Chemists of RUDN showed how new antineoplastic medicine interacts with proteins of blood
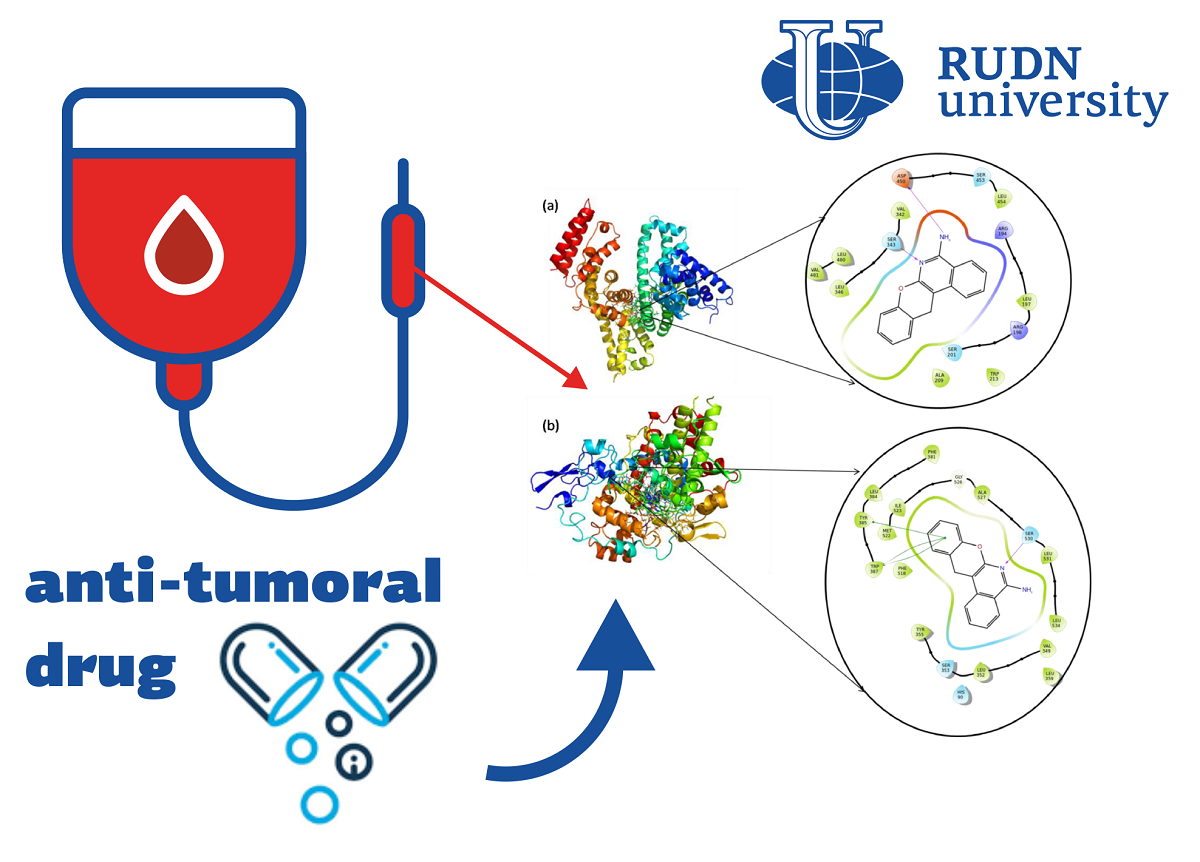
Heterocyclic compounds, in which there are several organic “rings” with atoms of other elements, are of interest to chemists and pharmacists due to a wide range of biological activity. Previously, RUDN University created a heterocyclic compound with a pronounced antitumor effect. In structure, it resembles the drugs aphthazole and panoprofen, which are usually used to combat inflammation. At the same time, the mechanism of their action is not fully known to scientists. One of the indicators of the effectiveness of the drug is its binding to blood proteins, so the study of this process is important for understanding the work of the drug. RUDN chemists continued to study the new drug and studied the features of its biophysical interaction with the body. To do this, they investigated how the drug binds to the protein cyclooxygenase-1 (PTGS1) and bovine serum albumin (BSA).
“Sincethe molecules of the created drug compound are similar to the commercial drugs pranoprofenom and aphthazole,itis interesting to understand the mechanism of its binding interaction with PTGS1 using various biophysical methods. Understanding the interaction with BSA is important because it is a well-known model of proteinmolecules a, which can take various drugs and transfer them to a given molecular environment,” said Alexey Festa, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Senior Lecturer at the Department of Organic Chemistry of RUDN University.
The chemists investigated the drug’s interaction with BSA and PTGS1 experimentally and theoretically, using fluorescence spectroscopy (fluorimetry)as well as computer molecular modeling. Fluorimetry allows you to determine the concentration of a substance by the intensity of fluorescence, which occurs when it is irradiated with a substance.
Fluorescence spectroscopy showed that when the drug interacts with albumin, the effect of the so-called static quenching occurs. This means that the substances have combined with each other, and a non-fluor natural product isobtained. This effect (together with subsequent theoretical simulation results) suggests that the compound follows the principle of hydrophobic interaction. It determines how the structure of the compound will look as a result. Molecular modeling using the molecular docking method showed that in conjunction with BSA and PTGS1, the drug is stable during the entire simulation time.
“Molecular docking studies show that the drug has a goodbinding ability both in combination with BSA and in combination with PTGS. At the same time, the theoretically calculated energyof the connection almost coincides with the one calculated experimentally.Analysis ofmolecular dynamics shows that the drug is stable both in the complex system with BSA and in the system with PTGS1,” — Cubramani Kartikean, postdoc Department of Organic Chemistry rudn University.
The results are published in the Journal of Molecular Structure.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.