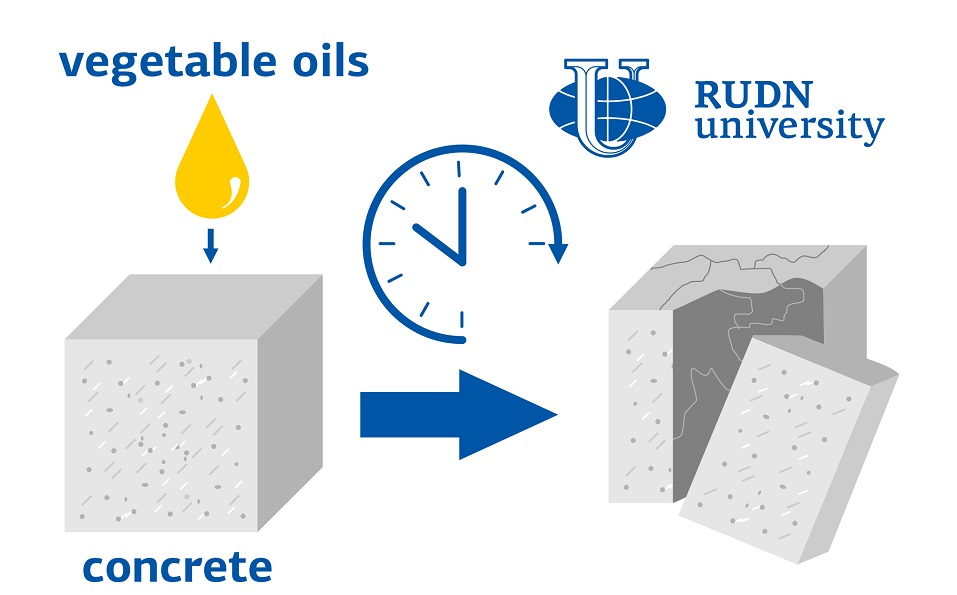
RUDN engineers: vegetable oil destroys concrete
Factories in various industries use vegetable oils. These can be both edible oils and technical ones, which are used, for example, for lubricating parts. Oils are often spilled on the concrete floor. When they come into contact with the main component of cement — calcium oxide — fatty acids are obtained. RUDN University engineers found out that fatty acids and oils can destroy concrete. Due to fatty acids, micro cracks appear in concrete. It then leads to large fractures — and so the material is destroyed.
“Edible and technical vegetable oils are used in many industries. They constantly fall on concrete and reinforced concrete structures and impregnate them. Oils contain high molecular weight fatty acids that destroy cement stone and concrete. Under the action of calcium oxide on fats and oils, alcohols and fatty acids are formed. We studied the aggressive effect of these acids from fatty vegetable oils on the strength of cement-sand mortar and concrete,” Alexander Svintsov, Doctor of Engineering, Professor at the Department of Construction of RUDN University.
Engineers studied the effect of oil on concrete and cement stone. They differ in the proportions of the components (water, sand, cement). In addition, there is a granite crumb in the concrete. RUDN engineers immersed samples of both materials in corn, olive or palm oil and left them at room temperature (from 16℃ to 24℃). Every ten days, the researchers took out the samples and studied their compressive strength.
After being immersed in oil, the materials became more brittle. After 60 days, the strength decreased by an average of 61.2%, and after 90 days, the samples began to spontaneously collapse. The engineers also built a mathematical model that predicts how much the strength of concrete will change after 70 days of exposure to oil.
“Our results are important for predicting changes in concrete structures under the influence of vegetable oil and for ensuring their comprehensive protection. An empirical mathematical model of strength at different durations of oil action is a new way to improve the operating conditions of industrial buildings in which vegetable oil is used in technological processes. This is important for the design, construction and operation of industrial buildings,” Alexander Svintsov, Doctor of Engineering, Professor at the RUDN University Construction Department.
Results published in Construction magazine and building materials.
Products derived from microalgae represent a cutting-edge development in the field of bioeconomy. The potential of this biological resource was discussed at the international research seminar “Foundations for a Green Sustainable Energy”, part of the BRICS Network University’s thematic group on “Energy”. The event was organized by the Institute of Ecology at RUDN University.
Ambassadors of Russian education and science met at a conference in RUDN University to discuss how they can increase the visibility of Russian universities and research organizations in the world, and attract more international students in Russia.
The international scientific seminar hosted by RUDN Institute of Ecology “Experience of participation in student organizations as a way to form career skills” united scholarship recipients of the International Student Mobility Awards 2024 and Open Doors, along with members of the scientific student society “GreenLab” and the professional student association “Kostyor (Bonfire)” shared their projects focused on environmental protection.