RUDN University doctors found out the role of macrophages in liver regeneration
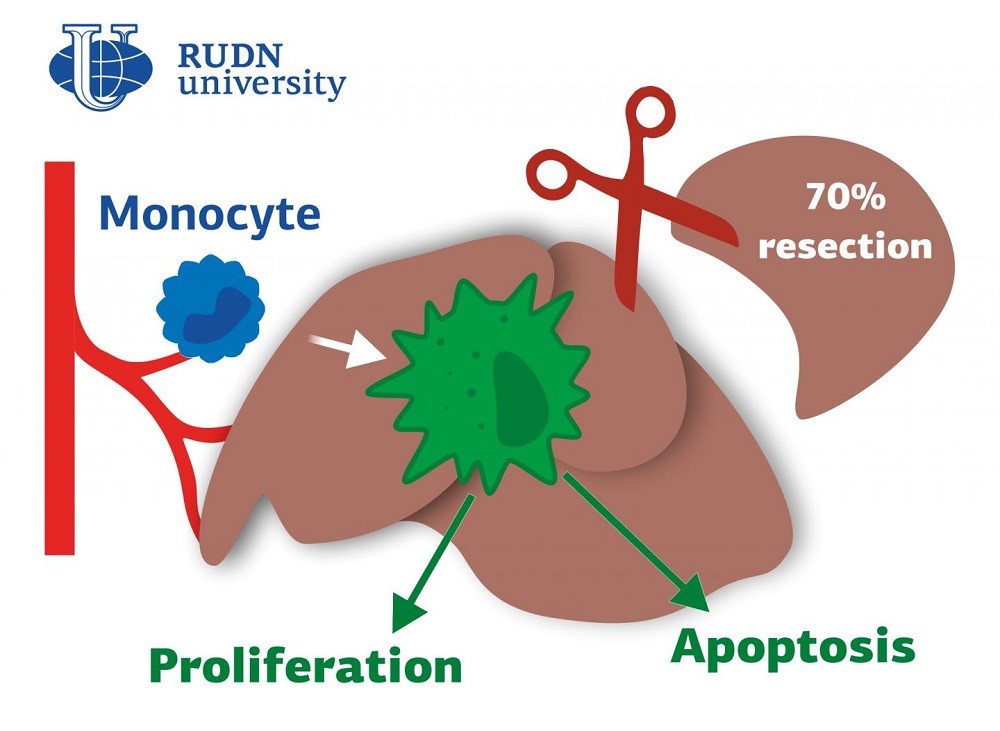
The liver in mammals is the most regenerative internal organ. It can restore the original size from as little as 25% of the preserved tissue. An important role in this process is played by macrophages. These are the cells that can engulf and digest particles. It is known, for example, that if the liver is affected by foreign substances, including drugs, macrophages migrate to the liver, absorb harmful microorganisms and dead cells, cause inflammation and thus contribute to the restoration of the organ. However, it is still unknown unambiguously how macrophages affect the growth of the liver after its resection, meaning the removal of a large part of the organ. RUDN University doctors investigated this issue in an experiment with laboratory mice.
“The role of macrophages in the liver growth after massive resections is uncertain. Some studies reveal the lack of immigration of macrophages to the liver during its recovery from partial resection, whereas other studies demonstrate such possibility. So, we focused our study on the macrophage population dynamics after 70% liver resection in mouse mode”, Andrey Elchaninov, MD, PhD, researcher at th Department of Histology, Cytology and Embryology of RUDN University.
Doctors used 184 laboratory mice of the BALB/c line. In 132 they removed 70% of the liver. Immediately after that, then a day later, three days later, and a week later, the scientists took liver samples for analysis. The resulting cells were studied using an immunohistochemical method. The sections were labelled with specific antibodies to the glycoproteins CD68, CD206 and other compounds that are found on the surface of macrophages. The antibodies are labelled with fluorescent dyes and glow when attached to macrophages — so one can count their number. RUDN University doctors also measured the rate of reproduction and cell death of macrophages.
It turned out that after resection, a large number of macrophages migrate to the liver. For example, a day after surgery, the number of macrophages with CD68 in the liver increases by 2 times, which persists after a week. It also turned out that the resection led to significant changes in the ratio of different types of macrophages. For example, the proportion of Ly6C cells in the week after surgery increased 4-fold — from 5% to 22%, and the proportion of CD86 fell from 50% to 15%. The role of macrophages is ambiguous. On the one hand, they release chemicals (chemoattractors) that attract white blood cells responsible for the body’s inflammatory response. On the other hand, they regulate the reproduction of liver cells and the metabolism in the organ.
“Corresponding profiles of macrophages in regeneration liver cannot be unambiguously defined as pro- or anti-inflammatory. Their typical features include elevated expression of leukocyte chemoattractant factors, and many of the differentially expressed sequences are related to the control of cell growth and metabolic processes in the liver. Our findings revealed essential roles of macrophages and macrophages proliferation in the mouse liver during its recovery from a massive resection”, from RUDN University.
The results are published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
RUDN scientist named neural networks that will help doctors interpret the results of an electroencephalogram (EEG) and other test of brain activity. The best of them works with almost 100% accuracy, while not only giving the result, but explaining why it turned out the way it did.
To obtain information about objects on the earth's surface and in near-Earth space, it is advisable to use not one, but several satellites. Such satellites move in different orbits, but operate as a whole. This allows us to increase the efficiency and accuracy of the obtained data but requires additional efforts to control the relative motion of satellites. RUDN engineers together with colleagues from Malaysia found a way to effectively control such formations of several satellites.
Ice rock, overnight in the mountains and 6100 meters above sea level... A scientist from the Agricultural Technological Institute went on an expedition to the Tien Shan.
RUDN scientist named neural networks that will help doctors interpret the results of an electroencephalogram (EEG) and other test of brain activity. The best of them works with almost 100% accuracy, while not only giving the result, but explaining why it turned out the way it did.
To obtain information about objects on the earth's surface and in near-Earth space, it is advisable to use not one, but several satellites. Such satellites move in different orbits, but operate as a whole. This allows us to increase the efficiency and accuracy of the obtained data but requires additional efforts to control the relative motion of satellites. RUDN engineers together with colleagues from Malaysia found a way to effectively control such formations of several satellites.