RUDN physicians have identified genetic characteristics that may affect the predisposition to re-stenosis
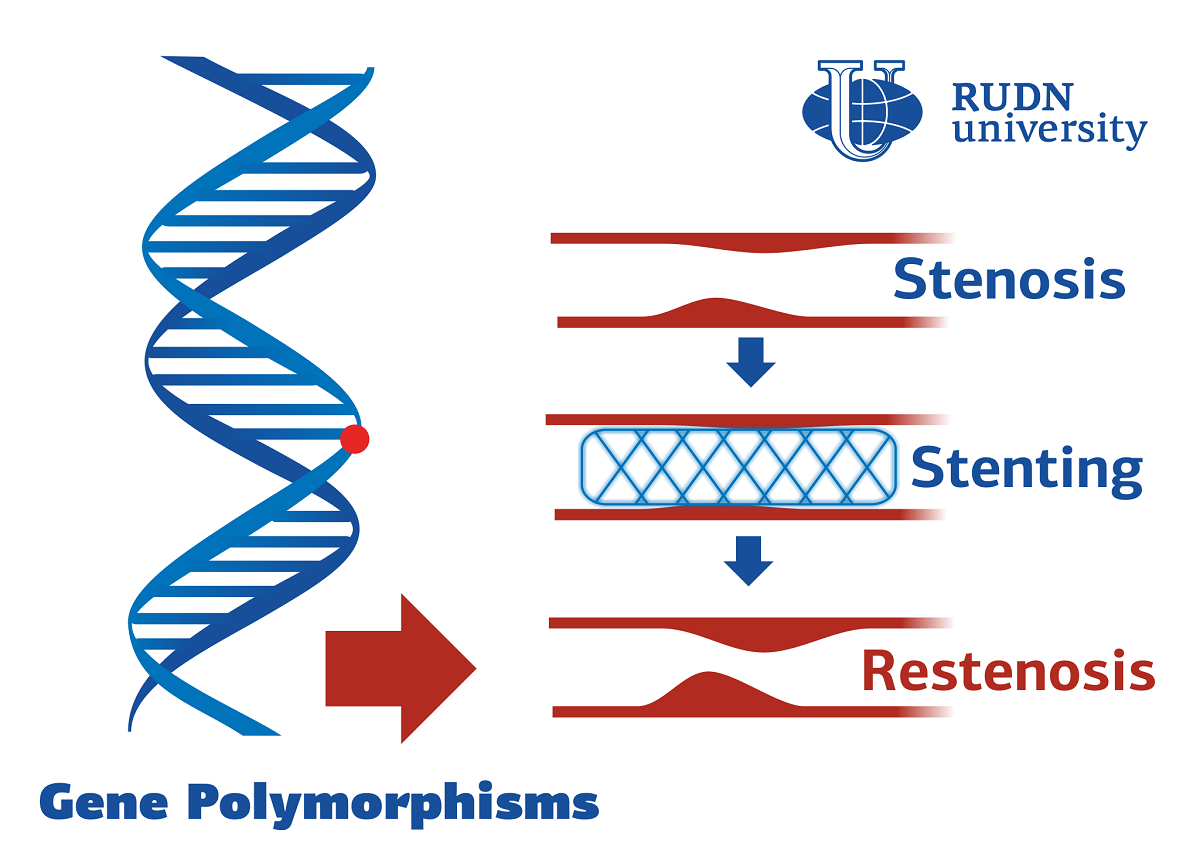
Coronary insufficiency — a discrepancy between blood flow in the vessels of the needs of the heart muscle in oxygen — occurs, for example, due to stenosis, narrowing of the lumen of the vessels. It is treated almost exclusively with surgery. A relatively new method of surgical treatment is drug-eluting stents (special “frames”). They reduced the risk of recurrence of stenosis. However, with an increase in the number of such procedures, the number of relapses (restenoses) also increases. The causes that cause recurrent stenosis are still not completely known. RUDN doctors have discovered genetic factors that may increase the risk of restenosis.
“Despite technological advances, restenosis remains a major limitation in interventional cardiology, resulting in the need for repeat surgery and, consequently, increased financial costs. Identification of risk factors and mechanisms underlying restenosis is necessary to understand the process, identify risks, and develop optimal treatment,” Doctor of Biology Madina Azova, Head of the Department of Biology and General Genetics, RUDN University.
The study included 175 patients, including 62 with intact coronary arteries as a control group, 59 without restenosis, and 54 with restenosis after stenting. Study participants with restenosis were divided into subgroups based on age (over or under 65 years of age) and the period during which restenosis developed (less than or more than a year after percutaneous coronary intervention). All patients were followed up for 2 years. The participants determined the genotype and recorded changes in the genes that are responsible for the functioning of the heart vessels.
It turned out that patients with and without repeated stenosis have differences in the genotype. Changes were found in the AGT gene, which is responsible for the synthesis of the hormone angiotensin, which causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure, in the angiotensin receptor genes AGTR1 and AGTR2, and in the REN gene, which encodes the renin protein that regulates blood pressure through the angiotensin system. These data suggest that the tendency to re-stenosis is determined by the genotype. However, for definitive conclusions, a study with a large number of patients is needed.
“In order to choose an effective tactic for treating patients with coronary heart disease, it is necessary to first carry out genotyping. This, along with age and clinical characteristics, will allow for a comprehensive assessment of the risk of developing restenosis after stenting and, accordingly, adjusting treatment if this patient belongs to a high-risk group for restenosis,” Madina Azova, Doctor of Biology, Head of the Department of Biology and General genetics of RUDN.
The results are published in the journal Biomolecules.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.
The project to develop a cellular model of the placenta became the winner in the Scientific Materials category of the Young Scientists 3.0 competition, organized with the support of the Presidential Grants Foundation and T-Bank.
Ten scientific journals published by RUDN University have been included in the highest level of the state list of scientific publications, the White List.
Forests are not only the lungs of the planet, but also home to millions of species. However, it has remained unclear how underground interactions between trees and fungi affect forest species richness in different climatic conditions. Previous studies have yielded conflicting results: in some regions, the dominance of certain fungi reduced tree diversity, while in others it increased it.