RUDN University Physicists Described a New Type of Amorphous Solid Bodies
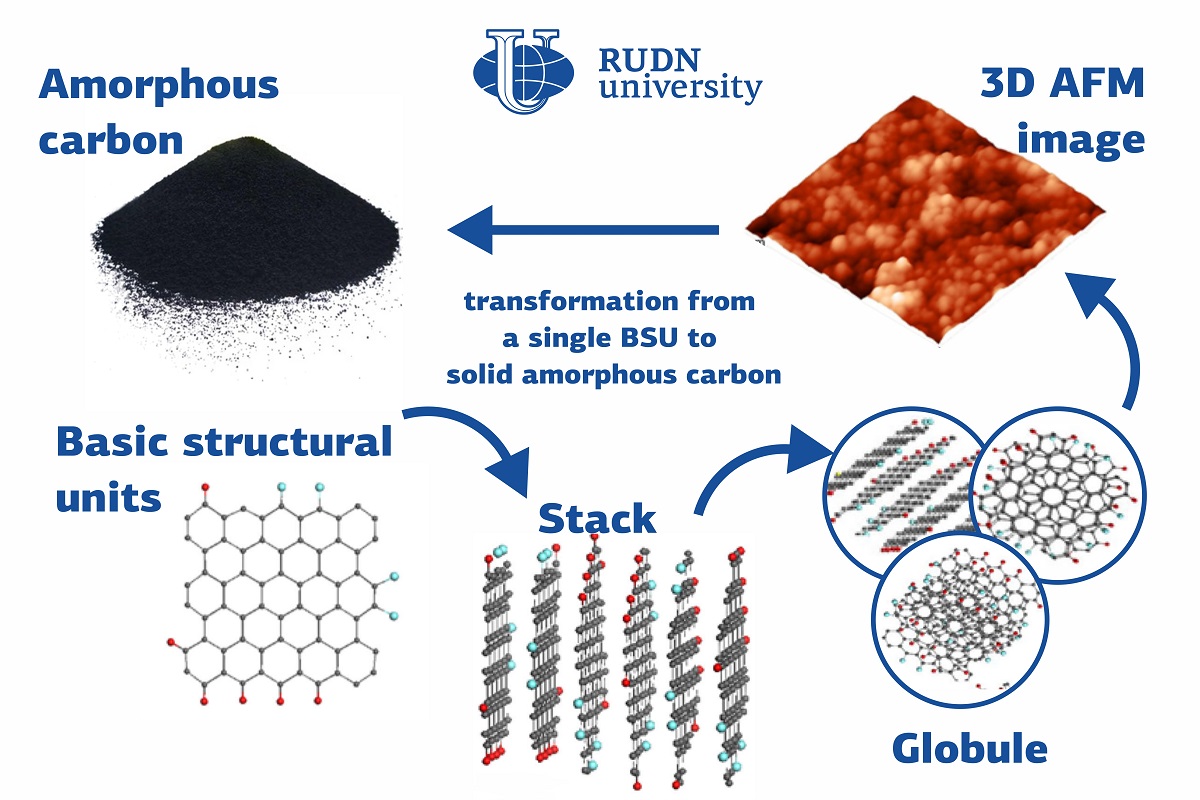
Solid carbon has many allotropic modifications. It means that substances with different chemical and physical properties can be built from one and the same atoms arranged in different structures. The variety of carbon allotropes is due to the special properties of its atoms, namely their unique ability to form single, double, and triple valence bonds. If, due to certain reaction conditions, only single bonds are formed (i.e. the so-called sp3-hybridization takes place), solid carbon has the shape of a three-dimensional grid of tetrahedrons, i.e. a diamond. If the conditions are favorable for the formation of double bonds (sp2-hybridization), solid carbon has the form of graphite—a structure of flat layers made of comb-like hexagonal cells. Individual layers of this solid body are called graphene. These two types of solid carbon structures are observed both in ordered crystals and non-ordered amorphous bodies. Solid carbon is widely spread in nature both as crystalline rock (graphite or diamond) deposits and in the amorphous form (brown and black coal, shungite, anthraxolite, and other minerals).
Unlike its crystalline form, natural amorphous carbon belongs to the sp2 type. A major study of the structure and elemental composition of sp2 amorphous carbon was conducted at the initiative and with the participation of a team of physicists from RUDN University. In the course of the study, the team also took spectral measurements using photoelectronic spectroscopy, inelastic neutron scattering, infrared absorption, and Raman scattering. Based on the results of the study, the team concluded that sp2 amorphous carbon is a fractal structure based on nanosized graphene domains that are surrounded by atoms of other elements (hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and so on). With this hypothesis, the team virtually re-wrote the history of amorphous carbon that has been known to humanity since the first-ever man-made fire.
“The discovery and experimental confirmation of the graphene nature of the ‘black gold’ will completely change the theory, modeling, and interpretation of experiments with this class of substances. However, some questions remain unanswered. What does solid-state physics make of this amorphous state of solid carbon? What role does amorphous carbon with sp2-hybridization play in the bigger picture? We tried to find our own answers,” said Elena Sheka, a Ph.D. in Physics and Mathematics, and a Consulting Professor at the Faculty of Physics and Mathematics and Natural Sciences, RUDN University.
The team spent two years thoroughly studying the nature of amorphous carbon. Other results of this ambitious project were published in Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, and Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, Nanomaterials. Together, these works confirm a breakthrough achieved by the physicists of RUDN University in this complex field of physics.
“We have analyzed many studies on amorphous sp2 carbon from the point of view of our general understanding of amorphous solid bodies. Based on our research, we can confirm that it belongs to a new type of amorphous substances,” added Elena Sheka from RUDN University.
The results of the study were published in the Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures journal.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.
Ambassadors of Russian education and science met at a conference in RUDN University to discuss how they can increase the visibility of Russian universities and research organizations in the world, and attract more international students in Russia.
The international scientific seminar hosted by RUDN Institute of Ecology “Experience of participation in student organizations as a way to form career skills” united scholarship recipients of the International Student Mobility Awards 2024 and Open Doors, along with members of the scientific student society “GreenLab” and the professional student association “Kostyor (Bonfire)” shared their projects focused on environmental protection.