A chemist from RUDN University came up with a new catalyst for fuel synthesis
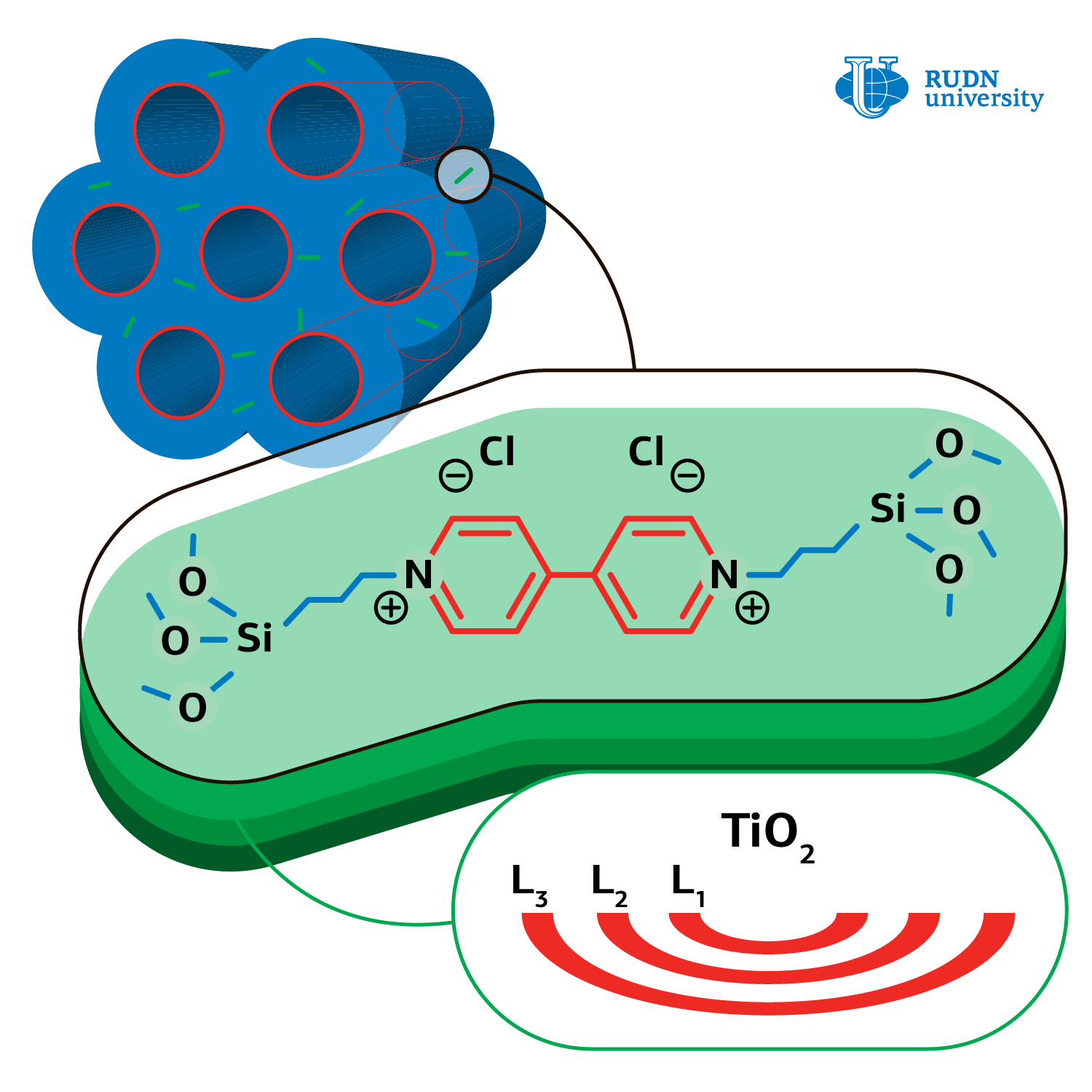
Hydrogen energetics development is not possible without methods of hydrogen secure storage and generation. Formic acid is a non-toxic and highly stable source of hydrogen. Н2 and СО2 are obtained by decomposition of acid under light irradiation on catalysts’NPs, the role of which is fulfilled by platinum, palladium, and other costly metals compounds. Chemists decided to test what the products of formic acid photo‑oxidation will be obtained if the cheaper layered amorphous oxide of titanium is used as a catalyst.
Professor Rafael Luque, United Institute of Chemical Research RUDN and his colleagues from Iran, Spain, China, and South Korea synthesized a catalyst — titanium amorphous oxide based on organic-silicate matrix. At the beginning the chemists obtained mesoporous (2-50 nm) matrix material, where bridging dimeric groups of organic viologen compound presented. Later the precursor — titanium butoxide was loaded, followed by matrix drying at 60 о С and its transformation into amorphous titanium oxide.
The chemists performed the reaction of formic acid oxidation in different conditions: different temperature regimes (from 25 to 60о С) and different quantity of catalyst from amorphous titanium oxide (from 5 to 20 mg), with different solvents (water, ethanol, methanol, and others). The results of experiments showed that the quickest reaction proceeds under UV radiation, in water and at room temperature, providing only CО2 and Н2О. Neither hydrogen, nor carbon monoxide, which poison any photo‑oxidation catalyst, were identified in products. Such products formation is due to the catalyst’s non-crystalline structure. In their work the authors came up with the photo-oxidation mechanism and specified basic stages.
The authors also found out that viologens improve the quality of catalyst, because it generates electron-proton vapors in photocatalysis, thus extending the lifetime of the catalyst. The catalyst can be easily reprocessed and reused at least in four cycles without noticeable ageing.
The scientists made an input in fundamental chemistry development, having investigated a new mechanism of formic acid formation. The results of the present research will allow to minimize risks and expenditures in common use of this type of catalyst in future development.
The article is published in the journal ChemCatChem.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.