A Chemist from RUDN University Developed A New Type of One-Molecule Thick Water-Repellent Film
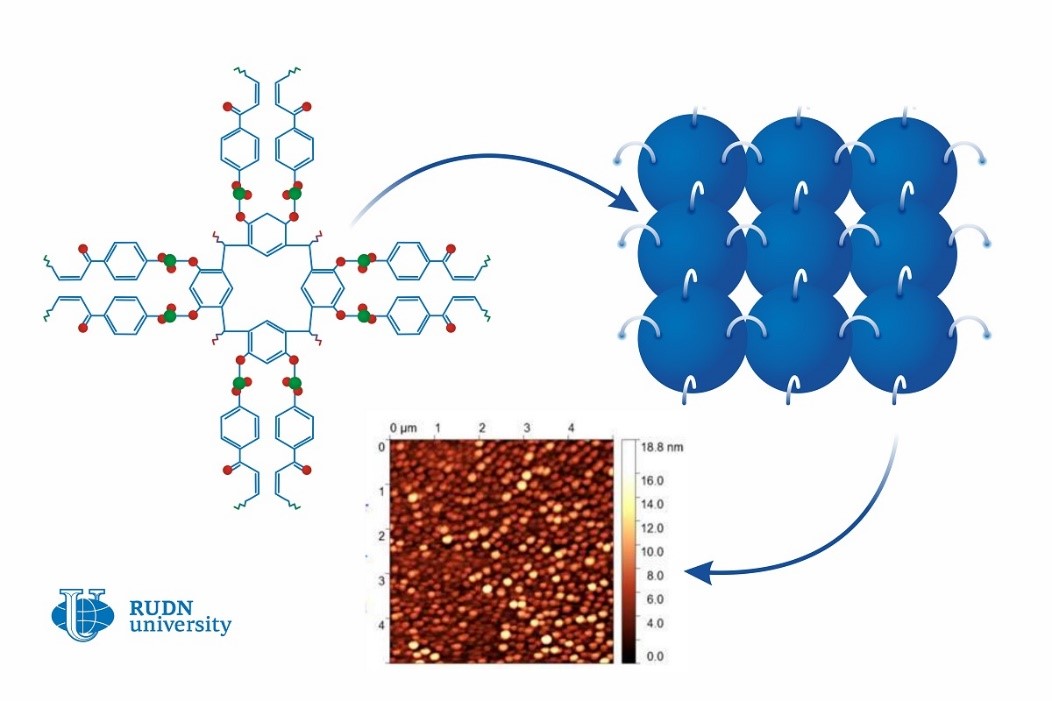
Calixarenes are large bowl-shaped organic molecules that consist of several rings. The outer ring of the bowl is hydrophilic, i.e. actively retains water. The innermost ring is hydrophobic or water-repellent. Calixarenes are known in the chemical industry as additives: for example, they play a role in the synthesis of ethylene and propylene polymers. Scientists from Belarus and Russia, including a chemist from RUDN University suggested a new way of using them. They developed 0.8-1.5 nm thick calixarene-based films that can work as water-repellent coatings.
“These 2D organic films can be used to create protective hydrophobic or anti-corrosion coatings for organic electronics or to develop molecular filters,” said Alexey Kletskov, a Candidate of Chemical Sciences, and a researcher at the Joint Institute for Chemical Research, RUDN University.
The team used the Langmuir-Blodgett method to construct a thin film from single molecules. The method had been developed especially for the molecules that have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts. When put in water, molecules like this align on the surface with their hydrophobic parts turned up. After that, they are pressed with special plungers, and when the required density is reached, the film is moved onto a solid base.
To strengthen the film, the team used UV radiation. It has enough energy to break down hydrocarbon chains that bind the outer and inner rings of each molecule together. First the chains are broken, and then they bind again, but this time with loose ends from other calixarene molecules. As a result, all molecules in the film become closely tied together.
The team studied the structure of the films using an atomic-force microscope and found out that the efficiency of UV radiation correlates with the length of the chains in the original macromolecules. Molecules with short chains formed more stable films, and in the case of long-chain molecules, UV radiation caused the films to have irregular structure with clusters. Therefore, UV light was found to not always be beneficial for film quality. Depending on the molecule structure, it can reduce the water-repellent properties of a film or have no considerable effect at all. It is an important factor to consider when using the films as hydrophobic coatings on different surfaces, from displays to construction coatings.
The results of the study were published in the Materials Today Communications journal.
RUDN summarized the results of the scientific competition "Project Start: work of the science club ". Students of the Faculty of Physics, Mathematics and Natural Sciences have created a project for a managed queuing system using a neural network to redistribute resources between 5G segments. How to increase flexibility, make the network fast and inexpensive and reach more users — tell Gebrial Ibram Esam Zekri ("Fundamental Computer Science and Information Technology", Master's degree, II course) and Ksenia Leontieva ("Applied Mathematics and Computer Science", Master's degree, I course).
The National Demographic Report, 2023 Demographic Well-Being of Russian Regions (hereinafter - the National Demographic Report) was prepared by the scientific team of the Institute of Demographic Studies of the Federal Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the Vologda Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Peoples' Friendship University of Russia, the Center for Family and Demography of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Tatarstan, as well as with the participation of leading scientists from the Republic of Bashkortostan, Stavropol Krai, Volgograd, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad, Nizhny Novgorod, Sverdlovsk Oblasts and Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra.
RUDN summarized the results of the scientific competition "Project Start: work of the science club ". Students of the Faculty of Physics, Mathematics and Natural Sciences have created a project for a managed queuing system using a neural network to redistribute resources between 5G segments. How to increase flexibility, make the network fast and inexpensive and reach more users — tell Gebrial Ibram Esam Zekri ("Fundamental Computer Science and Information Technology", Master's degree, II course) and Ksenia Leontieva ("Applied Mathematics and Computer Science", Master's degree, I course).
What is your first association with the word “laboratory”? Flasks and beakers? Microscopes and centrifuges? Yes, many of us would answer the same way.
The National Demographic Report, 2023 Demographic Well-Being of Russian Regions (hereinafter - the National Demographic Report) was prepared by the scientific team of the Institute of Demographic Studies of the Federal Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the Vologda Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Peoples' Friendship University of Russia, the Center for Family and Demography of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Tatarstan, as well as with the participation of leading scientists from the Republic of Bashkortostan, Stavropol Krai, Volgograd, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad, Nizhny Novgorod, Sverdlovsk Oblasts and Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra.