A Chemist from RUDN University Developed a New Method for Combating Antibiotic Resistance in Microbes
Bacteria that are protected by a biofilm are more resistant to antibiotics and other adverse environmental factors, and this resistance usually builds up faster than the modern industry is able to produce new drugs. Such bacteria include salmonella that is a major issue both for medicine and the food industry. Scientists constantly search for new approaches that would help reduce resistance levels in bacteria.
“Our strategy has already proven to be successful against biofilms formation on titanium implants, and we are currently working on expanding its applicability to the industrial and food production fields. Since the mechanism of action was partially elucidated, we have foreseen the potential of our technology to revolutionise the way to fight biofilm associated infections. Our future research will greatly benefit from these findings as resistance development usually poses a major threat to the success of antimicrobials,” said Prof. Erik V. Van der Eycken, the Head of the Joint Institute for Chemical Research at RUDN University.
The strategy is based on inhibiting the formation of bacterial films. In the course of the study, the team mixed two strains of salmonella: one of them was able to form biofilms, and the other wasn’t. Then, the speed of their growth was compared. Similarly, the speed of growth was measured for the same mixture of two strains in the presence of 5-aryl-2-aminomidazole, an inhibitor that slows down film formation. It turned out that the strains that were unable to form biofilms propagated more intensively and forced other strains out.
The team also discovered that salmonella did not develop resistance against biofilm inhibitors. Biofilms are quite beneficial for bacteria: the cells that don’t waste their resources on forming them begin to divide more actively. If some bacteria in a medium are resistant to an inhibitor, they divide slower and are eventually forced out of the culture, leaving the films for other bacteria to thrive on.
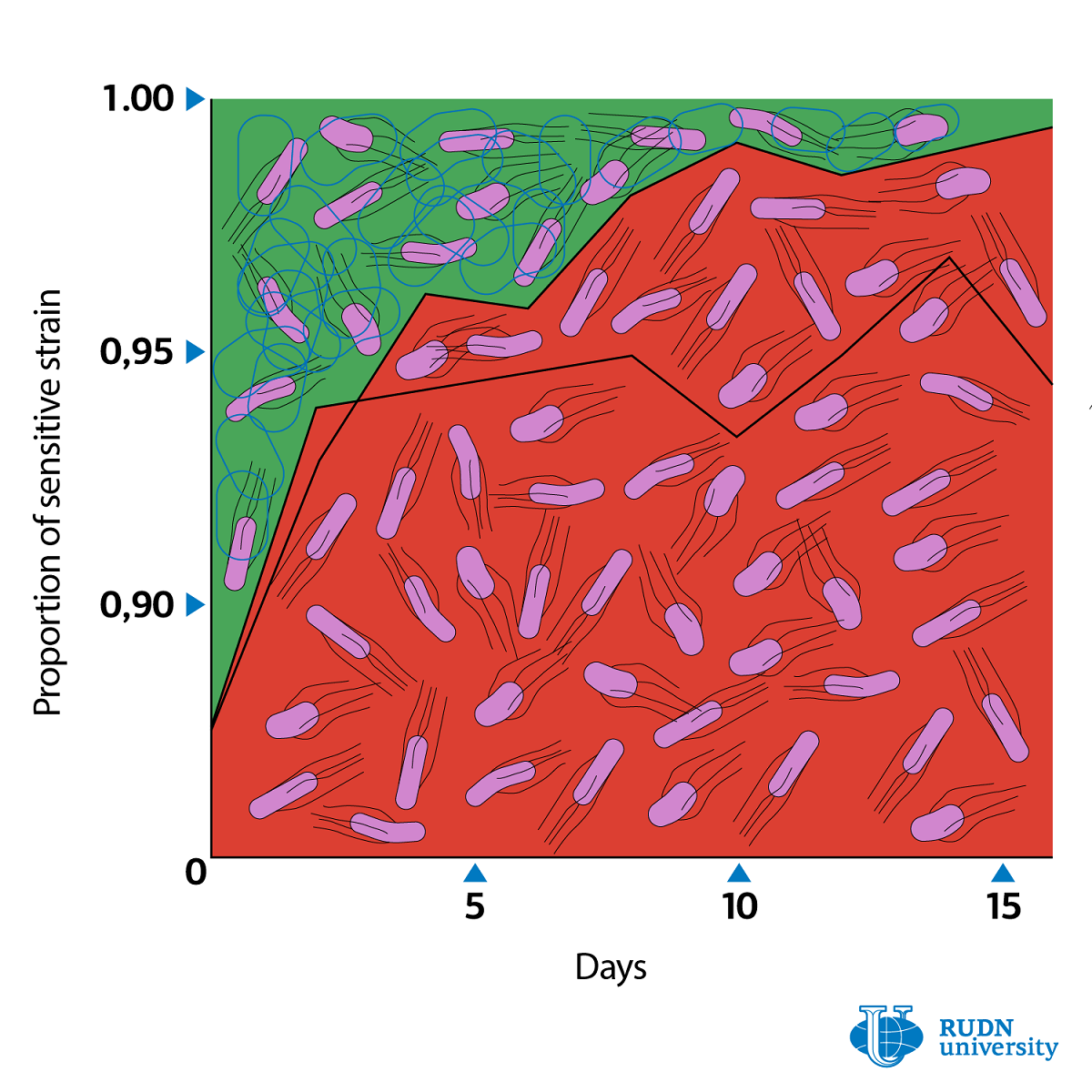
According to the team, the share of resistant strains reduced from 12% to 1% in 16 days after the incubation of the strain mixture with the inhibitor. The scientists concluded that resistant bacteria are driven out of their cultures and that general resistance against inhibitors is not favored by natural selection.
When the production of biofilm matrix is inhibited, it becomes more difficult for cells to attach to surfaces and their susceptibility to antimicrobial drugs increases. For example, salmonella strains form biofilms both inside and outside of a host making them hard to get rid of by means of mechanical treatment, disinfectants, antibiotics, or the host’s own immune system. The approach suggested by the team could make the fight against pathogenic microorganisms more successful while at the same time preventing the development of resistance.
The new method would increase the efficiency of antibacterial therapy and help combat the most widely spread biofilm infections in medicine, food industry, pharma, and agriculture.
The article was published in the Nature Communications journal.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.