The international research group and RUDN University chemists proposed new reagents for the removal of lead from wastewater
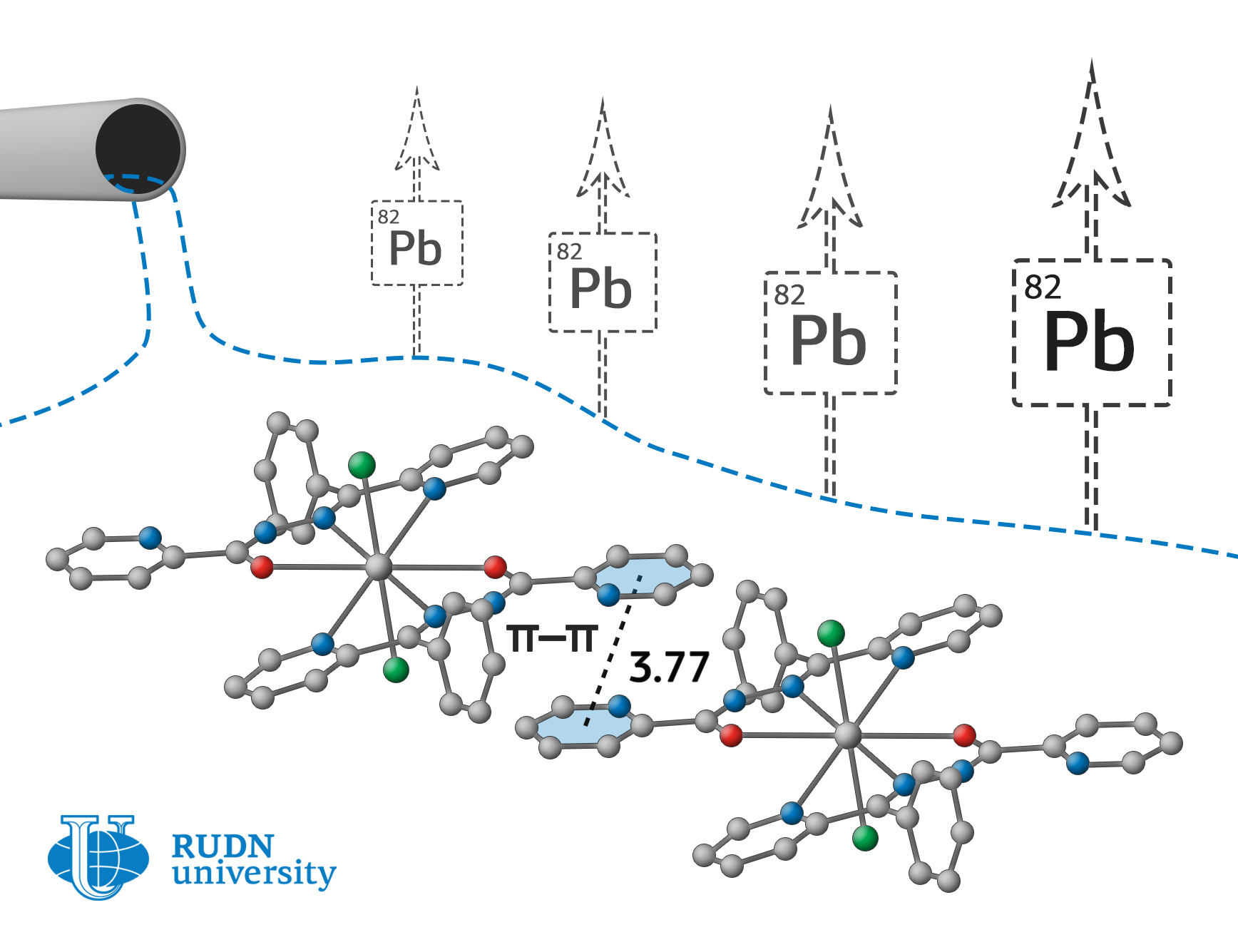
Complex compounds of lead are widely used for the synthesis of polymers and compounds necessary for the production of semiconductors, materials for nonlinear optics and ferroelectrics. The large radius of the divalent lead ion Pb (II) allows you to change the number of bound atoms, ions or molecules (ligands) from 4 to 9. Thus, it is possible to obtain a wide range of substances based on lead, that combine organic and inorganic components in a single molecule. The widespread use of lead compounds in production leads to the accumulation of toxic waste, what stimulates the solution to the problem of removing lead from wastewater.
Fedor Zubkov, an employee of the Organic Chemistry Department of RUDN University, together with colleagues from Iran, Spain, Italy, and Croatia have obtained compounds that can effectively bind lead in wastewater, as well as in human and animal body. Chemists have created it on the basis of nicotinic and picolinic acids hydrazides. Nitrate, chloride, and perchlorate-anions serve as counterions to positively charged lead ions and stabilize the complex due to strong electrostatic interactions.
To study the obtained complexes, chemists had to design a special device for the synthesis and simultaneous selective crystallization of reaction products. To do this, alcohol solution of a mixture of lead nitrate (II), the corresponding ligand, and sodium perchlorate was placed in the main part of the tube as a donor of counterions. The mixture was heated at 60 °C so that the side branch of the tube, also filled with alcohol, remained at room temperature. The crystals of the complex formed in the side vessel after several days of synthesis were filtered, washed with ether and dried in air. The yield of metal complex ranged from 67 to 87 % of the theoretically possible.
According to x-ray diffraction analysis, one of the complexes turned out to be binuclear, that is, it contains two lead ions bound by a common ligand. Using computer simulations, it was shown that all complexes form supramolecular ensembles with different types of intermolecular interactions. In the formation of such structures, anions of inorganic acids play an important role, which experiences a strong electrostatic attraction to the internal coordination sphere of the lead complex. As a result, metal organic coordination polymers (metal organic frameworks, MOFs) are formed, which are promising metal organic catalysts and selective acceptors of heavy-metal ions.
The resulted substances — supramolecular ensembles — allow to bound and precipitate even trace amounts of lead in wastewater. They can be used for drinking water treatment and even as an antidote for lead poisoning.
The article is published in the journal Crystals.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.