RUDN University chemists synthesized chitin-based antibiotics
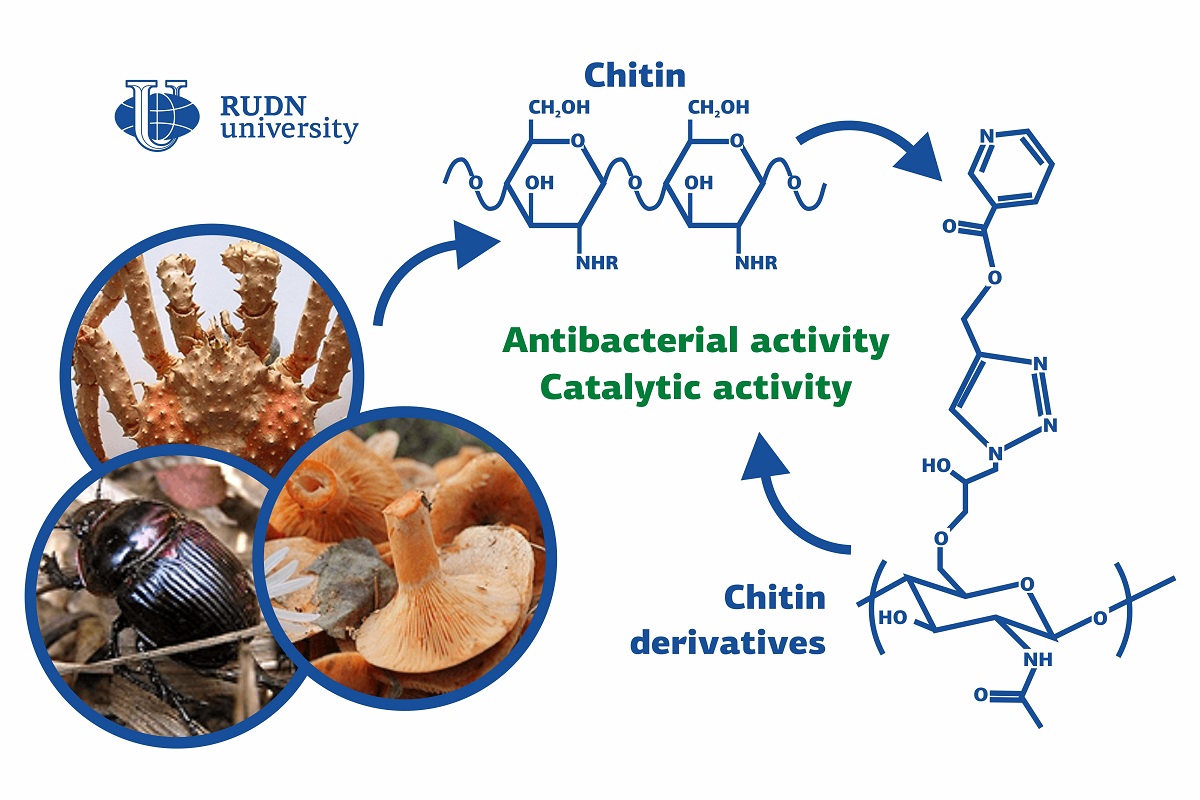
Chitin is the second most widely spread biopolymer on Earth. It is used as a basis for many medicinal drugs and surgical materials, such as burn ointments and gels to promote wound healing. However, chitin and its derivatives are still not fully integrated into medicine. They are not soluble in water or most organic solvents, which makes it difficult to obtain new compounds from them. A team from RUDN University suggested a simple and universal method to synthesize water-soluble chitin derivatives.
In their experiment, the chemists used chitin powder from king crab shells. It was treated with a nitrogen-containing substance at room temperature to obtain chitin derivatives with attached azide groups (three nitrogen atoms). At this stage, the team synthesized three derivatives with azide groups attached to 18%, 42%, and 65% or polymer units. At the second stage, more complex derivatives were constructed from different fragments: an azide group, chitin remains, and nicotinic acid ether. Reactions of this kind are usually carried out in an anaerobic atmosphere, but the team decided to simplify the process and to conduct the experiment under normal conditions. The reagents were subject to ultrasound for 15 minutes. As a result, the team obtained 6 new compounds with different azide group composition and various ethers of nicotinic acid.
The new substances contained groups of atoms with a positive charge that could hypothetically interfere with the work of negatively charged elements in bacterial cell walls. The team tested this theory on two microorganisms: S.aureus and E.coli. In the test, the chemists compared the effects of six new polymers and two antibiotics, ampicillin and gentamicin. The efficiency of each substance was assessed by the diameter of the area around it in which the bacteria died. Most chitin derivatives and their nanoparticles showed better results than the antibiotics, with the zone around one of them being 14.9 mm wider than around ampicillin, when tested on S.aureus. In the case of E.coli, one type of nanoparticles had a 17 mm wider zone around it than gentamicin.
"We managed to add previously unknown polymers to the group of water-soluble chitin derivatives. The new substances are non-toxic, show increased antibacterial activity, and can be used as catalysts in organic synthesis. We continue to study the properties of the new compounds. Right now, our group is researching their ability to treat bacterial infections in lab animals," said Andreii Kritchenkov, PhD, and an assistant researcher at the Department of Inorganic Chemistry, RUDN University.
The results of the study were published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.