RUDN University soil scientists: Green suburbs can be more harmful than city centers
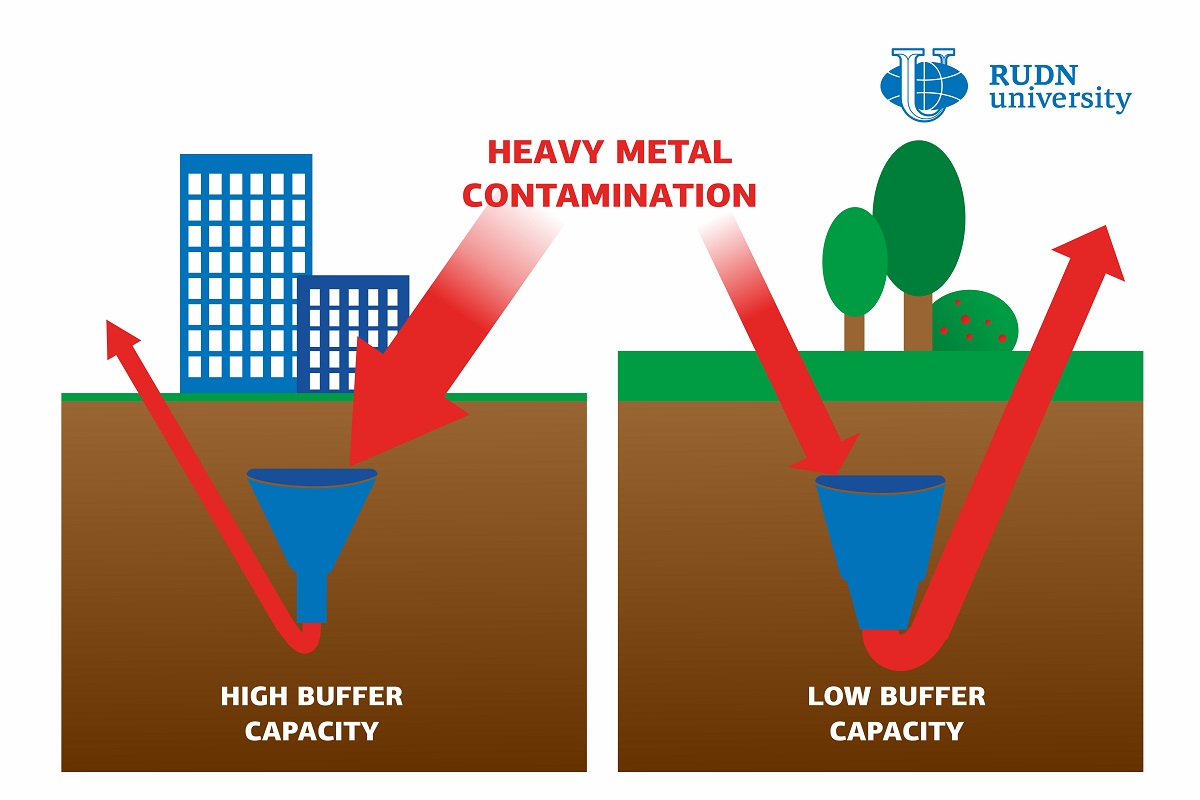
Industrial soil pollution with heavy metals poses a threat to human health. From the soil, harmful substances get into the water, dust, and plants. The intensity of these processes depends on the properties of the soil, namely its organic content, acidity, and texture. For example, clay and loam soils act as a geochemical barrier: they retain harmful substances and don't let them spread. However, traditional approaches to ecological monitoring overlook this barrier role and assess risks based only on the concentration of contaminating agents. Using these methods, one can miss potentially harmful zones or overestimate the danger. A team of soil scientists from RUDN University developed the first map of Moscow that takes into account not only the level of heavy metal pollution but also the barrier function of the soils.
The experiment covered nine administrative districts of Moscow with a total area of over 1,000 km2. The main sources of contamination across this territory were industrial facilities and automobiles. The researchers took soil samples from 224 points in public spaces, residential areas, and industrial zones. The samples were dried and ground to measure their soil texture, organic content, and acidity. Based on these parameters, the team calculated the ability of the samples to contain pollutants. Then, using spectral analysis, the researchers measured the concentrations of heavy metals: nickel, cadmium, manganese, lead, copper, zinc, arsenic, and mercury. After that, individual concentration and containment maps were developed and integrated into one general map.
In over 30% of the samples, heavy metal concentrations exceeded the norms of the Russian Agency for Health and Consumer Rights (Rospotrebnadzor). For example, the prohibitive amount of copper in 1 kg of soil is 33 to 132 mg (depending on soil type), and of arsenic--from 2 to 10 mg. However, in some cases, these norms were exceeded 2 to 5 times. The most polluted soils were the ones taken from public places downtown. However, loam soil with alkaline acidity that is typical for the center of Moscow has a high barrier activity index, which means it can retain the pollution. At the same time, more sandy and acidic in topsoils have weaker barrier functions, and though the concentration of harmful substances there is lower, they cannot withstand the pollution. The team concluded that in order to effectively assess the ecological situation in the city, one has to take into account both the level of pollution and the ability of the soil to stop it. Traditional monitoring approaches based solely on concentration levels do not give an adequate risk profile.
"We developed pollution level maps and the maps of soils as geochemical barriers, and they turned out not to match each other. In some cases, the ability of the soils to bind down heavy metals compensates for high pollution levels. On the other hand, in some green zones topsoils are unable to contain even the smallest amounts of pollutants. Our results show how important it is to see the bigger picture and take both factors into consideration," said Olga Romzaykina, a researcher at the Research Laboratory "Smart Technologies for Sustainable Urban Development under Global Change", RUDN University.
The results of the study were published in the Journal of Environmental Quality.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.
Matilda Pavlovna Mityaeva was born in 1925. In November 1942, she volunteered for frontline duty. She participated in the Great Patriotic War from November 1942 to June 1945 as part of the 53rd Infantry Division of the 475th Infantry Regiment. She was wounded twice.
The team led by Sergey Zyryanov, Head of the Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, became the winner of the All-Russian competition of scientific projects "Technologies for Human Health".
RUDN University constantly adapts to the changes of the modern world and responds to challenges flexibly. This allows us to keep the standard of a world-class research university. The sphere of science is no exception. Peter Dokukin, Head of the Research Division, presented the updated R&D Programme at the meeting of the RUDN University Academic Council.