RUDN chemist synthesized gold-based electrocatalysts
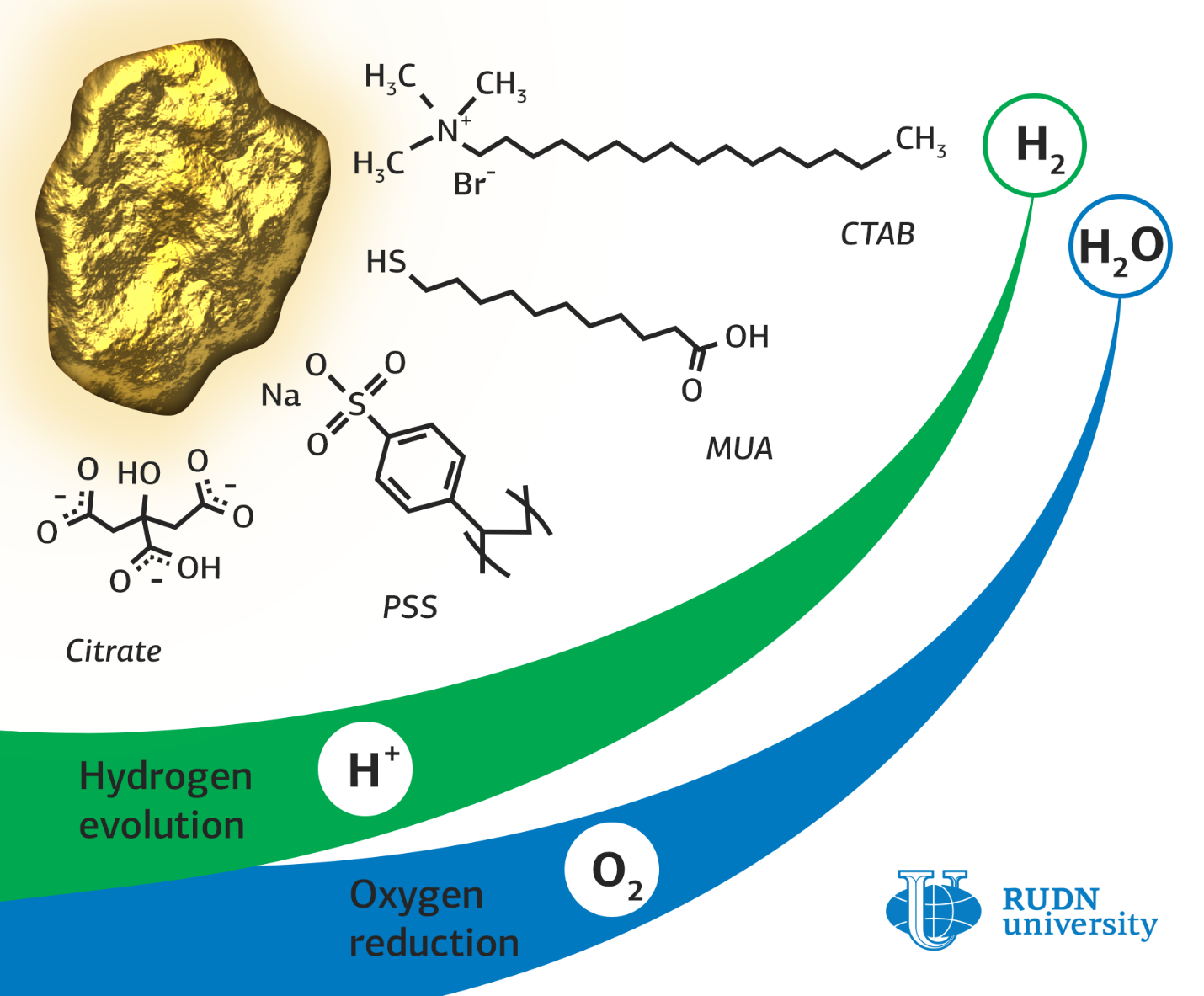
Catalysts based on metal nanoparticles, for example, gold or platinum, are needed for reactions in fuel cells and in the industrial production of hydrogen. If organic molecules, ligands, are attached to nanoparticles, the activity of the catalyst can be increased. However, there have been few papers that investigate the capabilities of such catalysts so far.
Rafael Luque, a RUDN chemist, synthesized a catalyst based on gold nanoparticles stabilized with citrate, a salt of citric acid. To obtain gold nanoparticles in complex with other organic substances, an exchange of ligands was carried out based on a concentration gradient. For this, nanoparticles were incubated in a solution of a new ligand, and then centrifuged to precipitate formed nanoparticles with attached ligands.
During the experiment in oxygen reduction reactions, the chemists found a significant effect of the type of ligand and its interaction with the gold surface on the absorption of O2 molecules. Gold nanoparticles with citrate proved to be the best in these reactions. The limiting current density of this type of catalyst — 5.58 milliamps per square centimeter — was two times higher than that of nanoparticles with other ligands. This means that with the same energy consumption, this catalyst will produce more oxygen.
In hydrogen production reactions, the best catalytic activity, as well as in oxygen reduction reactions, was demonstrated by citrate nanoparticles. Moreover, their efficiency was only half the efficiency of a platinum catalyst, which significantly exceeds the gold analogue in cost.
The study of the structures showed that gold nanoparticles with citrate lost some of their ligands, while nanoparticles with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and mercaptoundecanoic acid (MUA) remained almost unchanged. This may be due to the different strength of the bonds between gold and organic ligands. To test the stability, which is one of the most important characteristics of the catalysts, all samples were tested for 12 hours under a voltage that significantly exceeded the optimum. All nanoparticles retained their structure after testing; moreover, gold nanoparticles with citrate improved their electrocatalytic characteristics. This may indicate that new types of catalysts will work effectively under continuous operation.
Due to the stability of the new catalysts, these have an interesting potential to be employed in industry in the future. The ligand exchange method developed by the chemists can find application in the synthesis of catalysts with predetermined properties suitable for renewable hydrogen-based energy sources.
The article was published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.