RUDN University biologist developed new model for analyzing photosynthesis in vivo
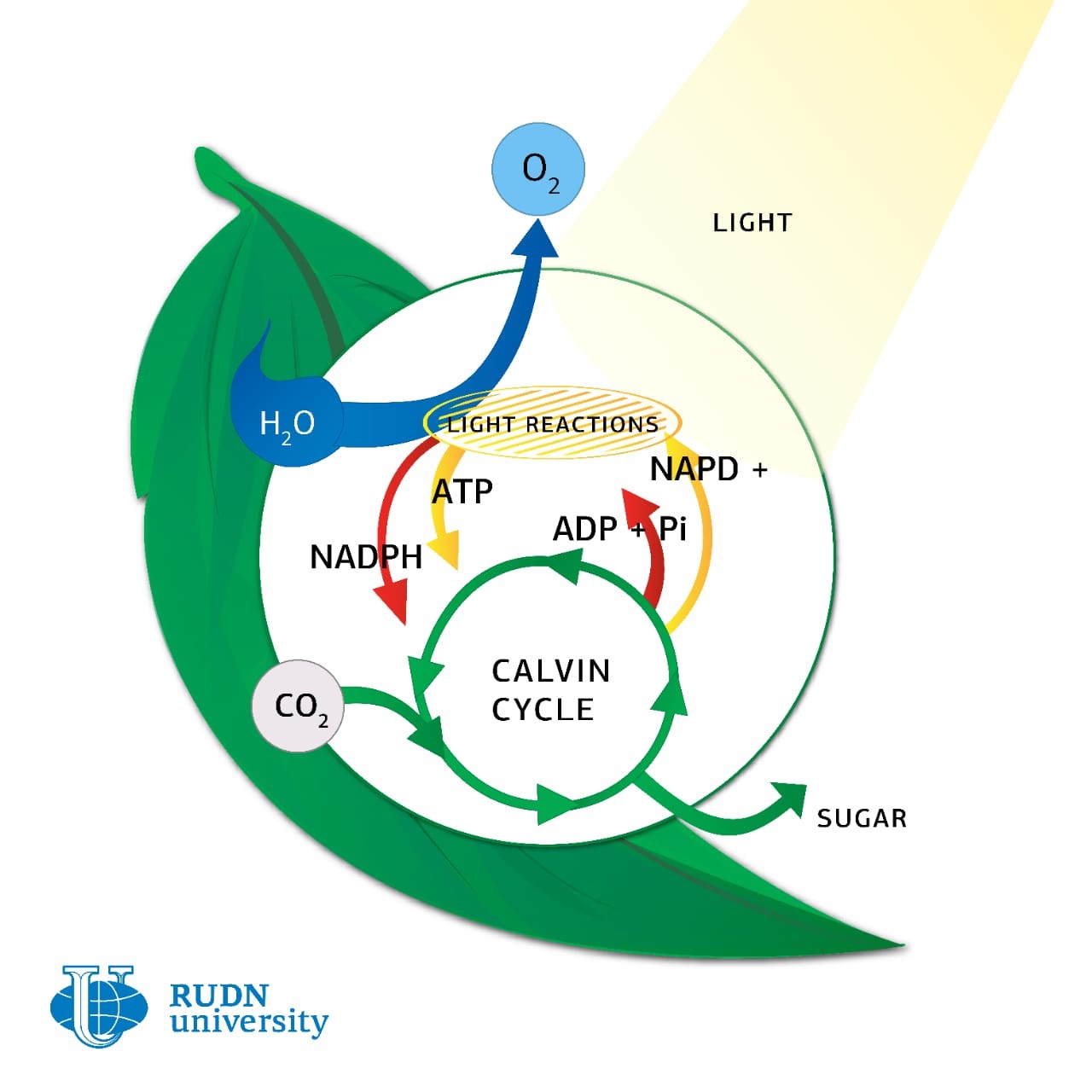
Measurements of the efficiency of photosynthesis in living systems are necessary because they allow us to estimate the carbon cycle, and therefore the impact on the climate. To study photosynthesis in vivo, the vegetation absorption coefficient is used – a value that shows how deep the incident radiation penetrates the canopy. It depends on biochemical, structural and external factors, so its evaluation is very difficult. Alexei Solovchenko, an employee of RUDN University, and his colleagues from the USA and Israel have found a new way to assess this indicator.
First, biologists calculated the ratio of absorption and transmission coefficients for individual leaves and canopy in general. Measuring these coefficients for the canopy “in sum” is difficult, but for a single leaf it is simple, so knowing the ratio between them, you can calculate the absorption and transmission of canopy, knowing the coefficients for a single leaf. Then the researchers of RUDN University obtained an equation that connects the canopy absorption coefficient to the pigments absorption coefficient – primarily chlorophyll – in leaves. It turned out that the canopy, unlike a single leaf, can absorb light in the infrared range, and also, the absorption coefficients of pigments for plants with different densities of canopy, may differ. Therefore, biologists had to make appropriate changes to the final model.
The researchers tested this mathematical model describing the canopy absorption coefficient on crops with different types of photosynthesis – corn (C4 photosynthesis), soybeans and rice (C3 photosynthesis), measuring the spectra of absorbed and reflected solar radiation.
The model showed that in the blue spectral region, the canopy of rice reflects more than the canopy of other crops. Scientists believe it is because rice grows in water. Also, absorption curves for plants with C3 type of photosynthesis (soybeans and rice) obtained with the model differed from those of plants with C4 type of photosynthesis (corn), due to biochemical differences.
Thus, the model created by biologists can "predict" the absorption of light by different types of plants with different types of photosynthesis, different canopy architectures and different pigment content in the leaf.
The article was published in Remote Sensing of Environment.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.