RUDN mathematicians have proposed a simple model for a 5G network for VR applications
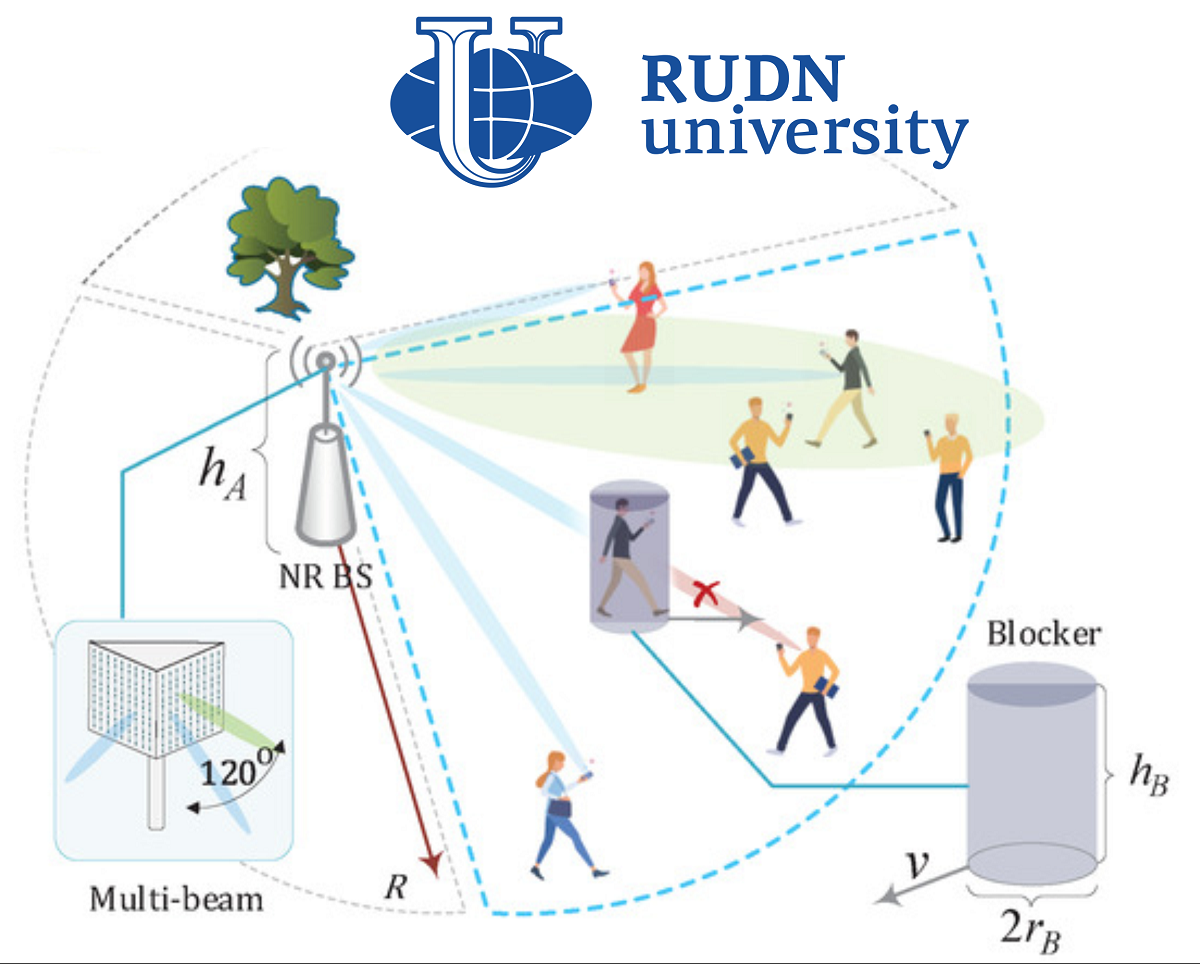
5G technologies are designed to support applications that need high speeds. To do this, various techniques are used, including multicasting. This is a routing scheme in which a station sends a network packet not to one user (unidirectional transmission) and not to all at once (broadcasting), but to a dedicated group of users. However, the use of multicasting can negatively affect the operation of the network when combined with a unidirectional scheme. RUDN mathematicians proposed a model based on the example of virtual reality applications, in which these two modes are combined. It allows you to estimate how many base stations are needed for a given network quality. The algorithm works no worse than alternative options, while it is simpler.
“Most studies of multi-level multicast/unidirectional services focus on optimizing an already defined network deployment scheme for specified traffic conditions. However, it is equally important for network operators to assess what density of base stations is required for a given traffic load in a given area. We have proposed a simple model for the preparation of a multi-level virtual reality service in millimeter networks,” — Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Daria Ostrikova, Deputy Director of the Institute of Applied Mathematics and Telecommunications of the RUDN.
Mathematicians have proposed a model in which several base stations are located. Each of them has three antennas covering 120°. Users of VR devices move around stations randomly according to the Poisson process model, sometimes blocking each other’s line of direct communication with the base station. The network in the proposed model operates on two levels. At the basic level, multicasting is used, and “point-to-point” unicast delivery is used to improve the quality of communication. RUDN mathematicians calculated the parameters of such a system and proposed an algorithm for grouping users for multicasting and calculating the density of base stations.
User groups for multicasting are created based on the maximum angle at which the signal will be transmitted at half the power at a given distance from the station. All users who fall into the sector specified in this way become part of the same group. Sectors that no user has entered are considered inactive. The calculation of the optimal number of base stations is based on an iterative principle — more stations are added at a new step until the probability of signal loss reaches the required minimum. In a numerical experiment, the new algorithm turned out to be no less effective than other schemes, but at the same time much simpler.
“Our numerical results show that the proposed grouping scheme, in which the number of groups and their configurations can be explicitly calculated, produces performance similar to other iterative algorithms. Our work provides a simple and efficient algorithm for estimating the density of base stations necessary to support a given density of multilayer VR devices with specified service quality guarantees,” — Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Daria Ostrikova, Deputy Director of the Institute of Applied Mathematics and Telecommunications of the RUDN.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.