RUDN University chemist created a catalyst from orange peel for organic compounds production
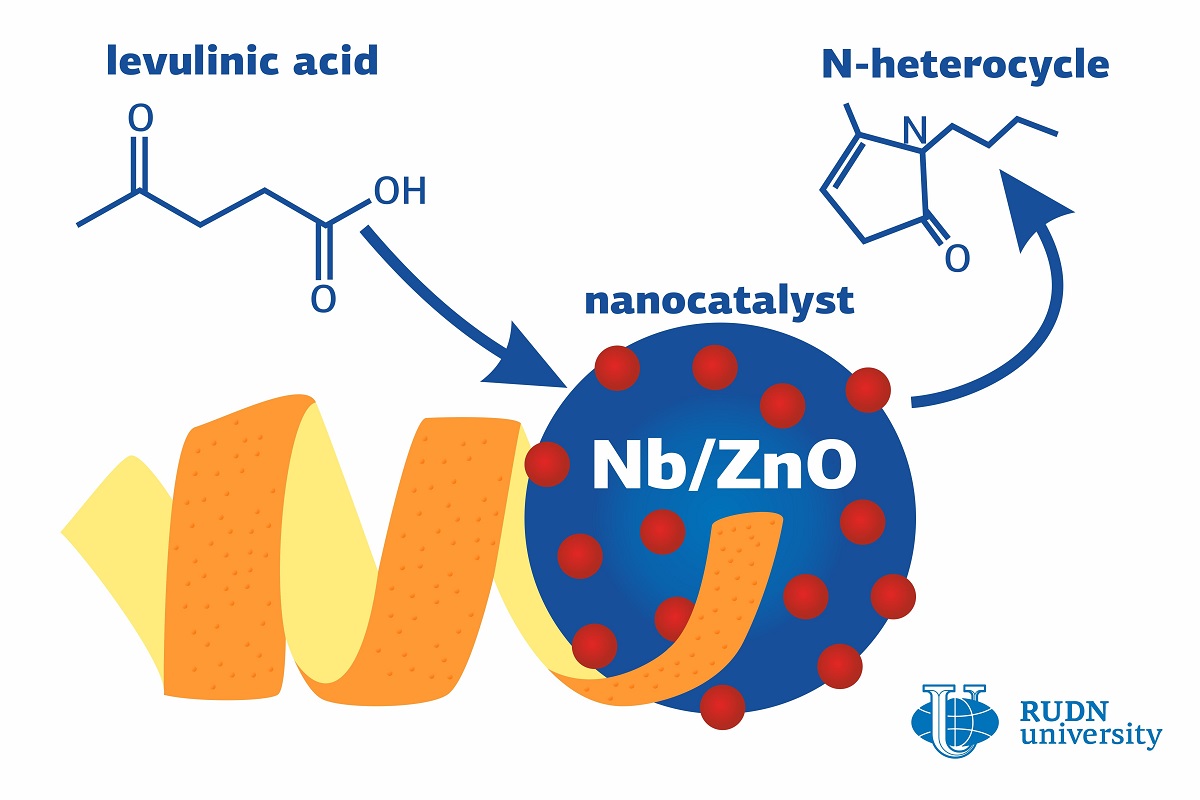
N-heterocycles are used in the production of plastics and medicinal drugs (quinine, morphine, pyramidon) and as dyes. Their synthesis requires the use of catalysts based on expensive noble metals such as gold, palladium, or iridium. All previous attempts to use other elements had been unsuccessful due to low efficiency or instability of the end products. However, a chemist from RUDN University developed a nanocatalyst based on cheaper metals—niobium and zinc. The new catalyst provides for almost 100% efficiency of N-heterocycle synthesis, and its precursor (or platform molecule) is levulinic acid.
“Levulinic acid is one of the top-10 most promising platform molecules that can be easily obtained from biomass. The transformation of levulinic acid into N-heterocycles has recently become a popular topic because N-heterocycles proved to be useful in the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and polymer industries”, said Rafael Luque, PhD, the head of the Molecular Design and Synthesis of Innovative Compounds for Medicine Science Center at RUDN University.
His team used a mechanochemical method to create the nanocatalyst: it means, its components were simply mixed in a special grinder without solvents or other additives. Orange peel served as a template for the catalyst preparation. Ground peel, dry zinc acetate, and 18 1-cm steel balls were put in the grinder and mixed at 350 revolutions per minute for 20 minutes. After that, the mixture was heated at 200? for two hours. As a result, zinc oxide nanoparticles were formed. Orange peel was used to give zinc acetate a surface to concentrate on, and also to help form intermediary compounds. The remains of the peel were partially removed from the mix in the course of heating. After that, zinc oxide nanoparticles were combined in the grinder with niobium-containing particles so that the concentration of the metal in the end product would reach 2.5% to 10%.
To test the new nanocatalyst, the chemists used it to transform levulinic acid into an N-heterocycle. The team selected the most efficient ratio of the catalyst: 10% of niobium to 90% of zinc oxide. In this case, almost all levulinic acid (94.5%) was turned into the end product without byproducts, and N-heterocycles accounted for 97.4% of the yield.
“This work shows that if we play with the catalyst structure, valuable compounds can be developed from biowaste. Using organic waste and eco-friendly methods, we can offer an alternative to the modern-day chemical industry that is extremely dependent on fossil fuels,” added Rafael Luque.
The results of the study were published in the Catalysis Today journal.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.