RUDN University chemists synthesized new fluorescent substances for medical applications
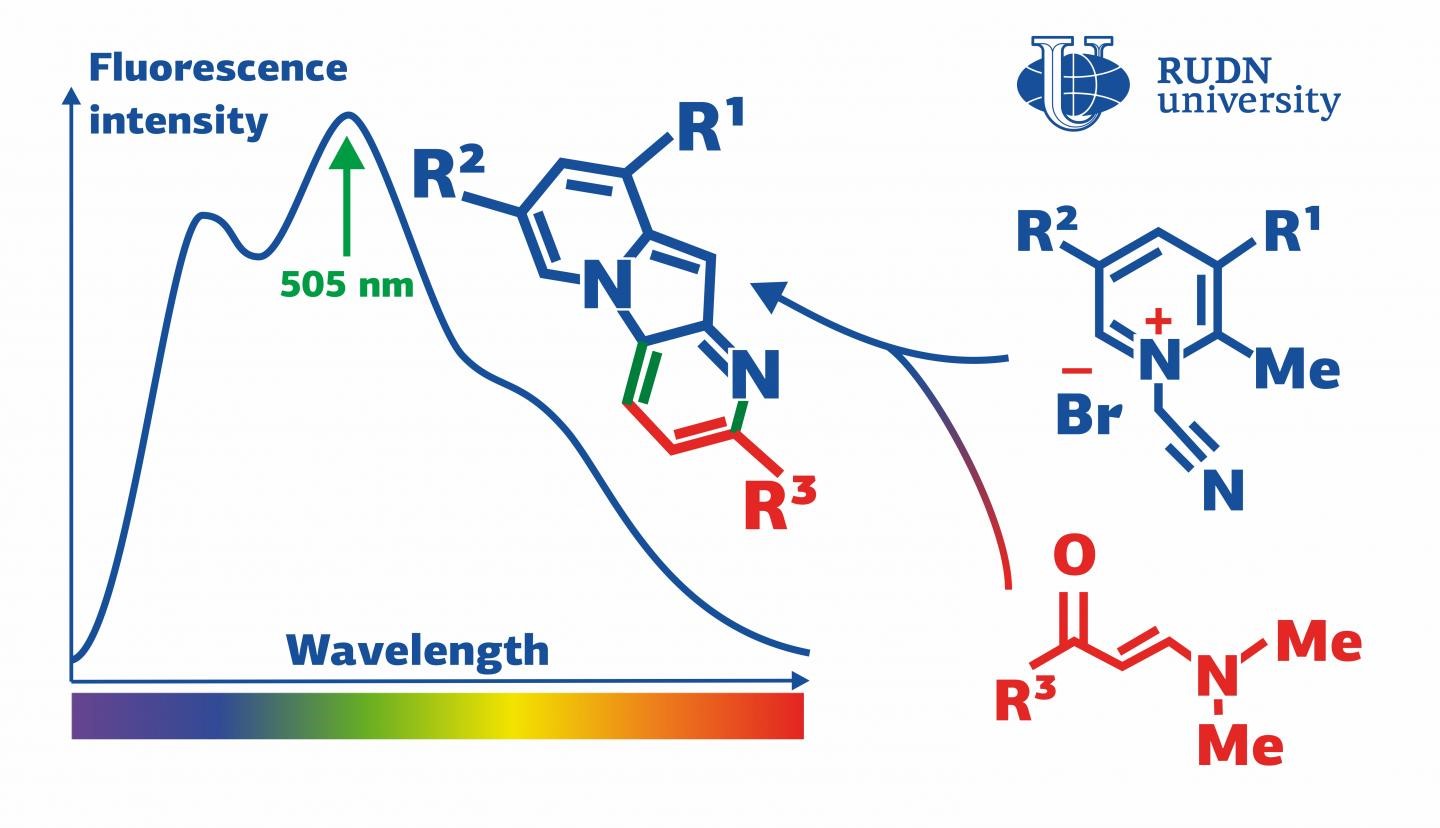
Indolizines are organic substances that contain two carbon cycles and one atom of nitrogen. They are used to produce dyes and solar panels, as well as anti-tumor and anti-diabetes drugs. Indolizines do not occur naturally but are constructed in labs, usually using the reactions of cycloaddition. These reactions involve pyridinium salts—electrically neutral molecules with positively and negatively charged ’poles’ that balance each other. A team of chemists from RUDN University discovered an unexpected reaction in which, instead of cycloaddition, a pyridinium salt undergoes two other consecutive processes. The end products of this reaction are indolizines with fluorescent properties.
“We found out that pyridinium salts that contain a methyl group bound with C(2) tend to enter into an unexpected domino reaction with enaminones, and consecutive cycloisomerization and cyclocondensation take place, while the reactions of cycloaddition that are typical for pyridinium salts are not observed,” said Alexey Festa, PhD, a Senior Lecturer at the Department of Organic Chemistry, RUDN University.
A team of chemists from RUDN University, MSU, and KU Leuven (Belgium) suggested an approach based on their earlier studies of reactivity of pyridinium salts. The team studied 1-(cyanomethyl)-2-alkylpyridinium salts in reactions with enaminones and chose optimal conditions for the production of indolizines. By changing the ratio of the initial components, the team managed to gain only a 50% reaction yield. However, after other pyridinium salts were used, the yield increased to 82%. The two-stage reaction turned out to be of the domino type, i.e. the first stage initiated the second one in the same flask without any additions of new reagents or changes in reaction conditions. The team used X-ray structural analysis to study the new indolizines and also paid attention to their optical properties.
Eight of the new indolizines were capable of intensive fluorescence (i.e. of absorbing light with a certain wavelength and emitting light with a longer one). This mechanism is based on the excitement of electrons, that is, their movement to a higher energy level under the influence of photons. This process is accompanied by energy release, and a part of it is emitted in the form of photons with reduced energy and therefore increased wavelength. The indolizines synthesized by the team were particularly effective in absorbing emissions with the wavelength of 403-420 nm that belong to the blue-violet range bordering on the UV light. The wavelength of the light emitted by the indolizines amounted to 505-528 nm which corresponds to the green range of the spectrum. These properties make indolizines a promising material for the manufacture of fluorescent tags that are used to study biological objects.
“Pyrido[2,3-b]indolizines obtained in the course of our reaction showed certain fluorescent properties. Namely, they emitted green light with a high quantum yield (a parameter that characterizes the efficiency of this process). The lowest yield values amounted to 55-63% and in the case of one new indolizine the yield reached 82%,” added Alexey Festa from RUDN University.
The article was published in Molecules
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.