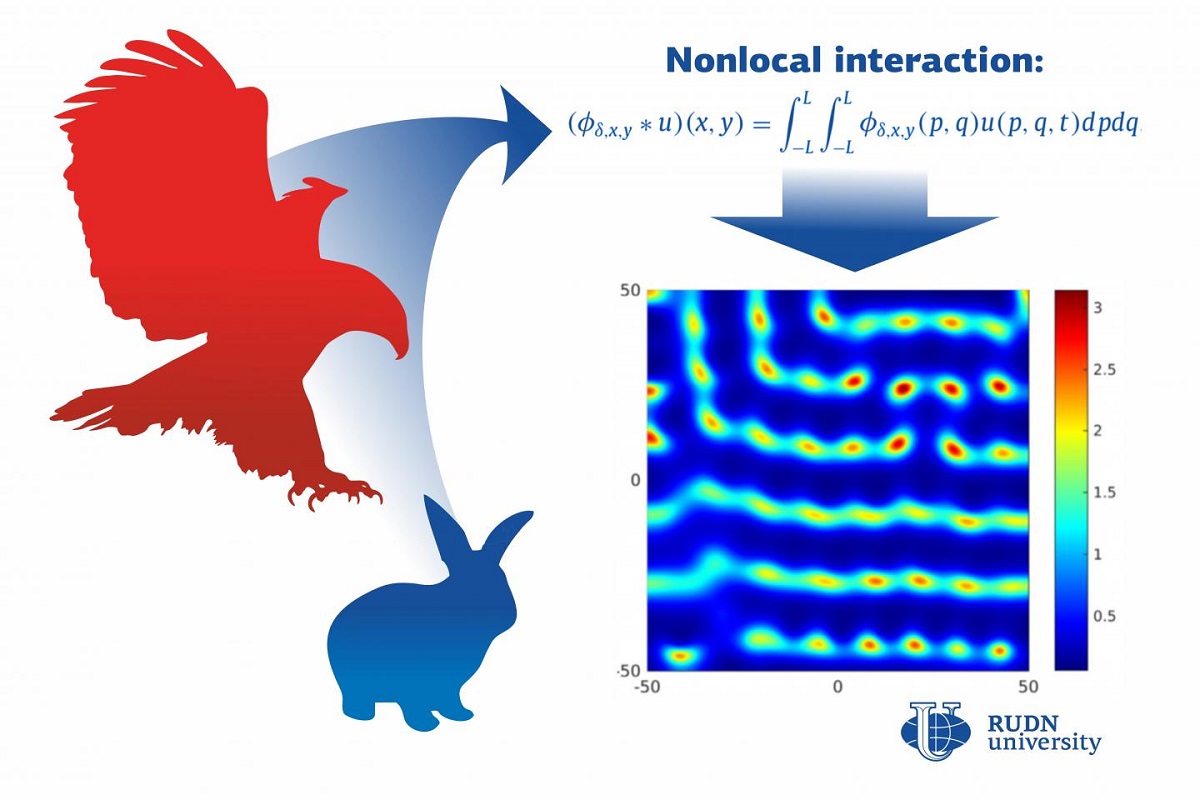
A Mathematician from RUDN University Refined the Model of Predator-Prey Relations in the Wild
Ecologists use mathematical models of ecosystems to understand their structure and predict their development. Predator-prey is one of the basic models of this kind. With its help scientists can for instance calculate changes in the numbers of carnivores and herbivores depending on numerous conditions: the breeding of the latter, starvation of the former, amounts of prey eaten by predators, migrations, and so on. However, this model only takes into account local interactions, i.e. direct interactions between predators and prey in each given spatial location, while actual ecosystems also include nonlocal ones. A mathematician from RUDN University working together with his colleagues from the UK and India enhanced the standard predator-prey model taking these less obvious factors into account. Using his work, ecologists will be able to better understand developments in natural systems.
One example of natural nonlocal interactions is arid regions. To grow there, plants need to have a vast root system to collect moisture from large territories, not just from the vicinity of their location. Mathematically, this nonlocality is expressed as an integral that sums up the effect of the whole system at each given point. The competition for food among herbivores is also nonlocal, so a model has to take into account the integral amount of food in a system, not at each particular place.
“Nonlocal properties of movement are of interest for researchers; however, the nonlocal origin of this dynamics is often discarded. Still, there are a lot of natural systems with nonlocal interactions. One of the best examples may be the vegetation-water system, especially in semi-arid regions. There, nonlocality is a direct result of extensive root networks. We have confirmed that the nonlocality of intraspecific interactions can be the cause of different system dynamics in the predator-prey model,” said Prof. Sergey Petrovskii from RUDN University.
The team tested their concept using computer modeling and found out that even if a system initially has equal numbers of carnivores and herbivores, after some time their quantities start to grow differently at different points due to nonlocal interactions. As a result, the total quantity of the system becomes dominated either by predators or prey, and different spatial patterns are formed. Another feature of a nonlocal system is bistability, i.e. possible coexistence of two patterns. This is an important attribute of nonlocality. It is the initial conditions that determine which pattern eventually succeeds.
Other participants of the study represented the University of Leicester (UK).
An article about his work was published in the Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation journal.
A RUDN agrotechnologist has identified wheat genotypes that are resistant to a dangerous fungal pathogen that infects plants even before the snow melts and reduces yields.
RUDN University engineers have calculated the parameters of a system that can prevent lunar power plants from overheating. These developments will be needed when planning for long-term lunar missions and colonizing the satellite.
Landfills are the third largest source of anthropogenic methane in the world. They account for ~11% of estimated global emissions. Methane is 80 times more powerful than carbon dioxide and is the second largest driver of man-made climate change. Scientists from around the world met at Zhejiang University's Hangzhou campus to determine the best available technologies for recovering energy and materials from non-recyclable residual waste.