RUDN University Physicists Determine the Optimal Conditions for Holding High-Energy Plasma Clouds in Pyrotron
Plasma is the fourth fundamental state of matter, not similar in physical properties to the others. The study of plasma states and phenomena is one of the most popular areas of modern physics. One of the potential applications of plasma in the future is controlled thermonuclear fusion. To realize fusion, it is necessary to create conditions for high-temperature plasma of a certain density confinement in a limited area for the time necessary to carry out a sufficient number of reactions. Confinement of plasma with a temperature of several million degrees one needs the unique methods of organizing a limited area of it’s location. The use of conventional materials is hopeless due to low temperature and radiation resistance. To keep the plasma under such condition, they use magnetic systems — traps with a specific topology of the magnetic field that limits the range of motion of charged particles. The most promising for fusion are closed toroidal magnetic configurations.
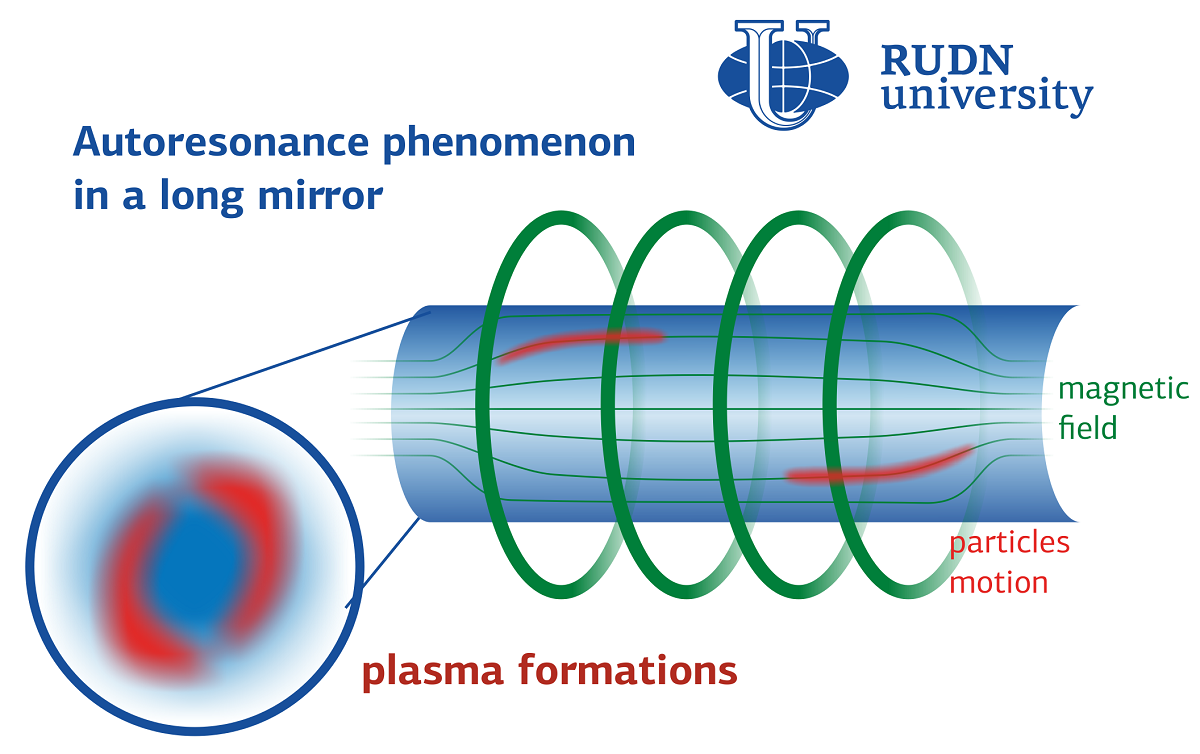
The international ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) project under construction is based on the concept of Soviet scientists — Tokamak. The simplest configuration for laboratory plasma is a linear trap with two areas of magnetic field amplification — magnetic mirrors (pyrotron). The scientists of the laboratory of Plasma Physics of RUDN University’s Institute of Physical Research and Technology investigate an original method of generating plasma clouds with an energetic electron component of 0.5 MeV scale under cyclotron autoresonance based on the autophasing phenomenon .
“In previous studies it has been shown that the cyclotron autoresonance (autophasing) phenomenon, that is, ECR interaction in a magnetic field grows in time and leads to the formation of a plasma bunches with an energetic electronic component.. This approach, implemented in the long-mirror variant, leads to the formation of long-lived plasma bunches. This is an ion-filled cloud of electrons, with an average energy of about several hundred keV, which is confined by magnetostatic mirror trap,” said Victor Andreev, Ph.D, Deputy Director for Research at the RUDN University’s Institute of Physical Research and Technology.
The original experimental installation is an axisymmetric system in which the microwave resonator is placed in a magnetic system of the installation provides for both an increase in magnetic field with time to maintain a group of electrons accelerated by the microwave field under autoresonance conditions and a regime for the accumulation of the generated plasma bunches and their confinement. The installation is equipped with various diagnostic systems that provide the study of the processes taking place in the conditions of maintaining the autoresonance mode of plasma generation. In experimental studies, the radiation losses of plasma in various spectral ranges are studied — optical, radio frequency and X-ray spectrometers.
The RUDN University physicists managed to establish the optimal time between the microwave and magnetic field pulses, which determine the maximum trapping efficiency of particles of initial plasma (200 microseconds). They also determined the volume occupied by the plasma bunches, as well as the number of charged electrons in them — about 50 billion particles with an energy of about 350 keV in about 80 cubic centimetres.
“The obtained results and the observed patterns of generation of plasma clouds with a hot electronic component in the autoresonance mode and further confinement in a long mirror allow us to proceed to more detailed experimental and numerical studies of the main plasma processes, in which special attention will be paid to increasing of the plasma density of generated bunches and their accumulation”, said Victor Andreev, Ph.D, Deputy Director for Research at the RUDN University’s Institute of Physical Research and Technology.
The results are published in Physics of Plasmas.
The RUDN Prize for Scientific Achievements in Chemistry for 2025, with a monetary award of 2 million rubles, was awarded to Alexander Davidovich Dilman, Deputy Director of the N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The researcher received the award during the celebration marking RUDN’s 66th anniversary.
Sergey Ivanov, a scholar from St. Petersburg, has been named the first winner of RUDN University’s International Prize for Scientific Achievements in Mathematics, worth 5 million rubles.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.