Chemists from RUDN University developed biodegradable antibacterial film for storing food
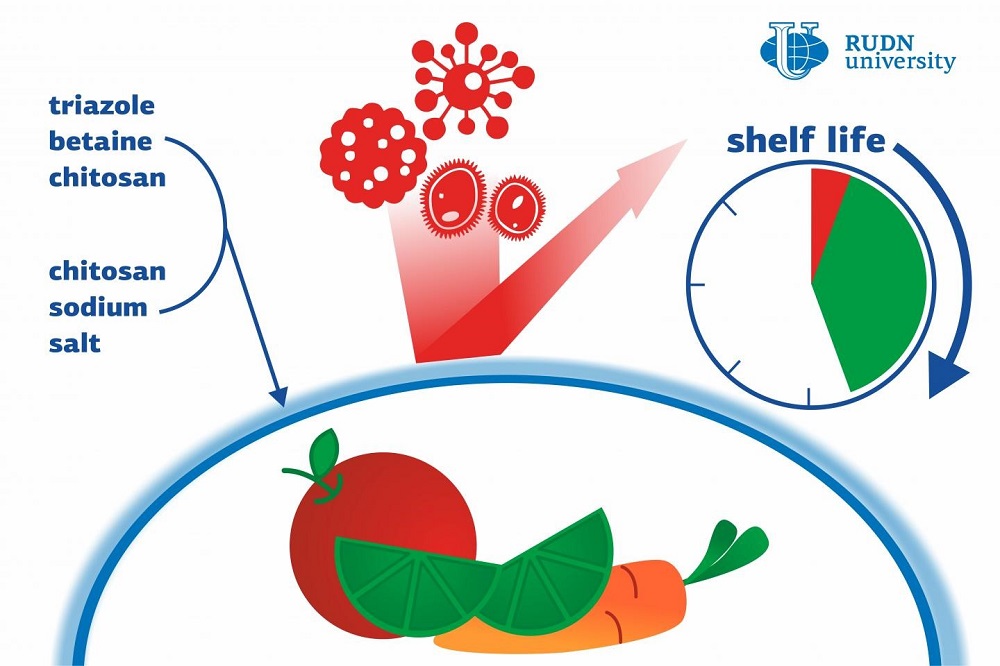
Food wraps are usually produced from chemical compounds based on synthetic polymers such as polyethylene and polypropylene. These materials are bad for the environment and take dozens, if not thousands of years to decompose. Naturally, a food coating should protect the food and contain no toxins that could contaminate it, but it is also important for it to decompose without a trace after being used. A team of chemists from RUDN University created such a coating from polysaccharides—natural macromolecules that are the building blocks of living organisms. Polysaccharides do not have a negative effect on health, are biodegradable and non-toxic.
The antibacterial coatings suggested by the team are based on chitosan, a polysaccharide that is found in carapaces of crabs or in lower fungi. Specifically, the chemists used two derivatives of chitosan: SC-Na, or chitosan succinyl sodium salt, and a compound of triazole, betaine, and chitosan (TBC). The latter possesses antibacterial properties comparable to those of modern-day antibiotics. According to the team, TBC nanoparticles embed into an SC-Na grid or matrix, creating a thin uniform film. It is much stronger than any of its individual components and lets less oxygen and steam in. In the course of the experiments, the scientists confirmed that the film is the most efficient when the SC-Na to TBC ratio is 1 to 1.
“We managed to obtain non-toxic chitosan derivatives with extraordinary antibacterial properties almost similar to those of commercial antibiotics and suggested that they could be used to increase film durability and antibacterial characteristics. We based our coating on SC-Na, a salt with high film-forming ability. Moreover, it is not toxic and works as an antioxidant, increasing the shelf life of food products. By changing the TBC/SC-Na ratio, we developed multifunctional food coatings with improved antibacterial, protective, and mechanical properties,” said Andreii Kritchenkov, a Candidate of Chemical Sciences, and a research assistant at the Department of Inorganic Chemistry, RUDN University.
To test their invention, the team put several bananas in the film for 10 days. In the course of the experiment, the scientists measured their weight, vitamin C content, and the level of carbon dioxide emission. After 10 days, these parameters were compared to the results from the control group that was kept without coating. Coated fruit turned out to have lost 3 times less weight and 8 times less vitamin C, and the frequency of their ’breathing’ was 2.6 times lower (i.e. metabolic processes that are associated with CO2 emissions slowed down).
Thanks to these properties, chitosan-based films can be used to store food products. After a film has been used, it will decompose without causing harm to the environment.
The article was published in Food Packaging and Shelf Life.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.