RUDN University Bioengineers Have Created Nanocontainers for Targeted Drug Delivery
One of the main problems of pharmaceuticals is the side effects that often occur due to the fact that the active substance of drugs gets into healthy organs. This is why, for example, chemotherapy is so difficult for patients in the treatment of cancer: toxic drugs act not only on the tumor cells, but also on the entire body. Targeted drug delivery systems can solve this problem. In recent years, many potential ‘carriers’ have been proposed: microcapsules with a polyelectrolyte shell, artificial liposomes of micro- and nanoscale sizes, and protein nanoparticles. Several dozen medicines packed in such containers are already used in practice or are undergoing clinical trials.
However, there are still a number of problems that prevent the widespread use of ‘smart’ carriers. One of them is the dependence of biodistribution of drugs in tissues on the size of containers. The smaller the size, the more likely it is that the drug will reach the diseased organ, and the less the dose of the drug is needed and the less the toxic effect. Another problem is the lack of information about toxicity, effects on the body and distribution in living tissues. Both of these problems were successfully solved by RUDN University biochemists in collaboration with colleagues from Russia and the UK.
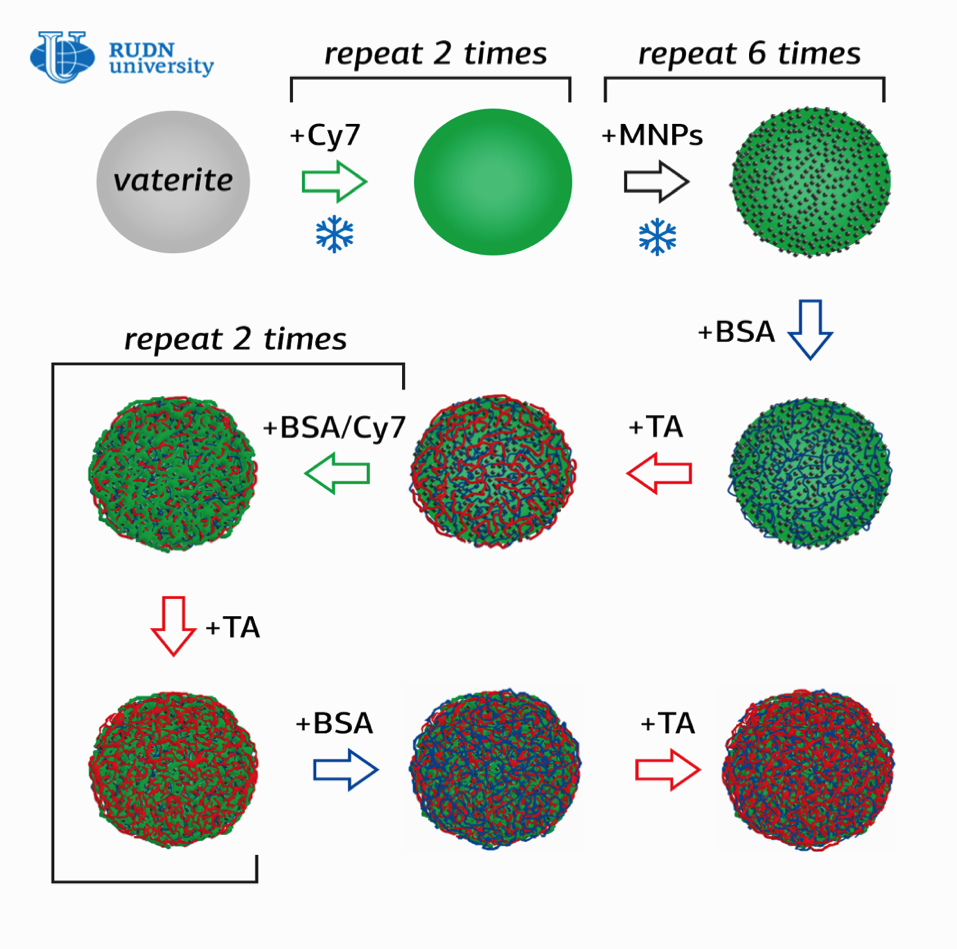
Olga Sindeeva, a researcher at the RUDN Surface Engineering Laboratory, and her co-authors created submicron magnetic-sensitive containers-particles of 400-600 nanometers in size with a shell of several layers of bovine serum albumin (BSA) with a Fluorescent Cy7™ tag and tannic acid (TA).
The novelty of the work is in the method of obtaining containers, in which nanoparticles of magnetite (MNPs), mixed iron oxide (II, III) were first adsorbed on the surface of porous granules of calcium carbonate, which were then coated in series with several layers of BSA-Cy7 and TA. Then the calcium carbonate was washed out of the containers with an aqueous solution with a chelating agent.
‘Using this method, we managed to double the content of magnetite in containers compared to what is obtained by adsorption and co-deposition methods. Thus, it is possible to increase the magnetic moment of nanocontainers and increase the speed of their movement in the circulatory system,’ explained Olga Sindeeva.
RUDN University bioengineers expect that the submicron size of the containers will increase the bioavailability of the drug that is loaded into the MNPs container (BSA-Cy7-TA).
Preliminary experiments on two cell lines, HeLa and fibroblasts, have shown that containers do not affect cell viability and can be used in vivo.
Then containers without medication were tested on live BALB/c mice of both sexes weighing about 20 grams, 10 individuals per group. Containers in the form of a suspension in saline solution were inserted into the tail vein of anesthetized mice. A suspension of containers without magnetite (BSA-Cy7-TA) was used as a control. Then one of the mice's hind legs was exposed to a magnetic field for an hour, and the other was left free for comparison. The distribution of nanocontainers in the tissues of living mice was observed using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and fluorescent imaging. Magnetometric analysis and histological examination of post mortem mouse tissues were also performed one hour after removing the magnet.
RUDN University biologists have shown that in the peripheral vessels of the hind limbs at rest at a low blood flow rate, MNPS(BSA-Cy7-TA) particles move in the direction of the limb to which the magnet is attached in the first hour after intravenous injection. MRI shows that the concentration of magnetite in the muscle next to the magnet passes through the maximum. The magnetite content at this time is 70 percent higher than in the free limb. Then the magnetite signal drops to the background values.
Based on the results of histological studies and magnetometry, researchers found that MNPs (BSA-Cy7-TA) were concentrated mainly in the lungs, and, to a lesser extent, in the liver and spleen, and their concentration in the lungs was 4-5 times higher. A small amount of the carrier was also found in other internal organs and in muscles, but in concentrations significantly lower than in the lungs. Thus, biochemists concluded that the distribution of intravenous containers depends on the blood supply to organs, that is, on the speed of blood flow, but is sensitive to the localization of the magnetic field.
Special attention was paid to the study of the toxicity of containers during intravenous administration and their effect on the body. Preliminary tests have shown that in vitro in plasma or blood, a significant part of the containers is subjected to destruction during the day. Research results suggest that containers manage to achieve the goal when administered intravenously. Then, by changing the fluorescence signal, you can see that the carrier particles gradually degrade and are removed from the body. The particles are non-toxic and hemosompatible, their size allows them to penetrate various body tissues, but in working doses they do not harm the respiratory and circulatory systems, kidneys and liver. Activation of the complement system, which is necessary for the biodegradation of the protein shell of containers, does not affect the level of white blood cells, and, therefore, does not lead to noticeable systematic inflammation.
Thus, RUDN University researchers were able to obtain containers with an increased content of magnetite and effectively manage their distribution in the body using a magnetic field.
In the future, the project participants intend to create ‘smart’ nanocapsules that can carry the drug to the diseased organ and only there ‘open’ to release the active substance. This method of drug delivery would help avoid side effects from treatment. In addition, the problem of treating patients with a whole bunch of diseases, as well as children or elderly people with weakened health, when the attending doctor is forced to refuse to prescribe the necessary therapy due to the risk of worsening the patient's condition, can be largely removed.
Research results in the journal Polymers
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.