RUDN University professor suggested how to clean up space debris
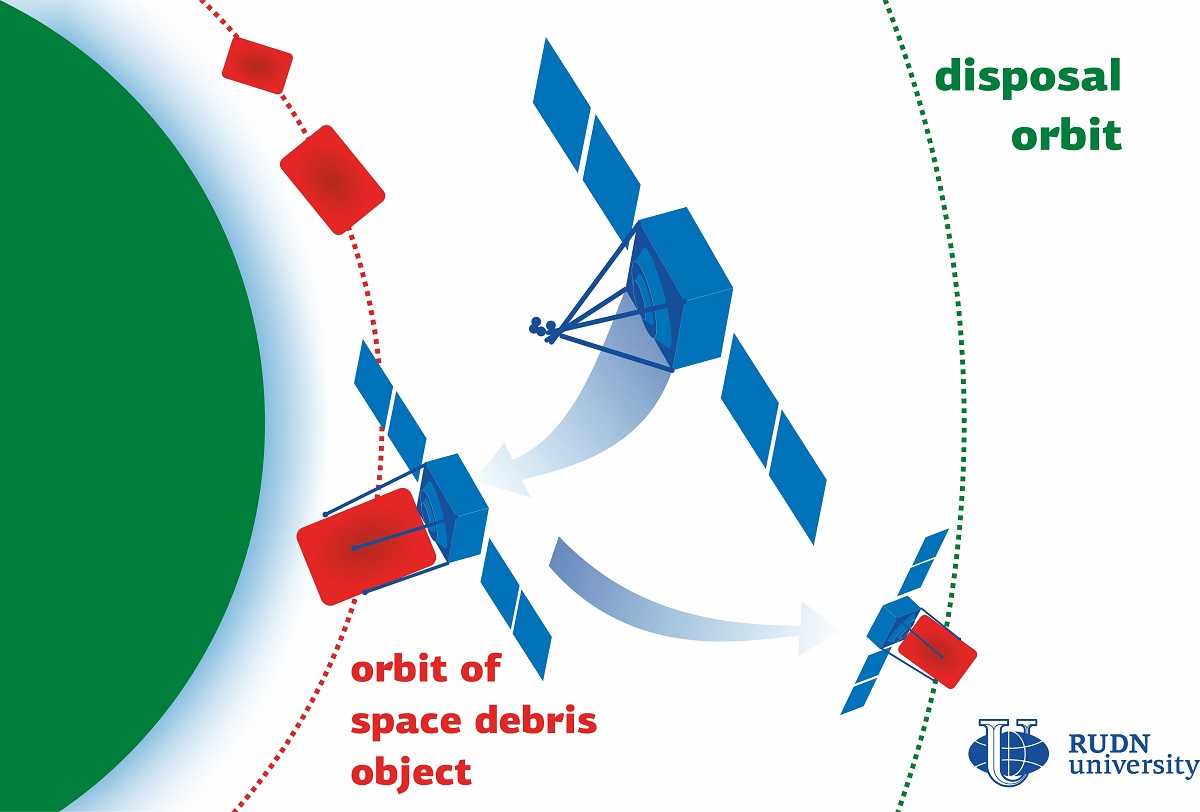
Besides satellites and the International Space Station, thousands of out-of-service spacecrafts, boosters, and other space debris objects move along different orbits around the Earth. Sometimes they collide and break down: for example, over 1,000 new observable fragments appeared in 2018 when eight objects fell to pieces in the near-Earth space. The more debris is left in space, the higher is the risk that it would damage the satellites, leaving us without communication and surveillance systems. Prof. Andrey Baranov from RUDN University together with his colleagues from Bauman Moscow State Technical University Dr. Dmitriy Grishko and Prof. Georgii Shcheglov studied the parameters of space debris in different orbits and came up with the most feasible ways for cleaning it up.
160 vehicle stages (from 1.1 to 9 tons each) are situated in low near-Earth orbits, i.e. at a height from 600 to 2,000 km. As for the geostationary orbit at the height of 35,786 km, the most potentially dangerous objects there are 87 boosters, each weighing from 3.2 to 3.4 tons. The size, weight, and parameters of these objects are quite different, therefore, they require different equipment to collect them and move to the so-called disposal orbit where the debris is safe to store.
A spacecraft-collector suggested by the team to clean up the near-Earth low orbits is 11.5 m long, 3 m in diameter, and weighs just over 4 tons. Such a collector can carry 8 to 12 modules with engine units on board. The movement of light vehicle stages will require 50 to 70 kg of fuel, while the transportation of a Zenit-2 stage that weighs 9 tons--around 350. The total weight of a spacecraft-collector at launch is expected to be from 8 to 12 tons. Modern-day boosters can easily place a weight like this into any orbit up to 1,000 km high. After a collector runs out of modules, it will attach itself to the last booster stage, move to the top layer of the atmosphere with it, and burn down.
As for the geostationary orbit, to clean it up the team suggested a spacecraft that is about 3.4 m long, 2.1 m wide, and weighs around 2 tons. According to their calculations, if loaded with modules, such a device would not be extremely efficient, and it would take 3-4 times more collectors to clean the orbit up. Therefore, in this case, the spacecraft-collector should work as a tow for space debris objects. Preliminary calculations suggest that it could operate for up to 15 years and transfer 40 to 45 space debris objects into the disposal orbit.
"Designing a spacecraft-collector for lower orbits is a more complicated task than creating one for the geostationary orbit. Best-case scenario, one spacecraft would be able to remove only 8 to 12 objects from lower orbits, while in the geostationary orbit it could transport 40 to 45. Therefore, cleaning up lower orbits is much more difficult. This factor should be taken into consideration by businesses and space agencies that plan to launch groups of hundreds or thousands of satellites in this area of the near-Earth space," explained Prof. Andrey Baranov, a PhD in Physics and Mathematics from the Department of Mechanics and Mechatronics, RUDN University.
Results were published in the Advances in Space Research journal.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.