RUDN University Biophysicist modelled the effect of antiseptics on bacterial membranes
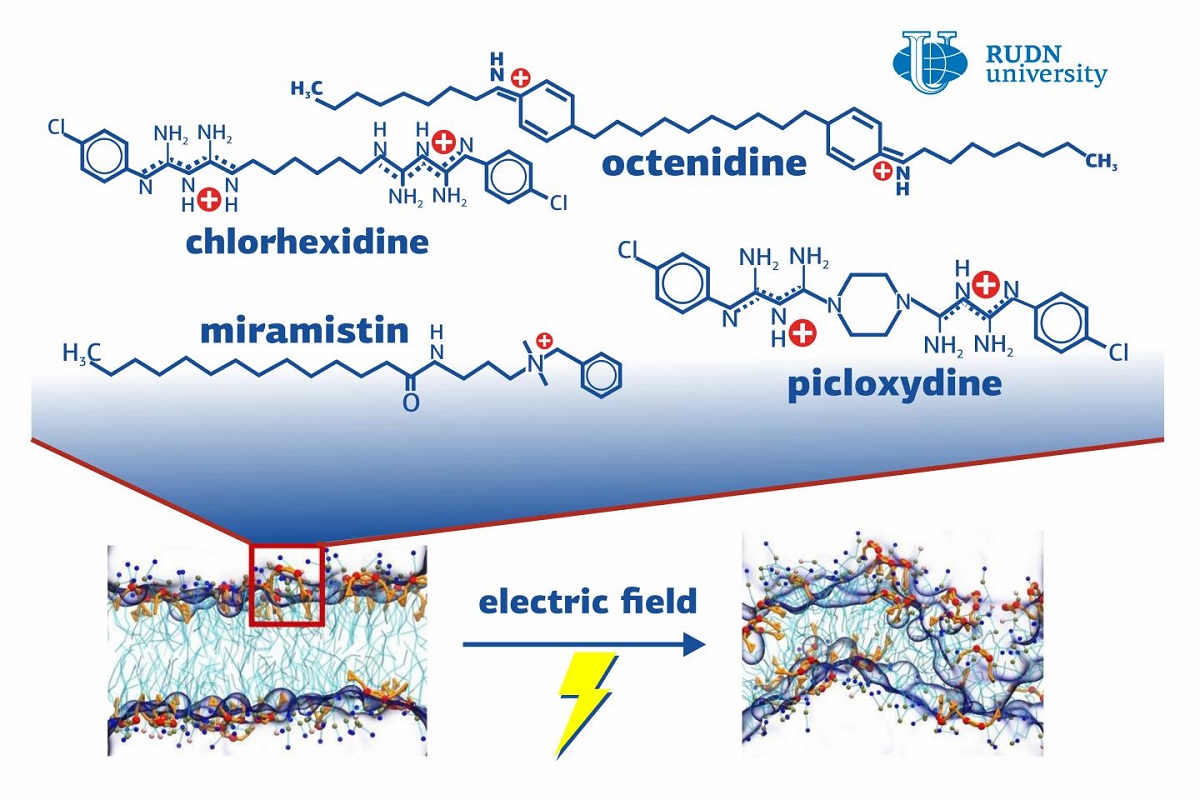
Antiseptics are chemical agents that affect the internal processes or external structures of harmful microorganisms causing them to die. For example, alcohols break down important building and regulation blocks of bacteria and viruses. Other antiseptics target the integrity of bacterial membranes. They are effectively used against a wide range of pathogens, but their mode of action remains elusive. Scientists are aware of some general patterns, such as the presence of electrically charged particles in the molecules of antiseptic agents. The team developed a computer model of a bacterial membrane and found out the mechanism of the antiseptic activity. The results of the study can help to combat bacterial resistance.
“Some pathogens, especially those associated with hospital infections, show resistance to antiseptics. It is important to understand the physics behind the interaction of antiseptics and microorganisms to use antiseptics more efficiently and to develop new agents,” said professor Ilya Kovalenko, Ph.D., Doctor of Science in Physics and Mathematics, working under Project 5-100 at RUDN University.
The scientists developed a model of a bacterial membrane and put the molecules of four antiseptics (miramistin, chlorhexidine, picloxydine, and octenidine) on it. All these substances are cationic antiseptics, i.e. their molecules are positively charged. However, to the researchers’ surprise, the antiseptics failed to damage the membrane and just slightly changed its structure. Even when the ratio of antiseptics to membrane lipids was increased from 1/24 to 1/4, the membrane was not destroyed.
The destruction of the membrane took place only when an external electric field (with the intensity of 150 mV/nm) was added to the model. The membrane started to restructure, and pores began to form around the molecules of the antiseptics. Then, water got into them and made them bigger; and eventually, the membrane was torn apart. This was because the membrane became thinner around positively charged molecules: the molecules of the membrane had no charge and therefore were pushed away. An uneven membrane became more susceptible to adverse external factors, which led to the death of the cell.
“We studied the reaction of the model membrane to several cationic antiseptics and found out that structural changes in the membrane in the presence of an electrical field play a key role in the formation of pores. We plan to use this model to predict the effect of existing and new antiseptics on different microorganisms,” added professor Ilya Kovalenko, Ph.D., Doctor of Science in Physics and Mathematics, working under Project 5-100 at RUDN University.
The results of the study were published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.