A RUDN University Biologist Described How a Harmless Bacterium Turns into a Phytopathogen
The bacteria of the genus Xanthomonas are phytopathogens and cause diseases on dozens of crops including wheat, rice, cabbage, tomatoes, fruit trees, and fodder grasses. However, some representatives of the same genus are not pathogens: though they live on leaves and stems, they only consume the plant secreted organic compounds and dust particles. It is yet unknown why some Xanthomonas bacteria are pathogenic, and some are not.
A biologist from RUDN University explored the following theory. The ancestors of these bacteria could have been harmless and borrowed pathogenic genes from other bacterial species. The researcher and his colleagues compared 32 strains of Xanthomonas arboricola, a species that includes many non-pathogenic strains. Bacteria were collected from tomatoes, oilseeds, sunflowers, and barley to be identified and cultivated on a nutrient substrate. Then, bacterial suspension was made to inoculate the leaves of various crop plants.
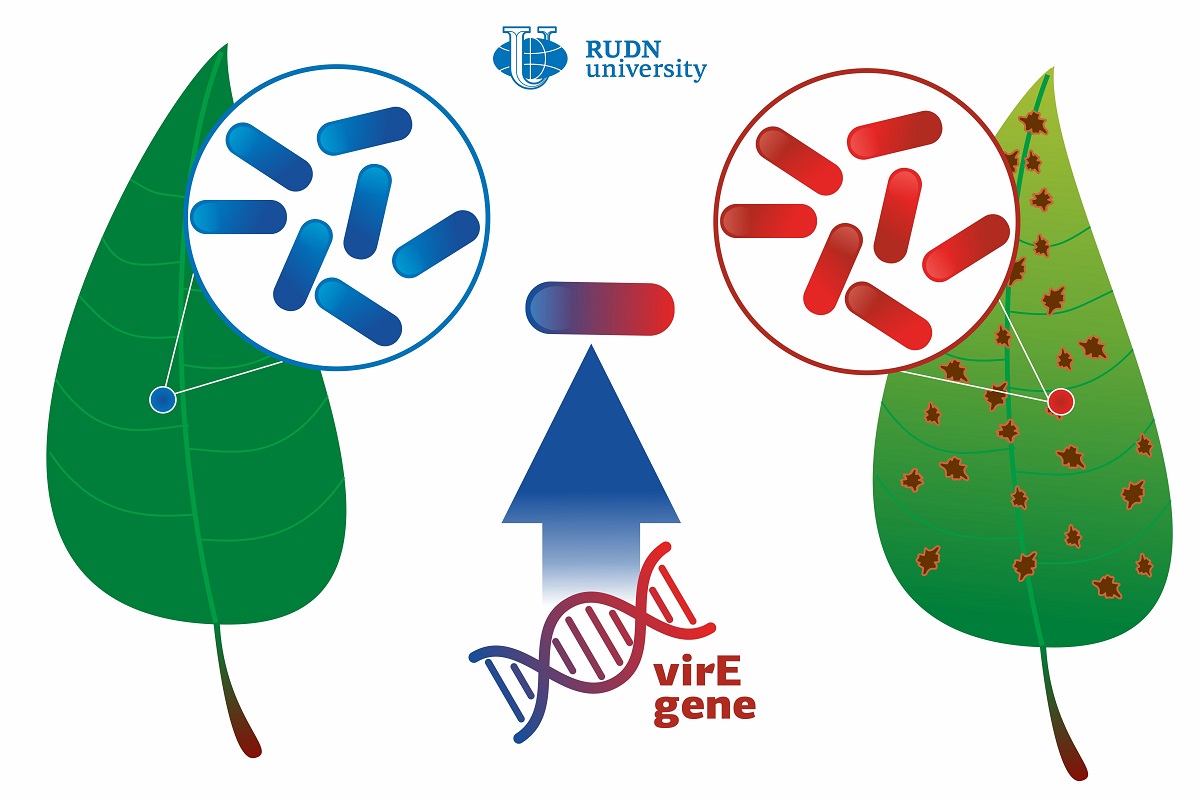
All studied strains turned out to be harmful to at least one crop. The genome of strain 3004 (the most aggressive one that infected barley, wheat, oilseed and vegetable brassicas, tomato, walnut, and sunflower) was sequenced, and a set of specific genes was studied in other strains. However, none of the strains appeared to contain the so-called ‘molecular syringe’ genes—a mechanism of the T3SS transportation system that Xanthomonas pathogens use to attack plant cells. Without this mechanism, the bacteria are suggested to be nonpathogenic. However, the experiment proved them to cause diseases and even death of plants. Therefore, this group of Xanthomonas has alternative way of pathogenicity.
The research team suggested that it could have happened due to lateral gene transfer: a process in which a bacterium receives genetic material from other microorganism, not from its direct ancestors. A key pathogenic factor in all studied strains was the VirE protein that belongs to T4SS, a different bacterial secretion system. The gene that codes this protein could have been borrowed from another species. Before that, X. arboricola strains could have been harmless for the plants they lived on.
“A consensus about the evolution of the genus Xanthomonas hasn’t been reached yet. Some believe that Xanthomonas bacteria had initially been pathogenic, but then some of them lost virulence genes. However, our results support a different point of view. The genome of X. arboricola that we sequenced looks highly mosaic, i.e. has many genes similar to other species. We believe that the ancestor strain of X. arboricola could have been harmless for plants until it received T4SS and T3SS genes by means of lateral transfer,” said Prof. Alexander Ignatov, DSc in Biology, from the Department of Agrobiotechnology at RUDN University.
The results of the study were published in the materials of the international conference PLAMIC2020.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.
Ambassadors of Russian education and science met at a conference in RUDN University to discuss how they can increase the visibility of Russian universities and research organizations in the world, and attract more international students in Russia.
The international scientific seminar hosted by RUDN Institute of Ecology “Experience of participation in student organizations as a way to form career skills” united scholarship recipients of the International Student Mobility Awards 2024 and Open Doors, along with members of the scientific student society “GreenLab” and the professional student association “Kostyor (Bonfire)” shared their projects focused on environmental protection.