RUDN University chemist created substances that stimulate plant growth
Compounds with a ferrocenylalkyl moiety in the molecules are valuable for their biological activity. Derivatives of ferrocene stimulate plant growth, and can also act as antidotes for herbicides, which is important for the environment. Until now, ferrocenyl alkylation (i.e. the reaction of insertion of organic groups into ferrocenyl fragment) was carried out only in acidic medium, usually using quaternary ammonium salts. However, this method is not used widely because of limited scope of compounds which could be synthesized this way.
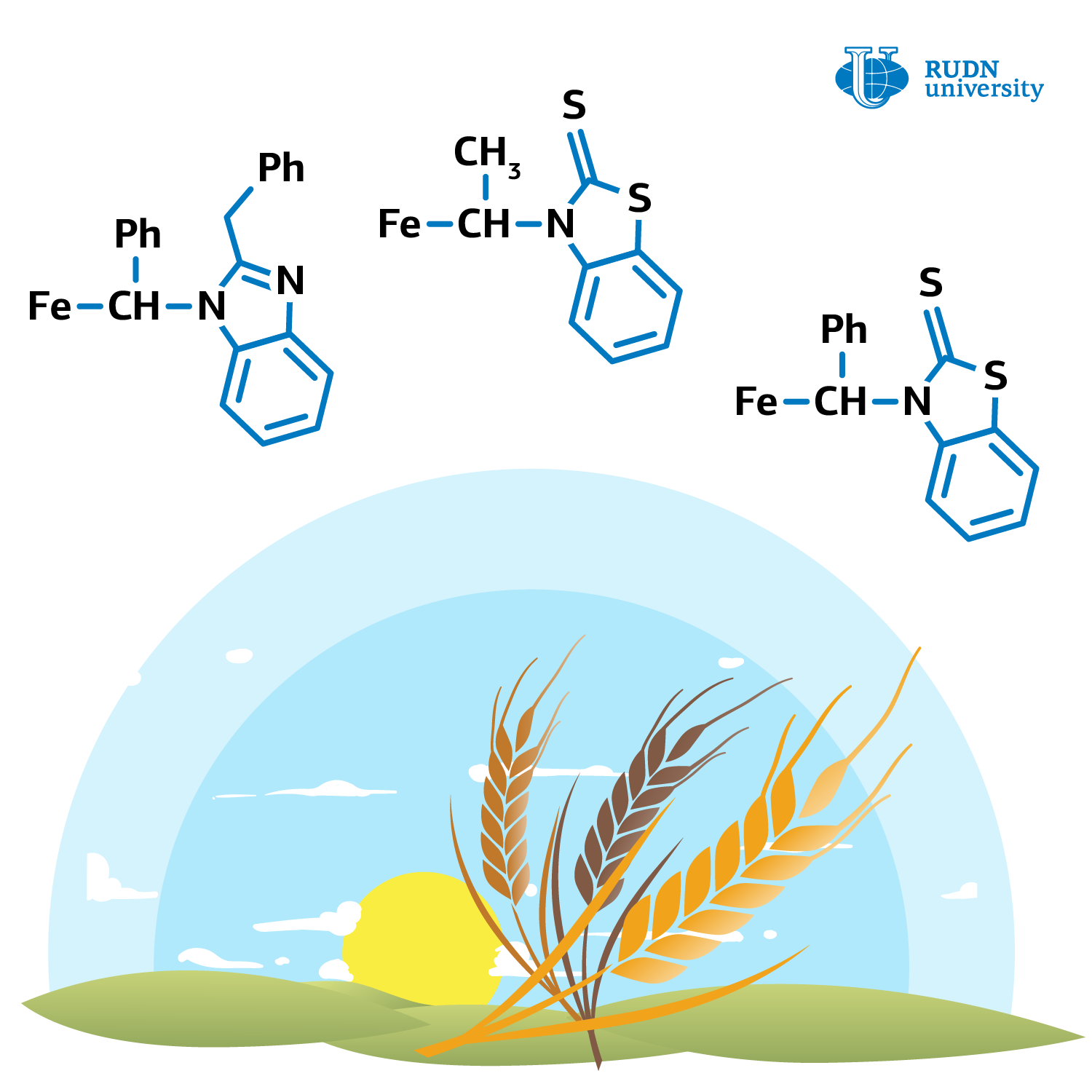
RUDN University chemist Alexandr Smol’yakov in collaboration with colleagues from INEOS RAS, MIREA, All‐Russian Research Institute of Phytopathology and Kurchatov Institute proved that it is possible to synthesize plant growth regulators by the insertion of heterocyclic azole fragments into ferrocene. For the first time, chemists performed a one‐pot α-ferrocenyl alkylation using acid-sensitive substrates (e.g., imidazole derivatives) in a neutral medium.
The chemists succeeded to synthesize numerous compounds: including nitrogen- or sulphur-containing 2-benzyl-1-(1-ferrocenylethyl)benzimidazole, N-(1-ferrocenylethyl)benzothiazole-2-thion, and N-(α-ferrocenylethyl)benzothiazole-2-thion. They were applied for pre-sowing treatment of corn seeds at dozes of 0.5 g, 1 g, and 10 g per 1 ton of seeds. Each compound, in an amount of 10 mg, was dissolved in either 10 ml of distilled water or 75% ethanol. 15 g of corn seeds were placed in a flask with the solution and shaken manually until the moisture was completely absorbed, and then transferred to Petri dishes, which were kept open for three days.
The treated corn seeds were then held for 7 more days at a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius. After that, the lengths of the sprouts and roots of these seeds were compared with those in the group of seeds that were germinated with distilled water, and another group that was exposed to herbicidal solution.
It turned out that the corn seeds treated with the compounds obtained during the research, produced sprouts with sizes 37-67% longer than those that did not undergo the treatment.
The obtained ferrocene derivatives of biomolecules are characterised by stability and low toxicity. Therefore, they can be widely used in agriculture. In particular, the compounds are effective as protection against a widely used herbicide from Zinger. The chemists have developed a technique for the creation of an environmentally friendly, low-toxic, and inexpensive preparation that increases crop productivity.
The article was published in the journal Applied Organometallic Chemistry.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.
Ambassadors of Russian education and science met at a conference in RUDN University to discuss how they can increase the visibility of Russian universities and research organizations in the world, and attract more international students in Russia.
The international scientific seminar hosted by RUDN Institute of Ecology “Experience of participation in student organizations as a way to form career skills” united scholarship recipients of the International Student Mobility Awards 2024 and Open Doors, along with members of the scientific student society “GreenLab” and the professional student association “Kostyor (Bonfire)” shared their projects focused on environmental protection.