.
The results will also help study the applied problems of mathematical physics arising in the study of porous materials and materials with cracks. For example, it will be possible to theoretically predict the pattern of diffusion and heat transfer in silica gels, porous glasses, various sponges, and foams, as well as in some building materials.
The article was published in Mathematical Notes.
The RUDN Prize for Scientific Achievements in Chemistry for 2025, with a monetary award of 2 million rubles, was awarded to Alexander Davidovich Dilman, Deputy Director of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The researcher received the award during the celebration marking RUDN’s 66th anniversary.
Sergey Ivanov, a scholar from St. Petersburg, has been named the first winner of RUDN University’s International Prize for Scientific Achievements in Mathematics, worth 5 million rubles.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.