RUDN Univesity Biologists Prove the Effectiveness of Silver Nanoparticles Against Phytopathogens
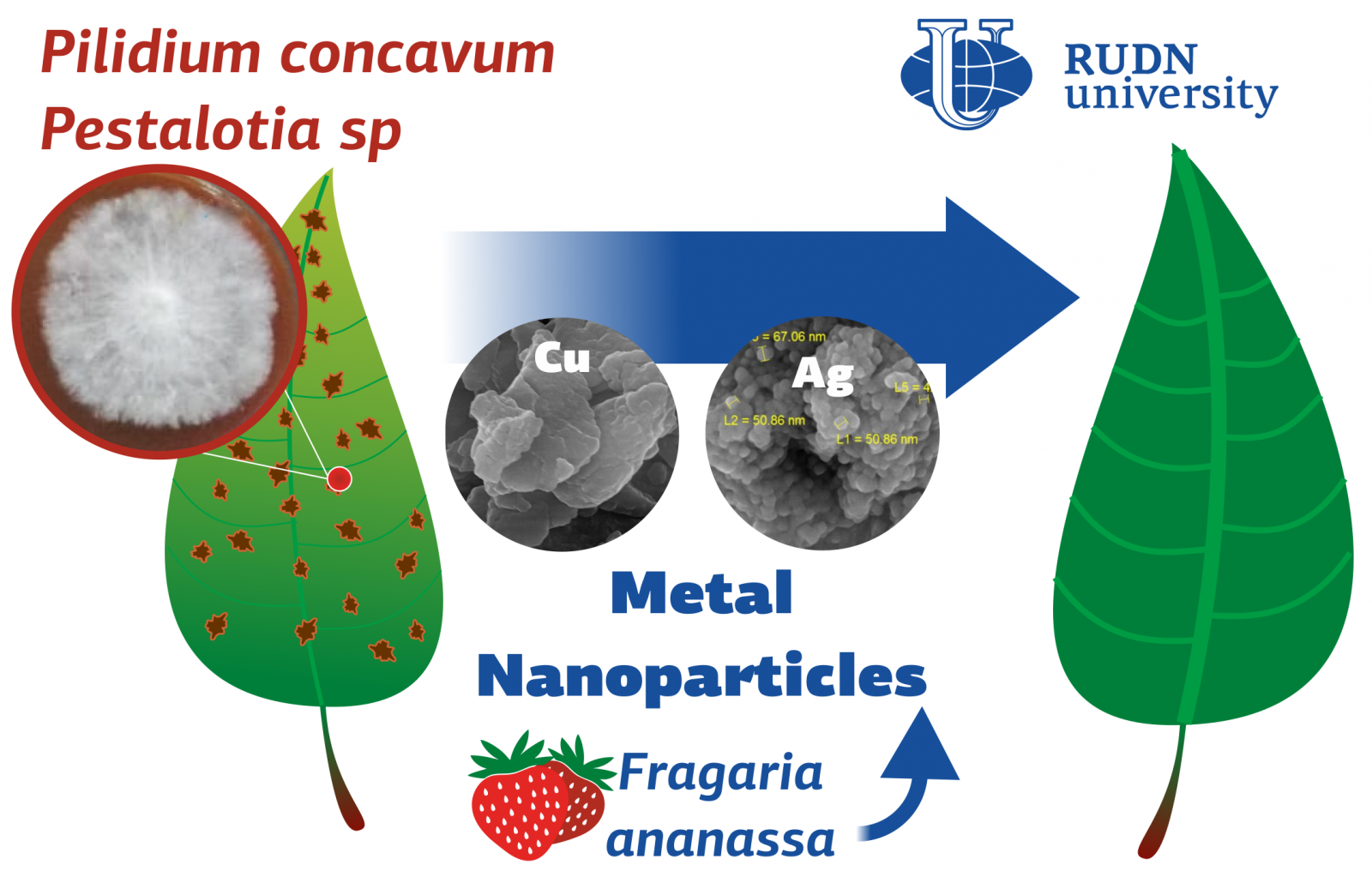
Phytopathogenic fungi Botrytis cinerea, Pilidium concavum and Pestalotia sp affect many plants: strawberries, nightshades, beans and others. RUDN University biologists have proposed a fundamentally new way to combat these phytopathogens. To do this, they used nanoparticles of metals, silver and copper. The nanoparticles are obtained by a green method based on strawberry leaf extract, without no harmful reagents. This is the first successful application of biogenic metal nanoparticles to combat these phytopathogens.
“For evaluation of antifungal activity of these NPs, three pathogenic fungi were selectd: Botrytis cinerea, as an unspecialized necrotrophic fungal pathogen that attacks over 200 different plant species, Pilidium concavum, which is an opportunistic pathogen that causes leaf spots and stem necrosis in a wide range of hosts, mainly on strawberry plants and Pestalotia sp., which is reported to be infectious for azalea leaves. There are just a few reports carried out on the last two fungi, and there is no report on the antifungal effect of nanoparticles on these fungi”, said Maryam Bayat, PhD student at RUDN University.
Scientists reported the synthesis of biogenic metal nanoparticles in previous works, and now they have presented their first experimental use against fungi. To do this, RUDN University biologists used two methods: he agar dilution method and the spore germination method. In the first case, they put a potential antifungal substance in the nutrient medium (agar) in different concentrations. Then a culture of the fungus is sown there followed by growth monitoring. In the second method, they place spores (cellular structures that fungi use for reproduction) in a nutrient medium with an antifungal substance.
Silver nanoparticles slowed the growth of B. Cinerea and P. Concavum by 28% and 65.4%, respectively, at 0.01% concentration. The mechanism of this antifungal action is not completely clear, but RUDN University biologists have suggested that silver nanoparticles form pores on the cell membrane of the fungus. It causes the death of the cell and inhibit the budding process. Germination of B. Cinerea spores was completely suppressed by a solution with 0.01% silver nanoparticles concentration. Copper nanoparticles turned out to be ineffective against fungi — they practically did not affect the growth of spores and fungi.
“According to the results, these nanoparticles have the potential to be used as an antimicrobial agent in antibacterial and antifungal remediation or as an additive in conventional formulations. Silver nanoparticles were found to be the more effective antimicrobial agent against all examined pathogens in comparison to copper nanoparticles”, said Meisam Zargar, PhD in agricultural sciences, professor at RUDN University.
The results are published in the Molecules
A RUDN agrotechnologist has identified wheat genotypes that are resistant to a dangerous fungal pathogen that infects plants even before the snow melts and reduces yields.
RUDN University engineers have calculated the parameters of a system that can prevent lunar power plants from overheating. These developments will be needed when planning for long-term lunar missions and colonizing the satellite.
Landfills are the third largest source of anthropogenic methane in the world. They account for ~11% of estimated global emissions. Methane is 80 times more powerful than carbon dioxide and is the second largest driver of man-made climate change. Scientists from around the world met at Zhejiang University's Hangzhou campus to determine the best available technologies for recovering energy and materials from non-recyclable residual waste.